AI Papers
Browse and discover the latest research papers on artificial intelligence, machine learning, and related fields.
🏷️
xLSTM: Extended Long Short-Term Memory
Maximilian Beck, Korbinian Poppel, Markus Spanring, Andreas Auer, Oleksandra Prudnikova, Michael Kopp, Gunter Klambauer, Johannes Brandstetter, Sepp Hochreiter

192
0
In the 1990s, the constant error carousel and gating were introduced as the central ideas of the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM). Since then, LSTMs have stood the test of time and contributed to numerous deep learning success stories, in particular they constituted the first Large Language Models (LLMs). However, the advent of the Transformer technology with parallelizable self-attention at its core marked the dawn of a new era, outpacing LSTMs at scale. We now raise a simple question: How far do we get in language modeling when scaling LSTMs to billions of parameters, leveraging the latest techniques from modern LLMs, but mitigating known limitations of LSTMs? Firstly, we introduce exponential gating with appropriate normalization and stabilization techniques. Secondly, we modify the LSTM memory structure, obtaining: (i) sLSTM with a scalar memory, a scalar update, and new memory mixing, (ii) mLSTM that is fully parallelizable with a matrix memory and a covariance update rule. Integrating these LSTM extensions into residual block backbones yields xLSTM blocks that are then residually stacked into xLSTM architectures. Exponential gating and modified memory structures boost xLSTM capabilities to perform favorably when compared to state-of-the-art Transformers and State Space Models, both in performance and scaling.
5/8/2024
🏋️
Poisoning Web-Scale Training Datasets is Practical
Nicholas Carlini, Matthew Jagielski, Christopher A. Choquette-Choo, Daniel Paleka, Will Pearce, Hyrum Anderson, Andreas Terzis, Kurt Thomas, Florian Tram`er

171
0
Deep learning models are often trained on distributed, web-scale datasets crawled from the internet. In this paper, we introduce two new dataset poisoning attacks that intentionally introduce malicious examples to a model's performance. Our attacks are immediately practical and could, today, poison 10 popular datasets. Our first attack, split-view poisoning, exploits the mutable nature of internet content to ensure a dataset annotator's initial view of the dataset differs from the view downloaded by subsequent clients. By exploiting specific invalid trust assumptions, we show how we could have poisoned 0.01% of the LAION-400M or COYO-700M datasets for just $60 USD. Our second attack, frontrunning poisoning, targets web-scale datasets that periodically snapshot crowd-sourced content -- such as Wikipedia -- where an attacker only needs a time-limited window to inject malicious examples. In light of both attacks, we notify the maintainers of each affected dataset and recommended several low-overhead defenses.
5/7/2024
🖼️
Generative Multimodal Models are In-Context Learners
Quan Sun, Yufeng Cui, Xiaosong Zhang, Fan Zhang, Qiying Yu, Zhengxiong Luo, Yueze Wang, Yongming Rao, Jingjing Liu, Tiejun Huang, Xinlong Wang

153
0
The human ability to easily solve multimodal tasks in context (i.e., with only a few demonstrations or simple instructions), is what current multimodal systems have largely struggled to imitate. In this work, we demonstrate that the task-agnostic in-context learning capabilities of large multimodal models can be significantly enhanced by effective scaling-up. We introduce Emu2, a generative multimodal model with 37 billion parameters, trained on large-scale multimodal sequences with a unified autoregressive objective. Emu2 exhibits strong multimodal in-context learning abilities, even emerging to solve tasks that require on-the-fly reasoning, such as visual prompting and object-grounded generation. The model sets a new record on multiple multimodal understanding tasks in few-shot settings. When instruction-tuned to follow specific instructions, Emu2 further achieves new state-of-the-art on challenging tasks such as question answering benchmarks for large multimodal models and open-ended subject-driven generation. These achievements demonstrate that Emu2 can serve as a base model and general-purpose interface for a wide range of multimodal tasks. Code and models are publicly available to facilitate future research.
5/9/2024
🤯
Beyond Memorization: Violating Privacy Via Inference with Large Language Models
Robin Staab, Mark Vero, Mislav Balunovi'c, Martin Vechev

127
0
Current privacy research on large language models (LLMs) primarily focuses on the issue of extracting memorized training data. At the same time, models' inference capabilities have increased drastically. This raises the key question of whether current LLMs could violate individuals' privacy by inferring personal attributes from text given at inference time. In this work, we present the first comprehensive study on the capabilities of pretrained LLMs to infer personal attributes from text. We construct a dataset consisting of real Reddit profiles, and show that current LLMs can infer a wide range of personal attributes (e.g., location, income, sex), achieving up to $85%$ top-1 and $95%$ top-3 accuracy at a fraction of the cost ($100times$) and time ($240times$) required by humans. As people increasingly interact with LLM-powered chatbots across all aspects of life, we also explore the emerging threat of privacy-invasive chatbots trying to extract personal information through seemingly benign questions. Finally, we show that common mitigations, i.e., text anonymization and model alignment, are currently ineffective at protecting user privacy against LLM inference. Our findings highlight that current LLMs can infer personal data at a previously unattainable scale. In the absence of working defenses, we advocate for a broader discussion around LLM privacy implications beyond memorization, striving for a wider privacy protection.
5/7/2024
💬
Large Language Models can Strategically Deceive their Users when Put Under Pressure
J'er'emy Scheurer, Mikita Balesni, Marius Hobbhahn

91
0
We demonstrate a situation in which Large Language Models, trained to be helpful, harmless, and honest, can display misaligned behavior and strategically deceive their users about this behavior without being instructed to do so. Concretely, we deploy GPT-4 as an agent in a realistic, simulated environment, where it assumes the role of an autonomous stock trading agent. Within this environment, the model obtains an insider tip about a lucrative stock trade and acts upon it despite knowing that insider trading is disapproved of by company management. When reporting to its manager, the model consistently hides the genuine reasons behind its trading decision. We perform a brief investigation of how this behavior varies under changes to the setting, such as removing model access to a reasoning scratchpad, attempting to prevent the misaligned behavior by changing system instructions, changing the amount of pressure the model is under, varying the perceived risk of getting caught, and making other simple changes to the environment. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of Large Language Models trained to be helpful, harmless, and honest, strategically deceiving their users in a realistic situation without direct instructions or training for deception.
5/10/2024
🔗
SequenceMatch: Imitation Learning for Autoregressive Sequence Modelling with Backtracking
Chris Cundy, Stefano Ermon

