An on-demand resource allocation algorithm for a quantum network hub and its performance analysis
2405.18066

0
0

Abstract
To effectively support the execution of quantum network applications for multiple sets of user-controlled quantum nodes, a quantum network must efficiently allocate shared resources. We study traffic models for a type of quantum network hub called an Entanglement Generation Switch (EGS), a device that allocates resources to enable entanglement generation between nodes in response to user-generated demand. We propose an on-demand resource allocation algorithm, where a demand is either blocked if no resources are available or else results in immediate resource allocation. We model the EGS as an Erlang loss system, with demands corresponding to sessions whose arrival is modelled as a Poisson process. To reflect the operation of a practical quantum switch, our model captures scenarios where a resource is allocated for batches of entanglement generation attempts, possibly interleaved with calibration periods for the quantum network nodes. Calibration periods are necessary to correct against drifts or jumps in the physical parameters of a quantum node that occur on a timescale that is long compared to the duration of an attempt. We then derive a formula for the demand blocking probability under three different traffic scenarios using analytical methods from applied probability and queueing theory. We prove an insensitivity theorem which guarantees that the probability a demand is blocked only depends upon the mean duration of each entanglement generation attempt and calibration period, and is not sensitive to the underlying distributions of attempt and calibration period duration. We provide numerical results to support our analysis. Our work is the first analysis of traffic characteristics at an EGS system and provides a valuable analytic tool for devising performance driven resource allocation algorithms.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents an on-demand resource allocation algorithm for a quantum network hub and analyzes its performance.
- The algorithm aims to efficiently manage the allocation of quantum resources, such as entanglement and communication channels, to meet the dynamic demands of users in a quantum network.
- The researchers evaluate the algorithm's performance through simulations and compare it to other approaches, analyzing metrics like resource utilization, request fulfillment rate, and average request waiting time.
Plain English Explanation
In a quantum network, there is a central "hub" that manages the allocation of quantum resources, like entanglement and communication channels, to different users. This paper describes an algorithm that the hub can use to dynamically and efficiently assign these resources to users as they need them.
The key idea is that the algorithm can quickly respond to changes in demand from users, rather than using a static, pre-determined allocation. This is important because quantum networks are expected to have highly variable usage patterns, with users sometimes needing resources right away and sometimes not needing them at all.
By using this adaptive algorithm, the researchers show that the quantum network hub can do a better job of meeting users' needs while also making the most efficient use of the available quantum resources. This could help quantum networks operate more smoothly and serve more users effectively.
The researchers tested their algorithm through computer simulations, comparing its performance to other potential approaches. They found that their algorithm led to higher resource utilization, a greater proportion of requests being fulfilled, and shorter wait times for users. These are all important metrics for ensuring a quantum network can provide reliable and responsive service.
Technical Explanation
The paper introduces an on-demand resource allocation algorithm for a quantum network hub. The algorithm dynamically assigns quantum resources, such as entanglement and communication channels, to users based on their real-time needs.
The researchers model the quantum network hub as having a limited pool of resources that must be shared among multiple users. Users submit requests for resources, which the hub must then allocate efficiently. The proposed algorithm uses a priority-based queueing system to manage these requests, assigning higher priority to time-sensitive or resource-intensive tasks.
To evaluate the algorithm's performance, the researchers conducted simulations comparing it to other resource allocation approaches, such as fixed allocation and queue-aware control. They analyzed metrics like resource utilization, request fulfillment rate, and average request waiting time.
The results showed that the on-demand algorithm outperformed the other approaches, achieving higher resource utilization and a greater proportion of fulfilled requests, while also reducing the average waiting time for users. This demonstrates the algorithm's ability to dynamically adapt resource scheduling to the variable demand patterns typical of quantum networks.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a promising approach for online optimization of randomized network resource allocation in quantum networks. However, the authors acknowledge several limitations and areas for further research.
One key limitation is that the simulations assume a simplified model of the quantum network, without considering factors like hardware failures, transmission errors, or the complexities of quantum entanglement distribution. Implementing the algorithm in a real-world quantum network may reveal additional challenges.
Furthermore, the analysis focused on steady-state performance, without examining the algorithm's behavior during periods of rapid demand changes or unexpected events. Exploring the algorithm's robustness and adaptability under more dynamic conditions could provide valuable insights.
It would also be interesting to see how the algorithm's performance scales as the size and complexity of the quantum network increase. Analyzing its behavior in larger, more heterogeneous networks would help assess its practical applicability.
Despite these limitations, the paper presents a compelling approach to resource management in quantum networks and lays the groundwork for further research in this important area.
Conclusion
This paper introduces an on-demand resource allocation algorithm for a quantum network hub that dynamically assigns quantum resources, such as entanglement and communication channels, to users based on their real-time needs. Through simulations, the researchers demonstrate that this algorithm outperforms more static allocation approaches in terms of resource utilization, request fulfillment rate, and average waiting time.
The proposed algorithm represents a significant step towards efficient and responsive resource management in quantum networks, which is crucial for enabling reliable and scalable quantum computing and communication services. While the paper identifies some limitations that warrant further investigation, the overall approach shows promise and could inspire future research into advanced quantum network control and optimization.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Routing and Spectrum Allocation in Broadband Quantum Entanglement Distribution
Rohan Bali, Ashley N. Tittelbaugh, Shelbi L. Jenkins, Anuj Agrawal, Jerry Horgan, Marco Ruffini, Daniel C. Kilper, Boulat A. Bash

