kosmos-2-patch14-224
Maintainer: ydshieh

56
🌀
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Run this model | Run on HuggingFace |
| API spec | View on HuggingFace |
| Github link | No Github link provided |
| Paper link | No paper link provided |
Create account to get full access
Model overview
The kosmos-2-patch14-224 model is a HuggingFace's transformers implementation of the original Kosmos-2 model from Microsoft. Kosmos-2 is a multimodal large language model that aims to ground language models to the real world. This model is an updated version of the original Kosmos-2 with some changes in the input format.
The model was developed and maintained by ydshieh, a member of the HuggingFace community. Similar models include the updated Kosmos-2 model from Microsoft and other multimodal language models like Cosmo-1B and CLIP.
Model inputs and outputs
Inputs
- Text prompt: A text prompt that serves as the grounding for the model's generation, such as "<grounding>An image of".
- Image: An image that the model should be conditioned on during generation.
Outputs
- Generated text: The model generates text that describes the provided image, grounded in the given prompt.
Capabilities
The kosmos-2-patch14-224 model is capable of various multimodal tasks, such as:
- Phrase Grounding: Identifying and describing specific elements in an image.
- Referring Expression Comprehension: Understanding and generating referring expressions that describe objects in an image.
- Grounded VQA: Answering questions about the contents of an image.
- Grounded Image Captioning: Generating captions that describe an image.
The model can perform these tasks by combining the information from the text prompt and the image to produce coherent and grounded outputs.
What can I use it for?
The kosmos-2-patch14-224 model can be useful for a variety of applications that involve understanding and describing visual information, such as:
- Image-to-text generation: Creating captions, descriptions, or narratives for images in various domains, like news, education, or entertainment.
- Multimodal search and retrieval: Enabling users to search for and find relevant images or documents based on a natural language query.
- Visual question answering: Allowing users to ask questions about the contents of an image and receive informative responses.
- Referring expression generation: Generating referring expressions that can be used in multimodal interfaces or for image annotation tasks.
By leveraging the model's ability to ground language to visual information, developers can create more engaging and intuitive multimodal experiences for their users.
Things to try
One interesting aspect of the kosmos-2-patch14-224 model is its ability to generate diverse and detailed descriptions of images. Try providing the model with a wide variety of images, from everyday scenes to more abstract or artistic compositions, and observe how the model's responses change to match the content and context of the image.
Another interesting experiment would be to explore the model's performance on tasks that require a deeper understanding of visual and linguistic relationships, such as visual reasoning or commonsense inference. By probing the model's capabilities in these areas, you may uncover insights about the model's strengths and limitations.
Finally, consider incorporating the kosmos-2-patch14-224 model into a larger system or application, such as a multimodal search engine or a virtual assistant that can understand and respond to visual information. Observe how the model's performance and integration into the overall system can enhance the user experience and capabilities of your application.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Models
🌀
kosmos-2-patch14-224