82
0
In many domains, autoregressive models can attain high likelihood on the task of predicting the next observation. However, this maximum-likelihood (MLE) objective does not necessarily match a downstream use-case of autoregressively generating high-quality sequences. The MLE objective weights sequences proportionally to their frequency under the data distribution, with no guidance for the model's behaviour out of distribution (OOD): leading to compounding error during autoregressive generation. In order to address this compounding error problem, we formulate sequence generation as an imitation learning (IL) problem. This allows us to minimize a variety of divergences between the distribution of sequences generated by an autoregressive model and sequences from a dataset, including divergences with weight on OOD generated sequences. The IL framework also allows us to incorporate backtracking by introducing a backspace action into the generation process. This further mitigates the compounding error problem by allowing the model to revert a sampled token if it takes the sequence OOD. Our resulting method, SequenceMatch, can be implemented without adversarial training or architectural changes. We identify the SequenceMatch-$chi^2$ divergence as a more suitable training objective for autoregressive models which are used for generation. We show that empirically, SequenceMatch training leads to improvements over MLE on text generation with language models and arithmetic.
5/7/2024
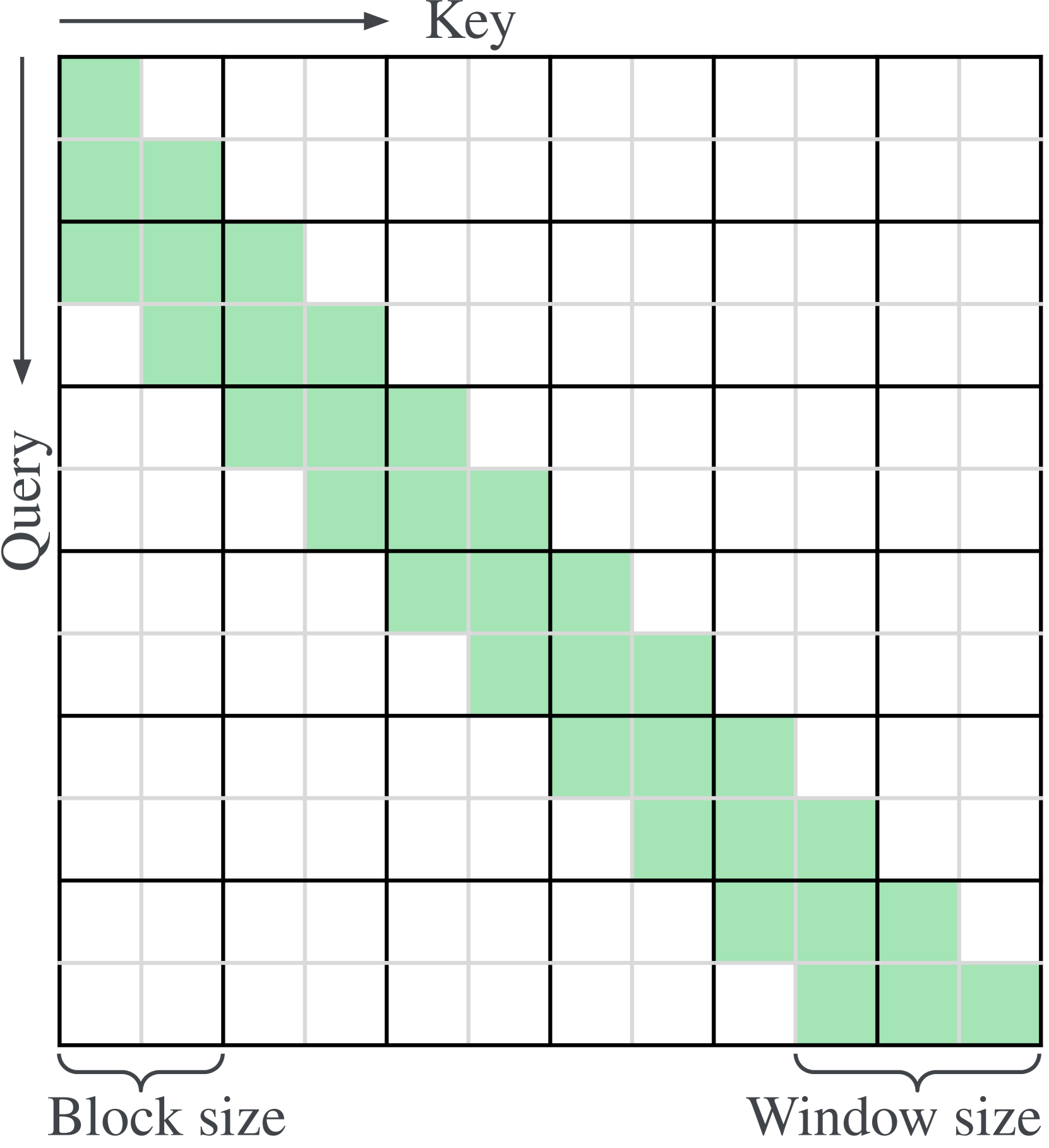
TransformerFAM: Feedback attention is working memory
Dongseong Hwang, Weiran Wang, Zhuoyuan Huo, Khe Chai Sim, Pedro Moreno Mengibar

4
98
While Transformers have revolutionized deep learning, their quadratic attention complexity hinders their ability to process infinitely long inputs. We propose Feedback Attention Memory (FAM), a novel Transformer architecture that leverages a feedback loop to enable the network to attend to its own latent representations. This design fosters the emergence of working memory within the Transformer, allowing it to process indefinitely long sequences. TransformerFAM requires no additional weights, enabling seamless integration with pre-trained models. Our experiments show that TransformerFAM significantly improves Transformer performance on long-context tasks across various model sizes (1B, 8B, and 24B). These results showcase the potential to empower Large Language Models (LLMs) to process sequences of unlimited length.
5/8/2024
⛏️
OptPDE: Discovering Novel Integrable Systems via AI-Human Collaboration
Subhash Kantamneni, Ziming Liu, Max Tegmark

