Catalyzing Social Interactions in Mixed Reality using ML Recommendation Systems
2404.19095

0
0
📉
Abstract
We create an innovative mixed reality-first social recommendation model, utilizing features uniquely collected through mixed reality (MR) systems to promote social interaction, such as gaze recognition, proximity, noise level, congestion level, and conversational intensity. We further extend these models to include right-time features to deliver timely notifications. We measure performance metrics across various models by creating a new intersection of user features, MR features, and right-time features. We create four model types trained on different combinations of the feature classes, where we compare the baseline model trained on the class of user features against the models trained on MR features, right-time features, and a combination of all of the feature classes. Due to limitations in data collection and cost, we observe performance degradation in the right-time, mixed reality, and combination models. Despite these challenges, we introduce optimizations to improve accuracy across all models by over 14 percentage points, where the best performing model achieved 24% greater accuracy.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Researchers developed a mixed reality-first social recommendation model that utilizes unique features from mixed reality (MR) systems to promote social interaction
- The model includes right-time features to deliver timely notifications
- The team measured performance across different model types trained on various combinations of user features, MR features, and right-time features
- Despite data collection and cost challenges, the researchers introduced optimizations that improved accuracy across all models by over 14 percentage points
Plain English Explanation
The researchers created an innovative social recommendation system that takes advantage of the unique capabilities of mixed reality (MR) technology. MR systems can track things like where people are looking, how close they are to each other, how noisy the environment is, how crowded it is, and how engaged people are in conversations.
The researchers used these MR-specific features, along with information about when to deliver recommendations, to build different recommendation models. They compared the performance of models trained on user data alone to models that also incorporated MR and timing data.
While the models that included MR and timing data faced some challenges due to limitations in data collection and cost, the researchers were able to make improvements that boosted the accuracy of all the models by a significant margin. The best performing model achieved 24% greater accuracy than the baseline.
The goal of this work is to use MR technology to enhance social interactions and connections between people. By understanding factors like gaze, proximity, and conversational intensity, the system can make more relevant and timely recommendations to users to facilitate meaningful social engagement.
Technical Explanation
The researchers developed a mixed reality-first social recommendation model that leverages features uniquely captured through MR systems, such as gaze recognition, proximity, noise level, congestion level, and conversational intensity. They extended these models to include right-time features to deliver timely notifications to users.
The team evaluated performance across various model types trained on different combinations of user features, MR features, and right-time features. They created four model types:
- Baseline model trained on user features only
- Model trained on MR features
- Model trained on right-time features
- Model trained on a combination of all feature classes
Due to limitations in data collection and cost, the researchers observed performance degradation in the right-time, MR, and combination models. However, they introduced optimizations that improved accuracy across all models by over 14 percentage points, with the best performing model achieving 24% greater accuracy than the baseline.
The goal of this work is to leverage spatial and social interaction dynamics captured through MR systems to enhance social recommendation and facilitate meaningful connections between people.
Critical Analysis
While the researchers were able to achieve significant performance improvements through their optimizations, the paper acknowledges some key limitations in their approach. The degradation in performance observed for the models incorporating MR and right-time features highlights the challenges of working with these more complex data sources. The researchers note that the limitations in data collection and cost impacted the quality and quantity of the data available for training these models.
Additionally, the paper does not provide much detail on the specific optimization techniques used or the underlying reasons for the performance differences between the model types. Further exploration of these aspects could help provide more insight into the tradeoffs and design choices involved in developing this type of mixed reality-based recommendation system.
It would also be valuable to see the researchers extend their evaluation to consider real-world deployment scenarios and user feedback. Understanding how the system performs in practical settings and how users perceive the recommendations and social interactions facilitated by the system could uncover additional areas for improvement or refinement.
Overall, this research represents an exciting step forward in leveraging mixed reality technology to enhance social experiences. By continuing to address the technical and practical challenges, the researchers have the opportunity to unlock new possibilities for fostering meaningful human connections through spatial computing.
Conclusion
This paper presents an innovative mixed reality-first social recommendation model that utilizes unique features collected through MR systems to promote social interaction and deliver timely notifications to users. While the researchers faced some challenges due to data limitations, they were able to introduce optimizations that significantly improved the accuracy of their models.
The core contribution of this work is demonstrating the potential of MR technology to enhance social experiences by capturing contextual information like gaze, proximity, and conversational dynamics. By incorporating these spatial and social interaction signals into recommendation models, the researchers have laid the groundwork for new ways to facilitate meaningful connections between people.
As mixed reality systems become more widespread, this research points to exciting opportunities to leverage these technologies to foster richer, more engaging social experiences. By continuing to refine their approaches and address the practical challenges, the researchers can help unlock the transformative potential of mixed reality for social interaction and human connection.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
📊
Quantifying Social Presence in Mixed Reality: A Contemporary Review of Techniques and Innovations
Sparsh Srivastava