128
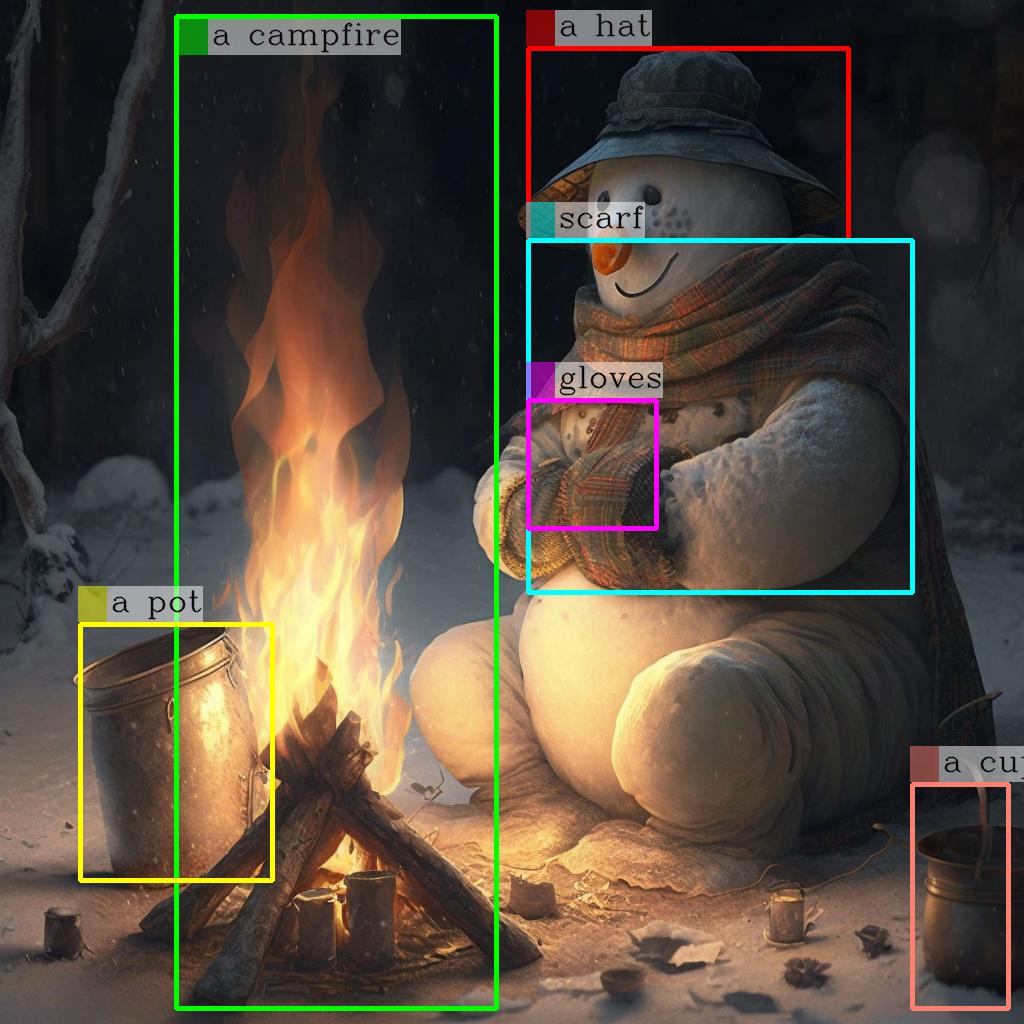
The kosmos-2-patch14-224 model is a HuggingFace implementation of the original Kosmos-2 model from Microsoft. Kosmos-2 is a multimodal large language model designed to ground language understanding to the real world. It was developed by researchers at Microsoft to improve upon the capabilities of earlier multimodal models. The Kosmos-2 model is similar to other recent multimodal models like Kosmos-2 from lucataco and Animagine XL 2.0 from Linaqruf. These models aim to combine language understanding with vision understanding to enable more grounded, contextual language generation and reasoning. Model Inputs and Outputs Inputs Text prompt**: A natural language description or instruction to guide the model's output Image**: An image that the model can use to ground its language understanding and generation Outputs Generated text**: The model's response to the provided text prompt, grounded in the input image Capabilities The kosmos-2-patch14-224 model excels at generating text that is strongly grounded in visual information. For example, when given an image of a snowman warming himself by a fire and the prompt "An image of", the model generates a detailed description that references the key elements of the scene. This grounding of language to visual context makes the Kosmos-2 model well-suited for tasks like image captioning, visual question answering, and multimodal dialogue. The model can leverage its understanding of both language and vision to provide informative and coherent responses. What Can I Use It For? The kosmos-2-patch14-224 model's multimodal capabilities make it a versatile tool for a variety of applications: Content Creation**: The model can be used to generate descriptive captions, stories, or narratives based on input images, enhancing the creation of visually-engaging content. Assistive Technology**: By understanding both language and visual information, the model can be leveraged to build more intelligent and contextual assistants for tasks like image search, visual question answering, and image-guided instruction following. Research and Exploration**: Academics and researchers can use the Kosmos-2 model to explore the frontiers of multimodal AI, studying how language and vision can be effectively combined to enable more human-like understanding and reasoning. Things to Try One interesting aspect of the kosmos-2-patch14-224 model is its ability to generate text that is tailored to the specific visual context provided. By experimenting with different input images, you can observe how the model's language output changes to reflect the details and nuances of the visual information. For example, try providing the model with a variety of images depicting different scenes, characters, or objects, and observe how the generated text adapts to accurately describe the visual elements. This can help you better understand the model's strengths in grounding language to the real world. Additionally, you can explore the limits of the model's multimodal capabilities by providing unusual or challenging input combinations, such as abstract or low-quality images, to see how it handles such cases. This can provide valuable insights into the model's robustness and potential areas for improvement.
Updated Invalid Date
🛠️
kivotos-xl-2.0