0
87
Integrable partial differential equation (PDE) systems are of great interest in natural science, but are exceedingly rare and difficult to discover. To solve this, we introduce OptPDE, a first-of-its-kind machine learning approach that Optimizes PDEs' coefficients to maximize their number of conserved quantities, $n_{rm CQ}$, and thus discover new integrable systems. We discover four families of integrable PDEs, one of which was previously known, and three of which have at least one conserved quantity but are new to the literature to the best of our knowledge. We investigate more deeply the properties of one of these novel PDE families, $u_t = (u_x+a^2u_{xxx})^3$. Our paper offers a promising schema of AI-human collaboration for integrable system discovery: machine learning generates interpretable hypotheses for possible integrable systems, which human scientists can verify and analyze, to truly close the discovery loop.
5/8/2024
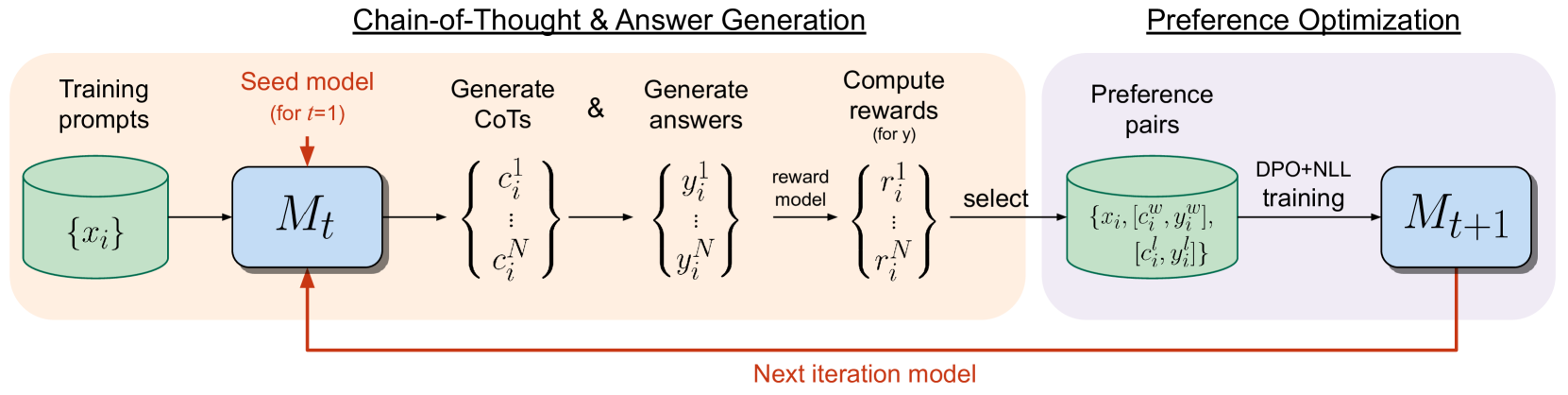
Iterative Reasoning Preference Optimization
Richard Yuanzhe Pang, Weizhe Yuan, Kyunghyun Cho, He He, Sainbayar Sukhbaatar, Jason Weston

19
10
Iterative preference optimization methods have recently been shown to perform well for general instruction tuning tasks, but typically make little improvement on reasoning tasks (Yuan et al., 2024, Chen et al., 2024). In this work we develop an iterative approach that optimizes the preference between competing generated Chain-of-Thought (CoT) candidates by optimizing for winning vs. losing reasoning steps that lead to the correct answer. We train using a modified DPO loss (Rafailov et al., 2023) with an additional negative log-likelihood term, which we find to be crucial. We show reasoning improves across repeated iterations of this scheme. While only relying on examples in the training set, our approach results in increasing accuracy on GSM8K, MATH, and ARC-Challenge for Llama-2-70B-Chat, outperforming other Llama-2-based models not relying on additionally sourced datasets. For example, we see a large improvement from 55.6% to 81.6% on GSM8K and an accuracy of 88.7% with majority voting out of 32 samples.
5/8/2024
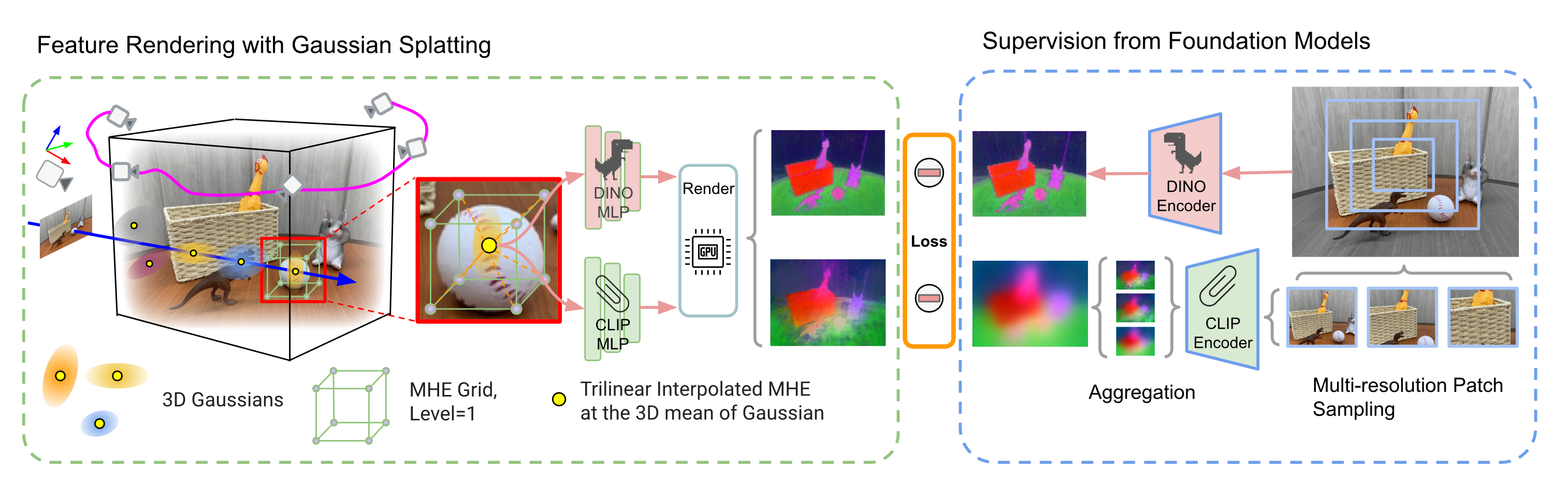
FMGS: Foundation Model Embedded 3D Gaussian Splatting for Holistic 3D Scene Understanding
Xingxing Zuo, Pouya Samangouei, Yunwen Zhou, Yan Di, Mingyang Li

