On the Benefits of Coding for Network Slicing
2404.17686

0
0
Abstract
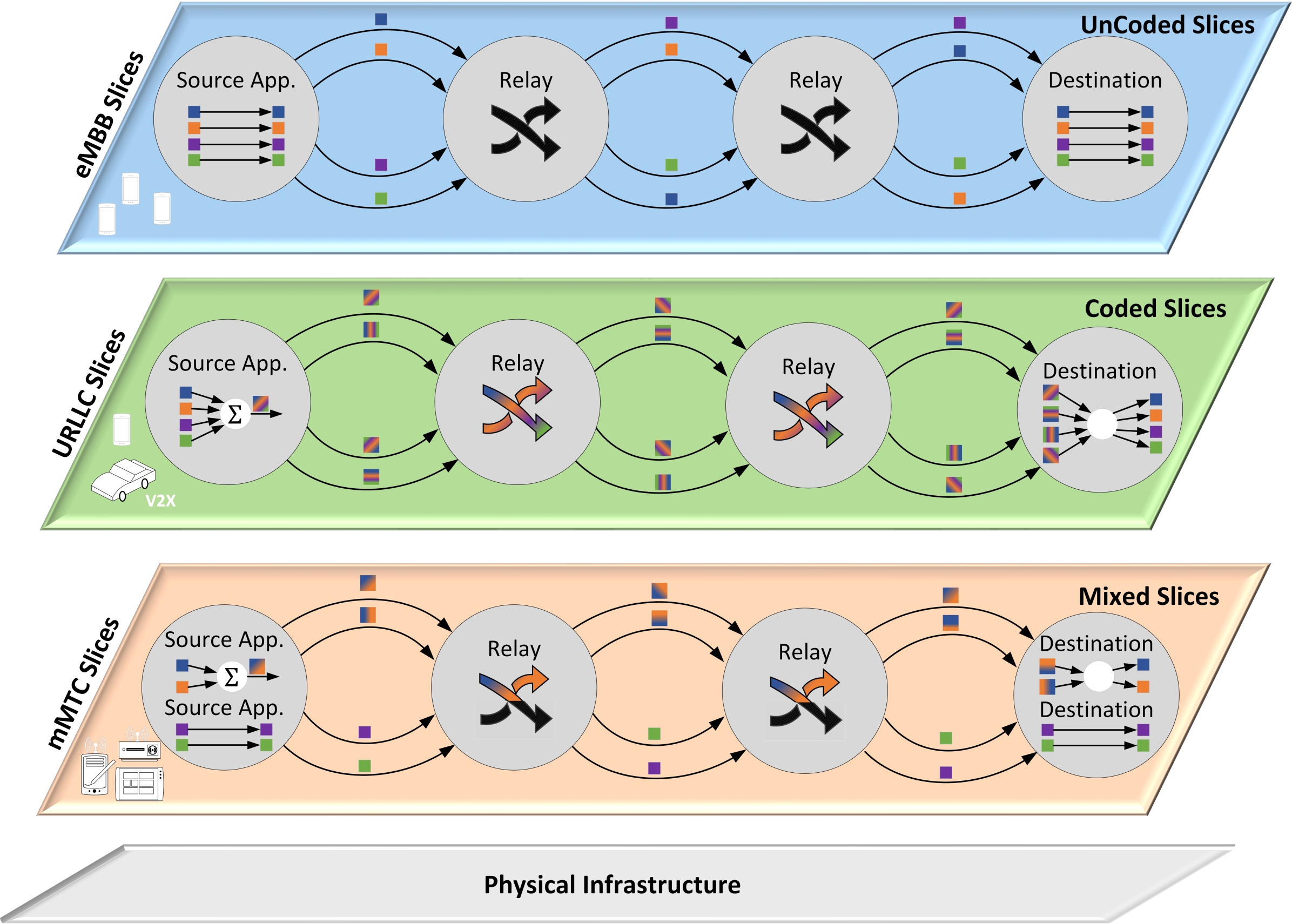
Network slicing has emerged as an integral concept in 5G, aiming to partition the physical network infrastructure into isolated slices, customized for specific applications. We theoretically formulate the key performance metrics of an application, in terms of goodput and delivery delay, at a cost of network resources in terms of bandwidth. We explore an un-coded communication protocol that uses feedback-based repetitions, and a coded protocol, implementing random linear network coding and using coding-aware acknowledgments. We find that coding reduces the resource demands of a slice to meet the requirements for an application, thereby serving more applications efficiently. Coded slices thus free up resources for other slices, be they coded or not. Based on these results, we propose a hybrid approach, wherein coding is introduced selectively in certain network slices. This approach not only facilitates a smoother transition from un-coded systems to coded systems but also reduces costs across all slices. Theoretical findings in this paper are validated and expanded upon through real-time simulations of the network.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Explores the benefits of using network coding techniques for network slicing in 5G and beyond networks
- Investigates how network coding can improve key performance metrics like delivery delay, goodput, and completion time
- Supported by the SNOB-5G project under the MIT Portugal Program and by JMA Wireless
Plain English Explanation
Network slicing is an important concept in 5G and future cellular networks, allowing network operators to create virtual network "slices" tailored to the specific needs of different applications and services. This paper explores how using network coding techniques can provide benefits for network slicing.
Network coding is a way of transmitting data where the intermediate network nodes combine, or "code", the incoming data packets before forwarding them. This can help improve the efficiency and reliability of data delivery.
The researchers investigated how applying network coding to network slicing could enhance key performance metrics like delivery delay, goodput (the actual useful data throughput), and completion time. They found that network coding can lead to significant improvements in these areas compared to traditional approaches without coding.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents an analytical model to study the impact of network coding on the performance of network slicing. It considers a scenario with multiple network slices, each serving a different set of users with their own traffic demands and quality of service requirements.