0
0
This literature review investigates the transformative potential of mixed reality (MR) technology, where we explore the intersection of contemporary technological advancements, modern deep learning recommendation systems, and social psychology frameworks. This interdisciplinary study informs the understanding of MR's role in improving social presence, catalyzing novel social interactions, and enhancing the quality of interpersonal communication in the real world. We also discuss the challenges and barriers blocking the wide-spread adoption of social networking in MR, such as device constraints, privacy and accessibility concerns, and social norms. Through carefully structured, closed-environment experiments with diverse participants of varying levels of digital literacy, we measure the differences in social dynamics, frequency, quality, and duration of interactions, and levels of social anxiety between MR-enhanced, mobile-enhanced, and control condition participants.
4/29/2024
📈
Towards Mixed Reality as the Everyday Computing Paradigm: Challenges & Design Recommendations
Amir Reza Asadi, Reza Hemadi

0
0
This research presents a proof-of-concept prototype of an all-in-one mixed reality application platform, developed to investigate the needs and expectations of users from mixed reality systems. The study involved an extensive user study with 1,052 participants, including the collection of diaries from 6 users and conducting interviews with 15 participants to gain deeper insights into their experiences. The findings from the interviews revealed that directly porting current user flows into 3D environments was not well-received by the target users. Instead, users expressed a clear preference for alternative 3D interactions along with the continued use of 2D interfaces. This study provides insights for understanding user preferences and interactions in mixed reality systems, and design recommendations to facilitate the mass adoption of MR systems.
4/17/2024
📉
Protecting Human Users Against Cognitive Attacks in Immersive Environments
Yan-Ming Chiou, Bob Price, Chien-Chung Shen, Syed Ali Asif