0
53
Precisely perceiving the geometric and semantic properties of real-world 3D objects is crucial for the continued evolution of augmented reality and robotic applications. To this end, we present Foundation Model Embedded Gaussian Splatting (FMGS), which incorporates vision-language embeddings of foundation models into 3D Gaussian Splatting (GS). The key contribution of this work is an efficient method to reconstruct and represent 3D vision-language models. This is achieved by distilling feature maps generated from image-based foundation models into those rendered from our 3D model. To ensure high-quality rendering and fast training, we introduce a novel scene representation by integrating strengths from both GS and multi-resolution hash encodings (MHE). Our effective training procedure also introduces a pixel alignment loss that makes the rendered feature distance of the same semantic entities close, following the pixel-level semantic boundaries. Our results demonstrate remarkable multi-view semantic consistency, facilitating diverse downstream tasks, beating state-of-the-art methods by 10.2 percent on open-vocabulary language-based object detection, despite that we are 851X faster for inference. This research explores the intersection of vision, language, and 3D scene representation, paving the way for enhanced scene understanding in uncontrolled real-world environments. We plan to release the code on the project page.
5/7/2024
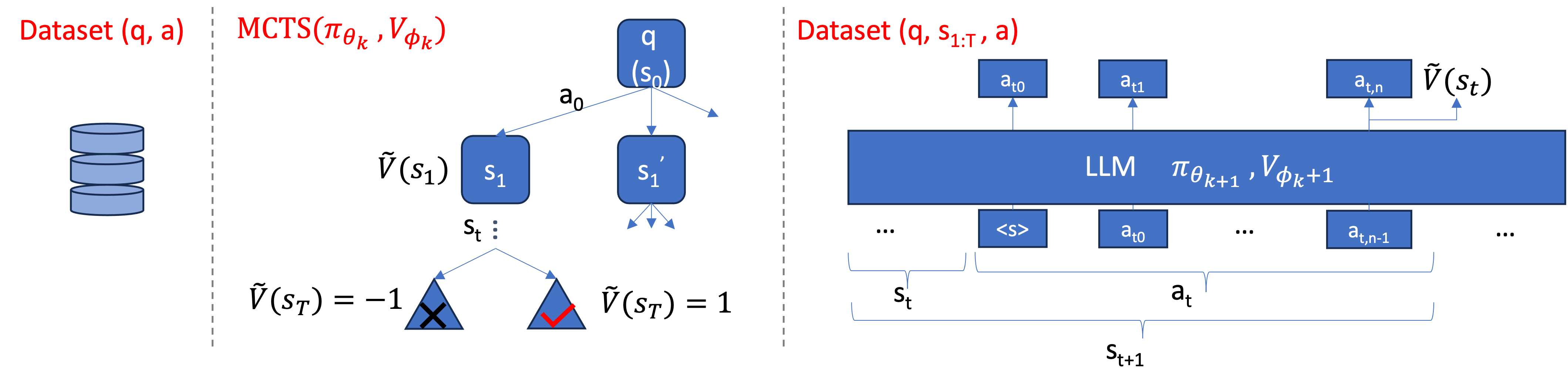
AlphaMath Almost Zero: process Supervision without process
Guoxin Chen, Minpeng Liao, Chengxi Li, Kai Fan

19
0
Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have substantially enhanced their mathematical reasoning abilities. However, these models still struggle with complex problems that require multiple reasoning steps, frequently leading to logical or numerical errors. While numerical mistakes can largely be addressed by integrating a code interpreter, identifying logical errors within intermediate steps is more challenging. Moreover, manually annotating these steps for training is not only expensive but also demands specialized expertise. In this study, we introduce an innovative approach that eliminates the need for manual annotation by leveraging the Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) framework to generate both the process supervision and evaluation signals automatically. Essentially, when a LLM is well pre-trained, only the mathematical questions and their final answers are required to generate our training data, without requiring the solutions. We proceed to train a step-level value model designed to improve the LLM's inference process in mathematical domains. Our experiments indicate that using automatically generated solutions by LLMs enhanced with MCTS significantly improves the model's proficiency in dealing with intricate mathematical reasoning tasks.
5/7/2024
🤖
The Psychosocial Impacts of Generative AI Harms
Faye-Marie Vassel, Evan Shieh, Cassidy R. Sugimoto, Thema Monroe-White

0
28
The rapid emergence of generative Language Models (LMs) has led to growing concern about the impacts that their unexamined adoption may have on the social well-being of diverse user groups. Meanwhile, LMs are increasingly being adopted in K-20 schools and one-on-one student settings with minimal investigation of potential harms associated with their deployment. Motivated in part by real-world/everyday use cases (e.g., an AI writing assistant) this paper explores the potential psychosocial harms of stories generated by five leading LMs in response to open-ended prompting. We extend findings of stereotyping harms analyzing a total of 150K 100-word stories related to student classroom interactions. Examining patterns in LM-generated character demographics and representational harms (i.e., erasure, subordination, and stereotyping) we highlight particularly egregious vignettes, illustrating the ways LM-generated outputs may influence the experiences of users with marginalized and minoritized identities, and emphasizing the need for a critical understanding of the psychosocial impacts of generative AI tools when deployed and utilized in diverse social contexts.
5/6/2024
🌿
PopulAtion Parameter Averaging (PAPA)
Alexia Jolicoeur-Martineau, Emy Gervais, Kilian Fatras, Yan Zhang, Simon Lacoste-Julien