86
kivotos-xl-2.0 is the latest version of the Yodayo Kivotos XL series, building upon the previous Kivotos XL 1.0 model. It is an open-source text-to-image diffusion model designed to generate high-quality anime-style artwork, with a specific focus on capturing the visual aesthetics of the Blue Archive franchise. The model is built upon the Animagine XL V3 framework, and has undergone additional fine-tuning and optimization by the Linaqruf team. Model Inputs and Outputs kivotos-xl-2.0 is a text-to-image generative model, taking textual prompts as input and generating corresponding anime-style images as output. The model can handle a wide range of prompts, from specific character descriptions to more abstract scene compositions. Inputs Textual prompts describing the desired image Outputs High-quality anime-style images that match the provided textual prompt Capabilities kivotos-xl-2.0 is capable of generating a variety of anime-style images, ranging from character portraits to complex scenes and environments. The model has been fine-tuned to excel at capturing the distinct visual style and aesthetics of the Blue Archive franchise, allowing users to create artwork that seamlessly fits within the established universe. What can I use it for? kivotos-xl-2.0 can be used for a variety of creative applications, such as: Generating character designs and illustrations for Blue Archive-themed projects Creating promotional or fan art for the Blue Archive franchise Experimenting with different anime-style art compositions and aesthetics Exploring the limits of text-to-image generation for anime-inspired artwork Things to try One interesting aspect of kivotos-xl-2.0 is its ability to capture the nuanced visual details and stylistic elements of the Blue Archive universe. Users can experiment with prompts that focus on specific characters, environments, or moods to see how the model interprets and translates these elements into unique and visually striking images.
Updated Invalid Date
kosmos-2

1
kosmos-2 is a large language model developed by Microsoft that aims to ground multimodal language models to the real world. It is similar to other models created by the same maintainer, such as Kosmos-G, Moondream1, and DeepSeek-VL, which focus on generating images, performing vision-language tasks, and understanding real-world applications. Model inputs and outputs kosmos-2 takes an image as input and outputs a text description of the contents of the image, including bounding boxes around detected objects. The model can also provide a more detailed description if requested. Inputs Image**: An input image to be analyzed Outputs Text**: A description of the contents of the input image Image**: The input image with bounding boxes around detected objects Capabilities kosmos-2 is capable of detecting and describing various objects, scenes, and activities in an input image. It can identify and localize multiple objects within an image and provide a textual summary of its contents. What can I use it for? kosmos-2 can be useful for a variety of applications that require image understanding, such as visual search, image captioning, and scene understanding. It could be used to enhance user experiences in e-commerce, social media, or other image-driven applications. The model's ability to ground language to the real world also makes it potentially useful for tasks like image-based question answering or visual reasoning. Things to try One interesting aspect of kosmos-2 is its potential to be used in conjunction with other models like Kosmos-G to enable multimodal applications that combine image generation and understanding. Developers could explore ways to leverage kosmos-2's capabilities to build novel applications that seamlessly integrate visual and language processing.
Updated Invalid Date
🤷
Florence-2-base

106
Florence-2-base is an advanced vision foundation model from Microsoft that uses a prompt-based approach to handle a wide range of vision and vision-language tasks. It can interpret simple text prompts to perform tasks like captioning, object detection, and segmentation. Florence-2 leverages the FLD-5B dataset, containing 5.4 billion annotations across 126 million images, to master multi-task learning. The model's sequence-to-sequence architecture enables it to excel in both zero-shot and fine-tuned settings, proving to be a competitive vision foundation model. Similar models include Florence-2-large, which is a larger version of the model, and Florence-2-base-ft and Florence-2-large-ft, which are the fine-tuned versions of the base and large models, respectively. Model inputs and outputs Inputs Text prompt**: A short text prompt that describes the task the model should perform, such as "", "", or "". Image**: An image that the model will use to perform the specified task. Outputs Task-specific output**: The model's response to the input prompt and image, which can include: Captions or descriptions of the image Bounding boxes and labels for detected objects Detailed captions for specific regions of the image Text output for optical character recognition (OCR) tasks Capabilities Florence-2 can perform a variety of vision and vision-language tasks, including image captioning, object detection, dense region captioning, and OCR. It can interpret simple text prompts to handle these tasks in both zero-shot and fine-tuned settings. The model's strong performance on benchmarks like COCO captioning, NoCaps, and TextCaps demonstrates its capabilities in image understanding and generation. What can I use it for? You can use Florence-2-base for a wide range of computer vision and multimodal applications, such as: Image captioning**: Generate detailed descriptions of images to assist with accessibility or visual search. Object detection**: Identify and localize objects in images to enable applications like autonomous driving or inventory management. Dense region captioning**: Produce captions that describe specific regions of an image, which can be useful for image analysis and understanding. Optical character recognition (OCR)**: Extract text from images to enable applications like document digitization or scene text understanding. The fine-tuned versions of the model, Florence-2-base-ft and Florence-2-large-ft, may be particularly useful if you have specific downstream tasks or datasets you need to work with. Things to try One interesting thing to try with Florence-2 is its ability to handle a variety of vision tasks through simple text prompts. You can experiment with different prompts to see how the model responds and explore its versatility. For example, you could try prompts like "", "", or "" and see how the model generates captions, detects objects, or describes specific regions of the image. You could also try comparing the performance of the base and fine-tuned versions of the model on your specific task or dataset to see if the fine-tuning provides a significant improvement.
Updated Invalid Date