Bayesian Intention for Enhanced Human Robot Collaboration

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper proposes a Bayesian approach for estimating human intentions to enhance human-robot collaboration.
- The method uses multimodal sensory inputs, including visual, auditory, and motion data, to infer the user's likely intentions.
- The goal is to enable robots to better anticipate and respond to human actions, leading to more natural and efficient collaboration.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a new way for robots to understand what a person is trying to do. Instead of just reacting to what the person is doing, the robot uses Bayesian inference to try to figure out the person's intention - what the person is aiming to accomplish.
The robot gathers information from different sensors, like cameras and microphones, to get a complete picture of the person's actions, movements, and behaviors. It then uses this multimodal data to estimate the person's likely intention.
By understanding the person's intention, the robot can anticipate what the person will do next and adapt its own actions accordingly. This allows the robot to collaborate with the person in a more natural and effective way, rather than just reacting to each individual action.
The key idea is that if the robot can "read the person's mind" and figure out what they're trying to accomplish, it can provide more useful assistance and the two can work together more smoothly.
Technical Explanation
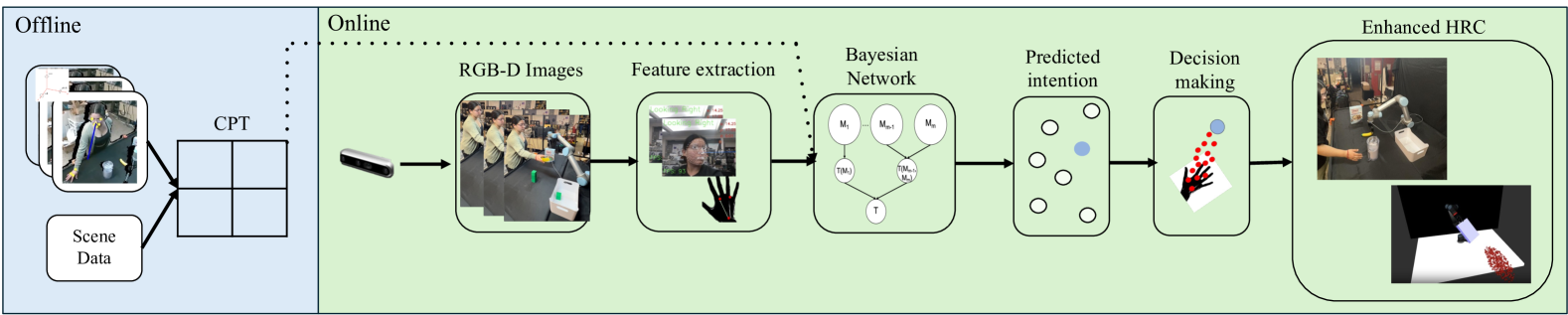
The paper presents a Bayesian approach for intent recognition in human-robot collaboration. The method uses a multimodal sensing system that integrates visual, auditory, and motion data to infer the user's likely intentions.
The key components of the system include:
-
Multimodal Sensory Input: The system gathers data from cameras, microphones, and motion sensors to capture a comprehensive view of the user's actions and behaviors.
-
Bayesian Inference: The system uses a Bayesian framework to estimate the probability distribution over possible user intentions, given the observed multimodal sensory inputs.
-
Intent Recognition: By continuously updating the probability distribution, the system can recognize the user's intentions and anticipate their future actions.
The authors evaluate the system's performance on a range of human-robot collaboration tasks, demonstrating improved efficiency and fluency compared to traditional reactive approaches.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a compelling approach for enhancing human-robot collaboration through intent recognition. The use of Bayesian inference and multimodal sensing are well-justified, as they allow the system to reason about the user's likely intentions based on a richer set of observations.
However, the paper does not address some potential limitations and areas for further research:
-
Generalization Ability: The system's performance may be sensitive to the specific tasks and environments used in the evaluation. More research is needed to understand how well the approach generalizes to a broader range of human-robot collaboration scenarios.
-
Explainability: The Bayesian inference process is inherently complex. Providing users with transparent and interpretable explanations of the system's intent recognition could be important for building trust and acceptance.
-
Ethical Considerations: As robots become more capable of "reading" human intentions, there may be concerns around privacy, autonomy, and the potential for misuse. The paper does not address these important ethical implications.
Overall, the paper presents a promising approach for enhancing human-robot collaboration through intent recognition. However, further research is needed to address the limitations and ensure the responsible development of such systems.
Conclusion
This paper introduces a Bayesian approach for intent recognition in human-robot collaboration. By using multimodal sensing and Bayesian inference, the system can better understand the user's likely intentions and anticipate their actions, leading to more natural and efficient collaboration.
The proposed method has the potential to significantly improve the fluency and effectiveness of human-robot interactions, especially in complex, dynamic environments. However, further research is needed to address issues of generalization, explainability, and ethical considerations to ensure the responsible development of such systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!