0
0
Integrating mixed reality (MR) with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, including vision, language, audio, reasoning, and planning, enables the AI-powered MR assistant [1] to substantially elevate human efficiency. This enhancement comes from situational awareness, quick access to essential information, and support in learning new skills in the right context throughout everyday tasks. This blend transforms interactions with both the virtual and physical environments, catering to a range of skill levels and personal preferences. For instance, computer vision enables the understanding of the user's environment, allowing for the provision of timely and relevant digital overlays in MR systems. At the same time, language models enhance comprehension of contextual information and support voice-activated dialogue to answer user questions. However, as AI-driven MR systems advance, they also unveil new vulnerabilities, posing a threat to user safety by potentially exposing them to grave dangers [5, 6].
5/10/2024
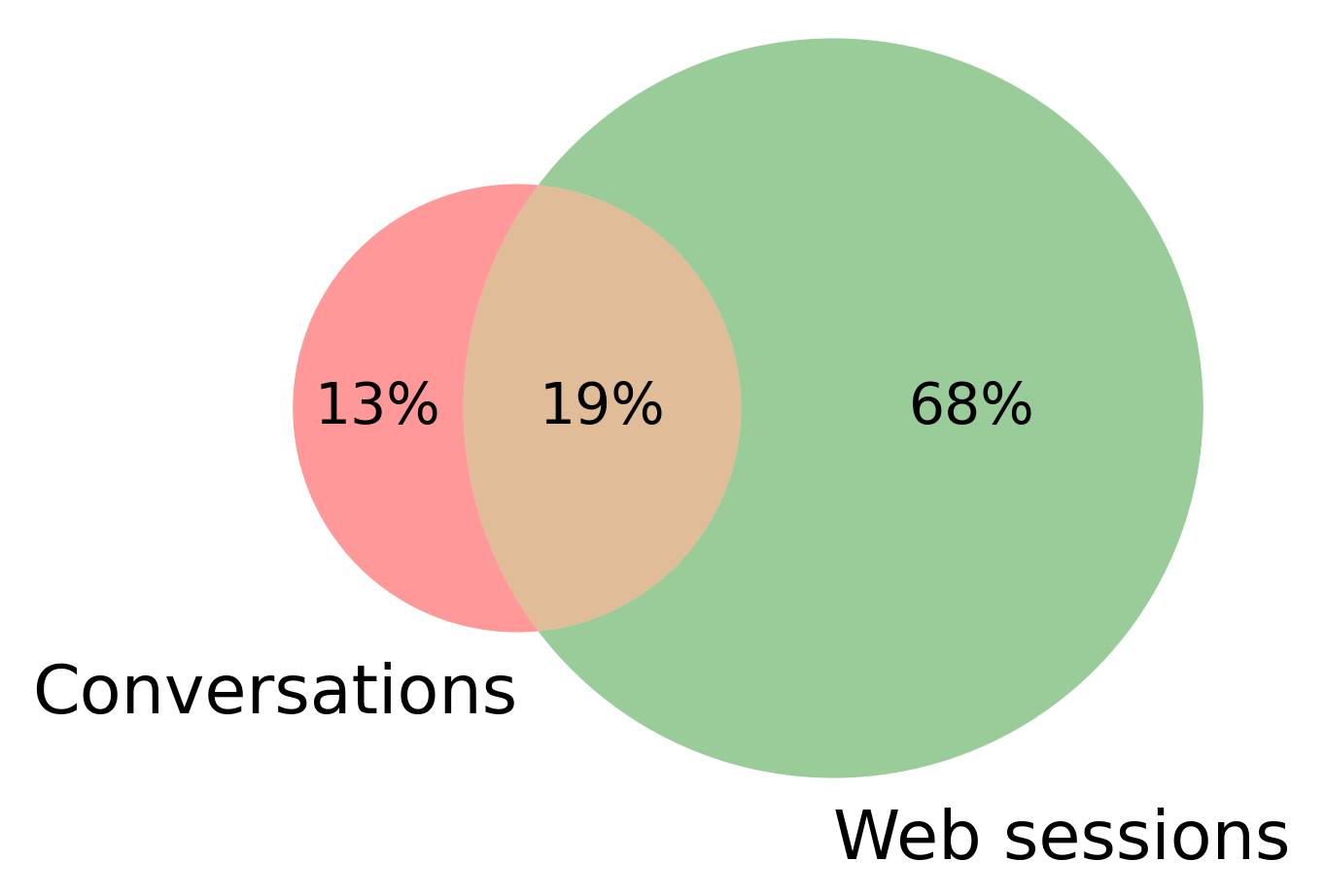
Dataset and Models for Item Recommendation Using Multi-Modal User Interactions
Simone Borg Bruun, Krisztian Balog, Maria Maistro

0
0
While recommender systems with multi-modal item representations (image, audio, and text), have been widely explored, learning recommendations from multi-modal user interactions (e.g., clicks and speech) remains an open problem. We study the case of multi-modal user interactions in a setting where users engage with a service provider through multiple channels (website and call center). In such cases, incomplete modalities naturally occur, since not all users interact through all the available channels. To address these challenges, we publish a real-world dataset that allows progress in this under-researched area. We further present and benchmark various methods for leveraging multi-modal user interactions for item recommendations, and propose a novel approach that specifically deals with missing modalities by mapping user interactions to a common feature space. Our analysis reveals important interactions between the different modalities and that a frequently occurring modality can enhance learning from a less frequent one.
5/8/2024