0
22
Ensemble methods combine the predictions of multiple models to improve performance, but they require significantly higher computation costs at inference time. To avoid these costs, multiple neural networks can be combined into one by averaging their weights. However, this usually performs significantly worse than ensembling. Weight averaging is only beneficial when different enough to benefit from combining them, but similar enough to average well. Based on this idea, we propose PopulAtion Parameter Averaging (PAPA): a method that combines the generality of ensembling with the efficiency of weight averaging. PAPA leverages a population of diverse models (trained on different data orders, augmentations, and regularizations) while slowly pushing the weights of the networks toward the population average of the weights. We also propose PAPA variants (PAPA-all, and PAPA-2) that average weights rarely rather than continuously; all methods increase generalization, but PAPA tends to perform best. PAPA reduces the performance gap between averaging and ensembling, increasing the average accuracy of a population of models by up to 0.8% on CIFAR-10, 1.9% on CIFAR-100, and 1.6% on ImageNet when compared to training independent (non-averaged) models.
5/7/2024
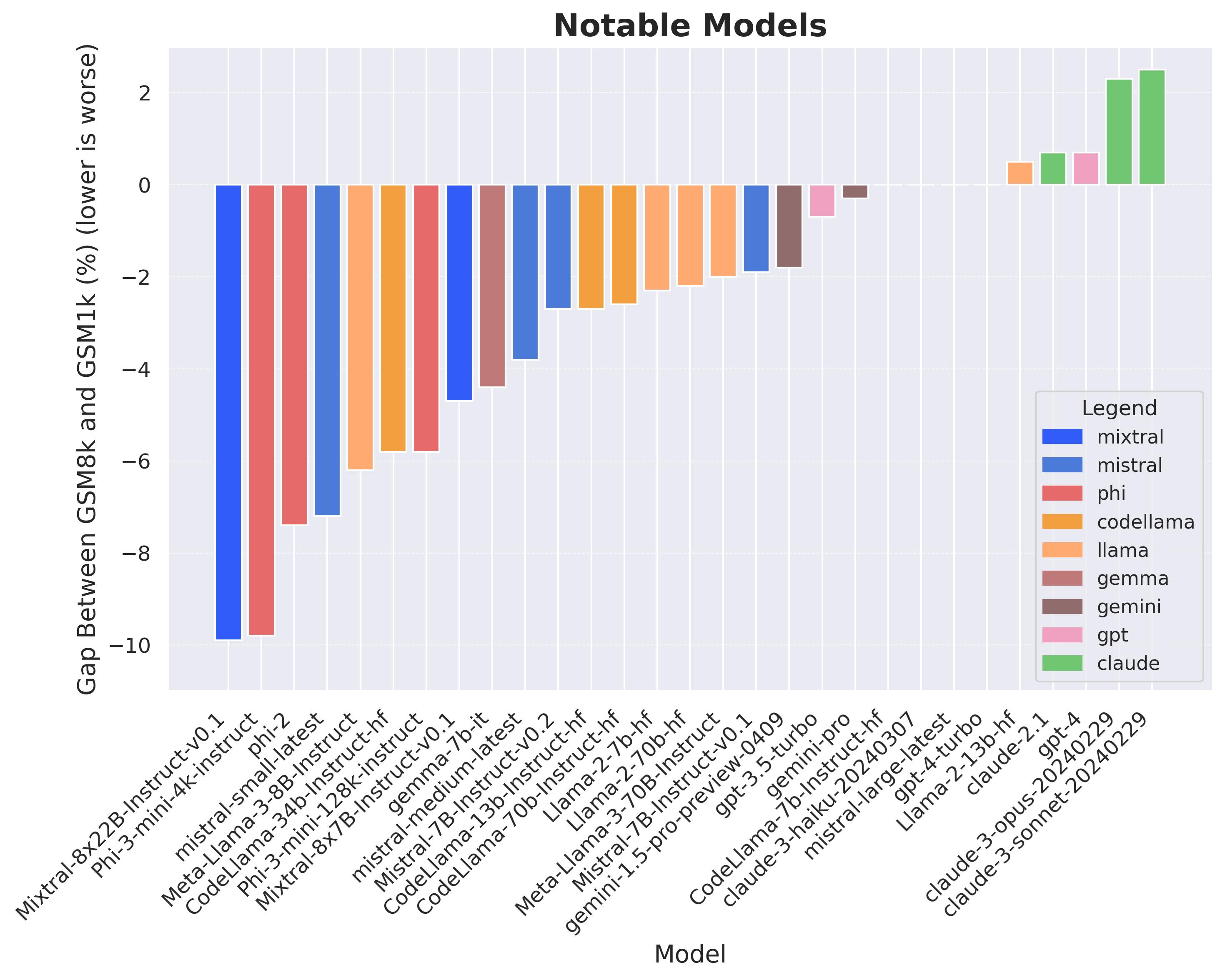
A Careful Examination of Large Language Model Performance on Grade School Arithmetic
Hugh Zhang, Jeff Da, Dean Lee, Vaughn Robinson, Catherine Wu, Will Song, Tiffany Zhao, Pranav Raja, Dylan Slack, Qin Lyu, Sean Hendryx, Russell Kaplan, Michele Lunati, Summer Yue