The authors derive mathematical expressions to calculate the delivery delay, goodput, and completion time for both coded and uncoded transmissions. These metrics are then used to quantify the benefits of incorporating network coding into the network slicing framework.
Through numerical analysis and simulations, the researchers demonstrate that network coding can reduce the delivery delay and completion time, while also increasing the overall goodput of the system. The improvements are particularly pronounced when the network is heavily loaded or the users have heterogeneous resource requirements.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough analytical and simulation-based evaluation of the advantages of using network coding in the context of network slicing. The authors have considered realistic scenarios and derived meaningful performance metrics to quantify the benefits.
However, the study is limited to a theoretical analysis and does not address practical implementation challenges, such as the additional complexity and overhead introduced by network coding operations at the network nodes. Further research is needed to understand the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of deploying network coding in real-world 5G and beyond network slicing deployments.
Additionally, the paper does not explore the potential interactions and trade-offs between network coding and other optimization techniques, such as dynamic bandwidth adaptation or machine learning-based KPI prediction, which could be important in real-world network slicing deployments.
Conclusion
This paper presents a promising approach to leveraging network coding techniques to improve the performance of network slicing in 5G and beyond networks. The analytical and simulation results demonstrate the potential benefits of network coding in terms of reduced delivery delay, increased goodput, and faster completion times.
While the theoretical analysis is strong, further research is needed to address practical implementation challenges and explore the interplay between network coding and other optimization techniques in the context of network slicing. Nonetheless, this work contributes to the growing body of research on enhancing network slicing capabilities through innovative approaches like network coding.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Slice-aware Resource Allocation and Admission Control for Smart Factory Wireless Networks
Regina Ochonu, Josep Vidal