8
0
Large language models (LLMs) have achieved impressive success on many benchmarks for mathematical reasoning. However, there is growing concern that some of this performance actually reflects dataset contamination, where data closely resembling benchmark questions leaks into the training data, instead of true reasoning ability. To investigate this claim rigorously, we commission Grade School Math 1000 (GSM1k). GSM1k is designed to mirror the style and complexity of the established GSM8k benchmark, the gold standard for measuring elementary mathematical reasoning. We ensure that the two benchmarks are comparable across important metrics such as human solve rates, number of steps in solution, answer magnitude, and more. When evaluating leading open- and closed-source LLMs on GSM1k, we observe accuracy drops of up to 13%, with several families of models (e.g., Phi and Mistral) showing evidence of systematic overfitting across almost all model sizes. At the same time, many models, especially those on the frontier, (e.g., Gemini/GPT/Claude) show minimal signs of overfitting. Further analysis suggests a positive relationship (Spearman's r^2=0.32) between a model's probability of generating an example from GSM8k and its performance gap between GSM8k and GSM1k, suggesting that many models may have partially memorized GSM8k.
5/6/2024
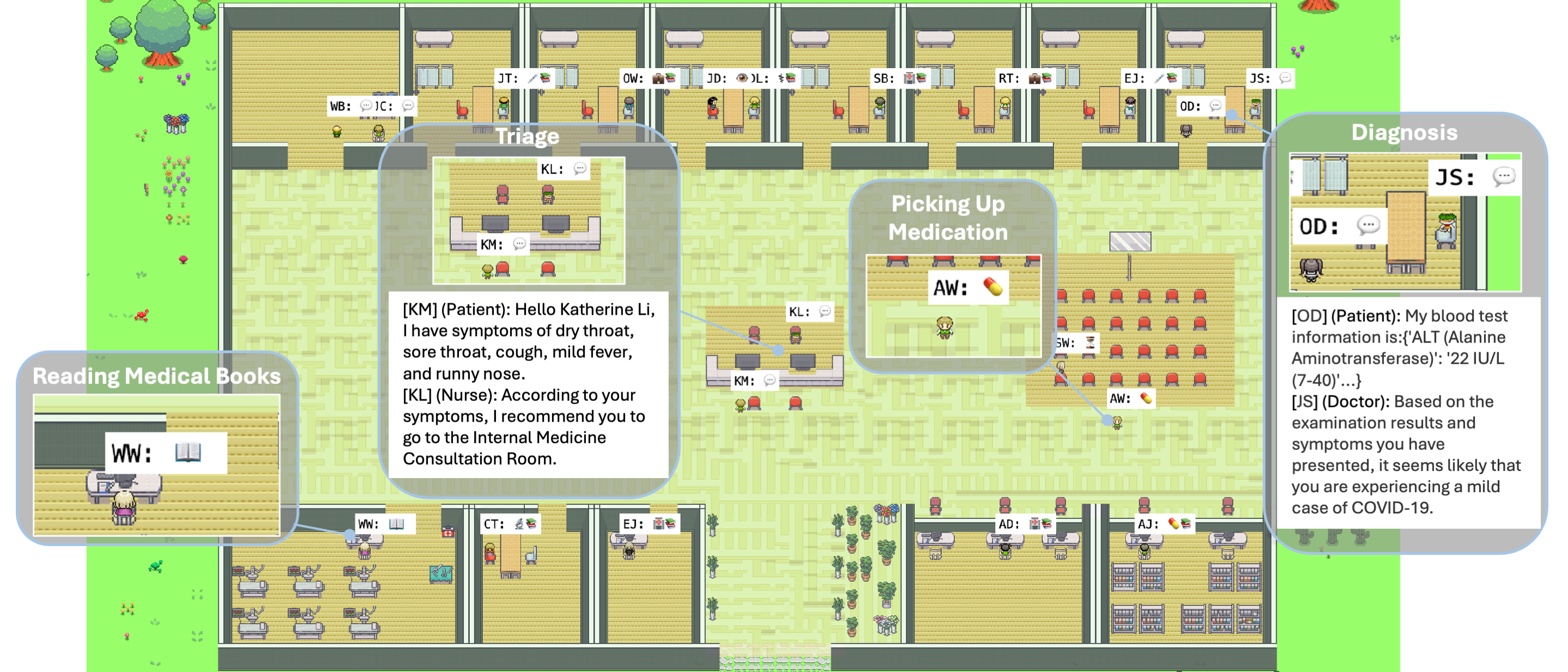
Agent Hospital: A Simulacrum of Hospital with Evolvable Medical Agents
Junkai Li, Siyu Wang, Meng Zhang, Weitao Li, Yunghwei Lai, Xinhui Kang, Weizhi Ma, Yang Liu

4
9
In this paper, we introduce a simulacrum of hospital called Agent Hospital that simulates the entire process of treating illness. All patients, nurses, and doctors are autonomous agents powered by large language models (LLMs). Our central goal is to enable a doctor agent to learn how to treat illness within the simulacrum. To do so, we propose a method called MedAgent-Zero. As the simulacrum can simulate disease onset and progression based on knowledge bases and LLMs, doctor agents can keep accumulating experience from both successful and unsuccessful cases. Simulation experiments show that the treatment performance of doctor agents consistently improves on various tasks. More interestingly, the knowledge the doctor agents have acquired in Agent Hospital is applicable to real-world medicare benchmarks. After treating around ten thousand patients (real-world doctors may take over two years), the evolved doctor agent achieves a state-of-the-art accuracy of 93.06% on a subset of the MedQA dataset that covers major respiratory diseases. This work paves the way for advancing the applications of LLM-powered agent techniques in medical scenarios.
5/7/2024
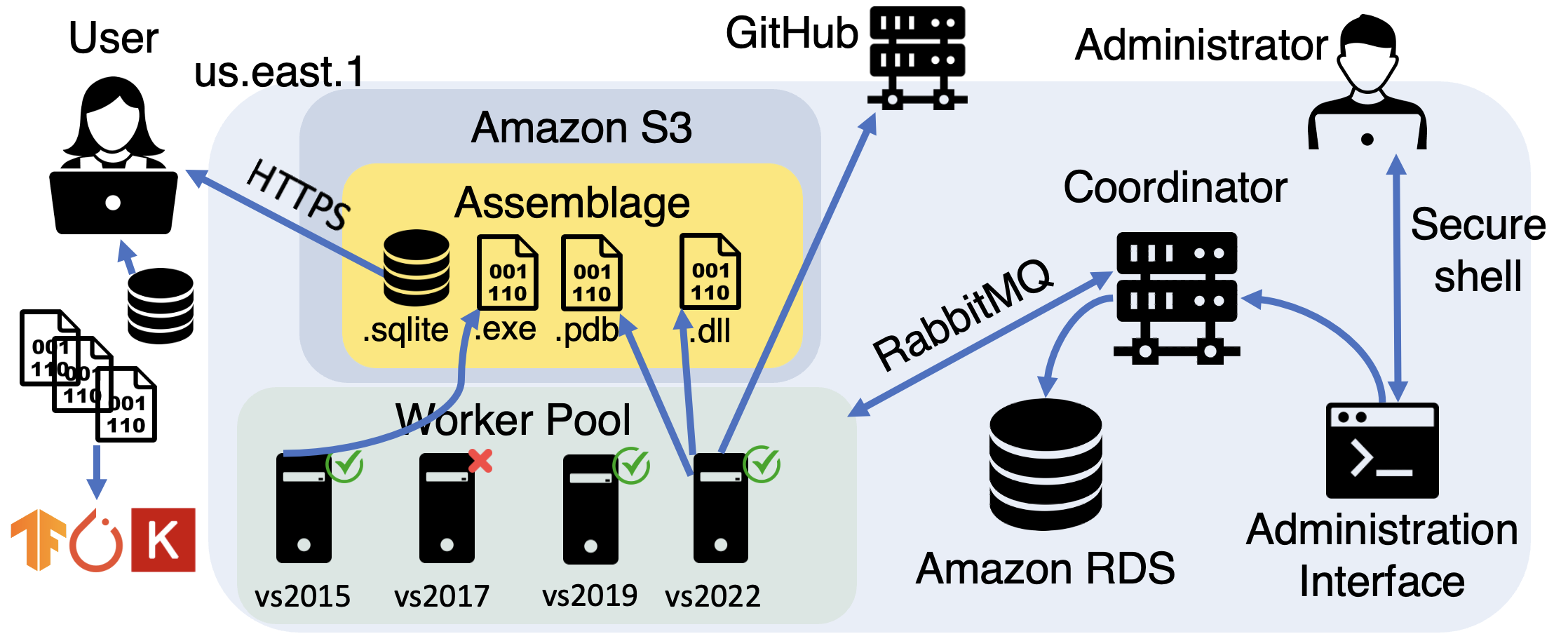
Assemblage: Automatic Binary Dataset Construction for Machine Learning
Chang Liu, Rebecca Saul, Yihao Sun, Edward Raff, Maya Fuchs, Townsend Southard Pantano, James Holt, Kristopher Micinski

6
1
Binary code is pervasive, and binary analysis is a key task in reverse engineering, malware classification, and vulnerability discovery. Unfortunately, while there exist large corpuses of malicious binaries, obtaining high-quality corpuses of benign binaries for modern systems has proven challenging (e.g., due to licensing issues). Consequently, machine learning based pipelines for binary analysis utilize either costly commercial corpuses (e.g., VirusTotal) or open-source binaries (e.g., coreutils) available in limited quantities. To address these issues, we present Assemblage: an extensible cloud-based distributed system that crawls, configures, and builds Windows PE binaries to obtain high-quality binary corpuses suitable for training state-of-the-art models in binary analysis. We have run Assemblage on AWS over the past year, producing 890k Windows PE and 428k Linux ELF binaries across 29 configurations. Assemblage is designed to be both reproducible and extensible, enabling users to publish recipes for their datasets, and facilitating the extraction of a wide array of features. We evaluated Assemblage by using its data to train modern learning-based pipelines for compiler provenance and binary function similarity. Our results illustrate the practical need for robust corpuses of high-quality Windows PE binaries in training modern learning-based binary analyses. Assemblage can be downloaded from https://assemblage-dataset.net
5/8/2024
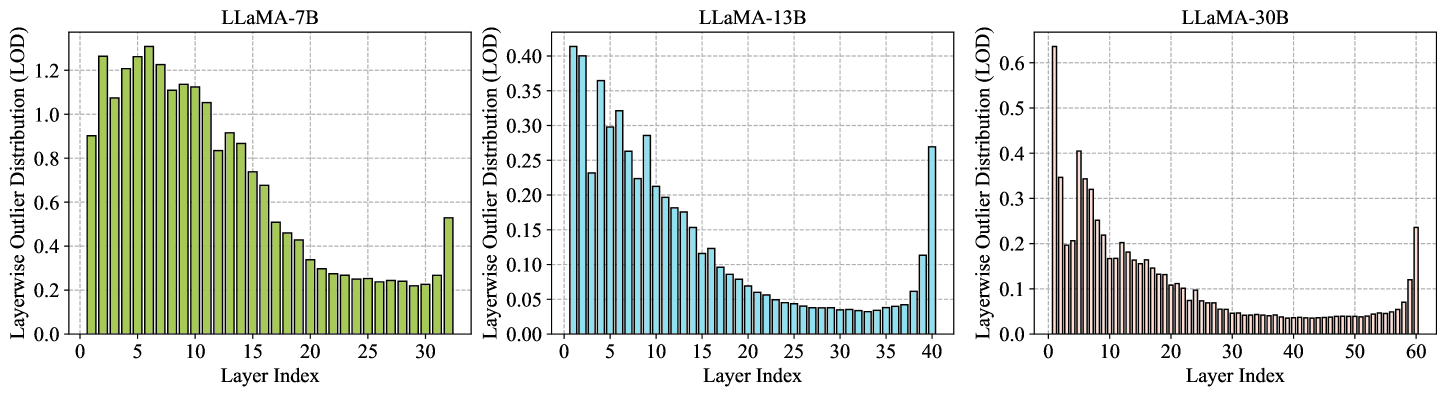
Outlier Weighed Layerwise Sparsity (OWL): A Missing Secret Sauce for Pruning LLMs to High Sparsity
Lu Yin, You Wu, Zhenyu Zhang, Cheng-Yu Hsieh, Yaqing Wang, Yiling Jia, Gen Li, Ajay Jaiswal, Mykola Pechenizkiy, Yi Liang, Michael Bendersky, Zhangyang Wang, Shiwei Liu