0
0
The 5th generation (5G) and beyond network offers substantial promise as the ideal wireless technology to replace the existing inflexible wired connections in traditional factories of today. 5G network slicing allows for tailored allocation of resources to different network services, each with unique Quality of Service (QoS) requirements. This paper presents a novel solution for slice-aware radio resource allocation based on a convex optimisation control framework for applications in smart factory wireless networks. The proposed framework dynamically allocates minimum power and sub-channels to downlink mixed service type industrial users categorised into three slices: Capacity Limited (CL), Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC), and Time Sensitive (TS) slices. Given that the base station (BS) has limited transmission power, we enforce admission control by effectively relaxing the target rate constraints for current connections in the CL slice. This rate readjustment occurs whenever power consumption exceeds manageable levels. Simulation results show that our approach minimises power, allocates sub-channels to users, maintains slice isolation, and delivers QoS-specific communications to users in all the slices despite time-varying number of users and changing network conditions.
5/17/2024
✅
Learning to Slice Wi-Fi Networks: A State-Augmented Primal-Dual Approach
Yiu{g}it Berkay Uslu, Roya Doostnejad, Alejandro Ribeiro, Navid NaderiAlizadeh

0
0
Network slicing is a key feature in 5G/NG cellular networks that creates customized slices for different service types with various quality-of-service (QoS) requirements, which can achieve service differentiation and guarantee service-level agreement (SLA) for each service type. In Wi-Fi networks, there is limited prior work on slicing, and a potential solution is based on a multi-tenant architecture on a single access point (AP) that dedicates different channels to different slices. In this paper, we define a flexible, constrained learning framework to enable slicing in Wi-Fi networks subject to QoS requirements. We specifically propose an unsupervised learning-based network slicing method that leverages a state-augmented primal-dual algorithm, where a neural network policy is trained offline to optimize a Lagrangian function and the dual variable dynamics are updated online in the execution phase. We show that state augmentation is crucial for generating slicing decisions that meet the ergodic QoS requirements.
5/10/2024
Data-driven Bandwidth Adaptation for Radio Access Network Slices
Panagiotis Nikolaidis, Asim Zoulkarni, John Baras

0
0
The need to satisfy the QoS requirements of multiple network slices deployed at the same base station poses a major challenge to network operators. The problem becomes even harder when the desired QoS involves packet delays. In that case, network utility maximization is not directly applicable since the utilities of the slices are unknown. As a result, most related works learn online the utilities of all slices and how to split the resources among them. Unfortunately, this approach does not scale well for many slices. Instead, it is needed to perform learning separately for each slice. To this end, we develop a bandwidth demand estimator; a network function that periodically receives as input the traffic of the slice and outputs the amount of bandwidth that its MAC scheduler needs to deliver the desired QoS. We develop the bandwidth demand estimator for QoS involving packet delay metrics based on a model-based reinforcement learning algorithm. We implement the algorithm on a cellular testbed and conduct experiments with time-varying traffic loads. Results show that the algorithm delivers the desired QoS but with significantly less bandwidth than non-adaptive approaches and other baseline online learning algorithms.
4/30/2024

Proactive Service Assurance in 5G and B5G Networks: A Closed-Loop Algorithm for End-to-End Network Slicing
Nguyen Phuc Tran, Oscar Delgado, Brigitte Jaumard

0
0
The customization of services in Fifth-generation (5G) and Beyond 5G (B5G) networks relies heavily on network slicing, which creates multiple virtual networks on a shared physical infrastructure, tailored to meet specific requirements of distinct applications, using Software Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV). It is imperative to ensure that network services meet the performance and reliability requirements of various applications and users, thus, service assurance is one of the critical components in network slicing. One of the key functionalities of network slicing is the ability to scale Virtualized Network Functions (VNFs) in response to changing resource demand and to meet Customer Service Level agreements (SLAs). In this paper, we introduce a proactive closed-loop algorithm for end-to-end network orchestration, designed to provide service assurance in 5G and B5G networks. We focus on dynamically scaling resources to meet key performance indicators (KPIs) specific to each network slice and operate in parallel across multiple slices, making it scalable and capable of managing completely automatically real-time service assurance. Through our experiments, we demonstrate that the proposed algorithm effectively fulfills service assurance requirements for different network slice types, thereby minimizing network resource utilization and reducing the over-provisioning of spare resources.
6/26/2024