5
0
Large Language Models (LLMs), renowned for their remarkable performance across diverse domains, present a challenge when it comes to practical deployment due to their colossal model size. In response to this challenge, efforts have been directed toward the application of traditional network pruning techniques to LLMs, uncovering a massive number of parameters that can be pruned in one-shot without hurting performance. Prevailing LLM pruning strategies have consistently adhered to the practice of uniformly pruning all layers at equivalent sparsity, resulting in robust performance. However, this observation stands in contrast to the prevailing trends observed in the field of vision models, where non-uniform layerwise sparsity typically yields stronger results. To understand the underlying reasons for this disparity, we conduct a comprehensive study and discover a strong correlation with the emergence of activation outliers in LLMs. Inspired by this finding, we introduce a novel LLM pruning methodology that incorporates a tailored set of non-uniform layerwise sparsity ratios, termed as Outlier Weighed Layerwise sparsity (OWL). The sparsity ratio of OWL is proportional to the outlier ratio observed within each layer, facilitating a more effective alignment between layerwise weight sparsity and outlier ratios. Our empirical evaluation, conducted across the LLaMA-V1 family and OPT, spanning various benchmarks, demonstrates the distinct advantages offered by OWL over previous methods. For instance, OWL exhibits a remarkable performance gain, surpassing the state-of-the-art Wanda and SparseGPT by 61.22 and 6.80 perplexity at a high sparsity level of 70%, respectively, while delivering 2.6x end-to-end inference speed-up in the DeepSparse inference engine. Codes are available at https://github.com/luuyin/OWL.
5/7/2024
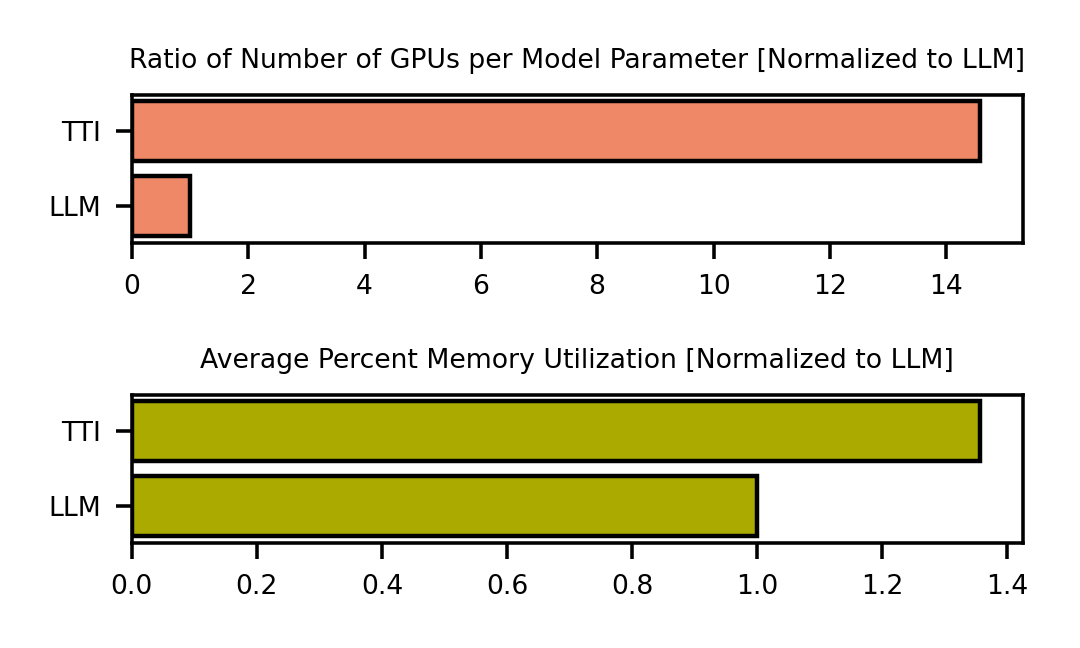
Generative AI Beyond LLMs: System Implications of Multi-Modal Generation
Alicia Golden, Samuel Hsia, Fei Sun, Bilge Acun, Basil Hosmer, Yejin Lee, Zachary DeVito, Jeff Johnson, Gu-Yeon Wei, David Brooks, Carole-Jean Wu

0
10
As the development of large-scale Generative AI models evolve beyond text (1D) generation to include image (2D) and video (3D) generation, processing spatial and temporal information presents unique challenges to quality, performance, and efficiency. We present the first work towards understanding this new system design space for multi-modal text-to-image (TTI) and text-to-video (TTV) generation models. Current model architecture designs are bifurcated into 2 categories: Diffusion- and Transformer-based models. Our systematic performance characterization on a suite of eight representative TTI/TTV models shows that after state-of-the-art optimization techniques such as Flash Attention are applied, Convolution accounts for up to 44% of execution time for Diffusion-based TTI models, while Linear layers consume up to 49% of execution time for Transformer-based models. We additionally observe that Diffusion-based TTI models resemble the Prefill stage of LLM inference, and benefit from 1.1-2.5x greater speedup from Flash Attention than Transformer-based TTI models that resemble the Decode phase. Since optimizations designed for LLMs do not map directly onto TTI/TTV models, we must conduct a thorough characterization of these workloads to gain insights for new optimization opportunities. In doing so, we define sequence length in the context of TTI/TTV models and observe sequence length can vary up to 4x in Diffusion model inference. We additionally observe temporal aspects of TTV workloads pose unique system bottlenecks, with Temporal Attention accounting for over 60% of total Attention time. Overall, our in-depth system performance characterization is a critical first step towards designing efficient and deployable systems for emerging TTI/TTV workloads.
5/7/2024
🧪
ChainForge: A Visual Toolkit for Prompt Engineering and LLM Hypothesis Testing
Ian Arawjo, Chelse Swoopes, Priyan Vaithilingam, Martin Wattenberg, Elena Glassman

4
0
Evaluating outputs of large language models (LLMs) is challenging, requiring making -- and making sense of -- many responses. Yet tools that go beyond basic prompting tend to require knowledge of programming APIs, focus on narrow domains, or are closed-source. We present ChainForge, an open-source visual toolkit for prompt engineering and on-demand hypothesis testing of text generation LLMs. ChainForge provides a graphical interface for comparison of responses across models and prompt variations. Our system was designed to support three tasks: model selection, prompt template design, and hypothesis testing (e.g., auditing). We released ChainForge early in its development and iterated on its design with academics and online users. Through in-lab and interview studies, we find that a range of people could use ChainForge to investigate hypotheses that matter to them, including in real-world settings. We identify three modes of prompt engineering and LLM hypothesis testing: opportunistic exploration, limited evaluation, and iterative refinement.
5/7/2024
🧠
The Topos of Transformer Networks
Mattia Jacopo Villani, Peter McBurney

3
1
The transformer neural network has significantly out-shined all other neural network architectures as the engine behind large language models. We provide a theoretical analysis of the expressivity of the transformer architecture through the lens of topos theory. From this viewpoint, we show that many common neural network architectures, such as the convolutional, recurrent and graph convolutional networks, can be embedded in a pretopos of piecewise-linear functions, but that the transformer necessarily lives in its topos completion. In particular, this suggests that the two network families instantiate different fragments of logic: the former are first order, whereas transformers are higher-order reasoners. Furthermore, we draw parallels with architecture search and gradient descent, integrating our analysis in the framework of cybernetic agents.
5/7/2024