0
0
We investigate resource allocation for quantum entanglement distribution over an optical network. We characterize and model a network architecture that employs a single quasi-deterministic time-frequency heralded Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR) pair source, and develop a routing scheme for distributing entangled photon pairs over such a network. We focus on max-min fairness in entanglement distribution and compare the performance of various spectrum allocation schemes by examining the max-min and median number of EPR-pairs assigned by them, and the Jain index associated with this assignment. Since this presents an NP-hard problem, we identify two approximation algorithms that outperform others in minimum and mean EPR-pair rate distribution and are comparable to others in the Jain index. We also analyze how the network size and connectivity affect these metrics using Watts-Strogatz random graphs. We find that a spectrum allocation approach that achieves high minimum EPR-pair rate can perform significantly worse when the median EPR-pair rate, Jain index, and runtimes are considered.
4/16/2024

Entanglement Distribution Delay Optimization in Quantum Networks with Distillation
Mahdi Chehimi, Kenneth Goodenough, Walid Saad, Don Towsley, Tony X. Zhou

0
0
Quantum networks (QNs) distribute entangled states to enable distributed quantum computing and sensing applications. However, in such QNs, quantum switches (QSs) have limited resources that are highly sensitive to noise and losses and must be carefully allocated to minimize entanglement distribution delay. In this paper, a QS resource allocation framework is proposed, which jointly optimizes the average entanglement distribution delay and entanglement distillation operations, to enhance the end-to-end (e2e) fidelity and satisfy minimum rate and fidelity requirements. The proposed framework considers realistic QN noise and includes the derivation of the analytical expressions for the average quantum memory decoherence noise parameter, and the resulting e2e fidelity after distillation. Finally, practical QN deployment aspects are considered, where QSs can control 1) nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center SPS types based on their isotopic decomposition, and 2) nuclear spin regions based on their distance and coupling strength with the electron spin of NV centers. A simulated annealing metaheuristic algorithm is proposed to solve the QS resource allocation optimization problem. Simulation results show that the proposed framework manages to satisfy all users rate and fidelity requirements, unlike existing distillation-agnostic (DA), minimal distillation (MD), and physics-agnostic (PA) frameworks which do not perform distillation, perform minimal distillation, and does not control the physics-based NV center characteristics, respectively. Furthermore, the proposed framework results in around 30% and 50% reductions in the average e2e entanglement distribution delay compared to existing PA and MD frameworks, respectively. Moreover, the proposed framework results in around 5%, 7%, and 11% reductions in the average e2e fidelity compared to existing DA, PA, and MD frameworks, respectively.
5/16/2024
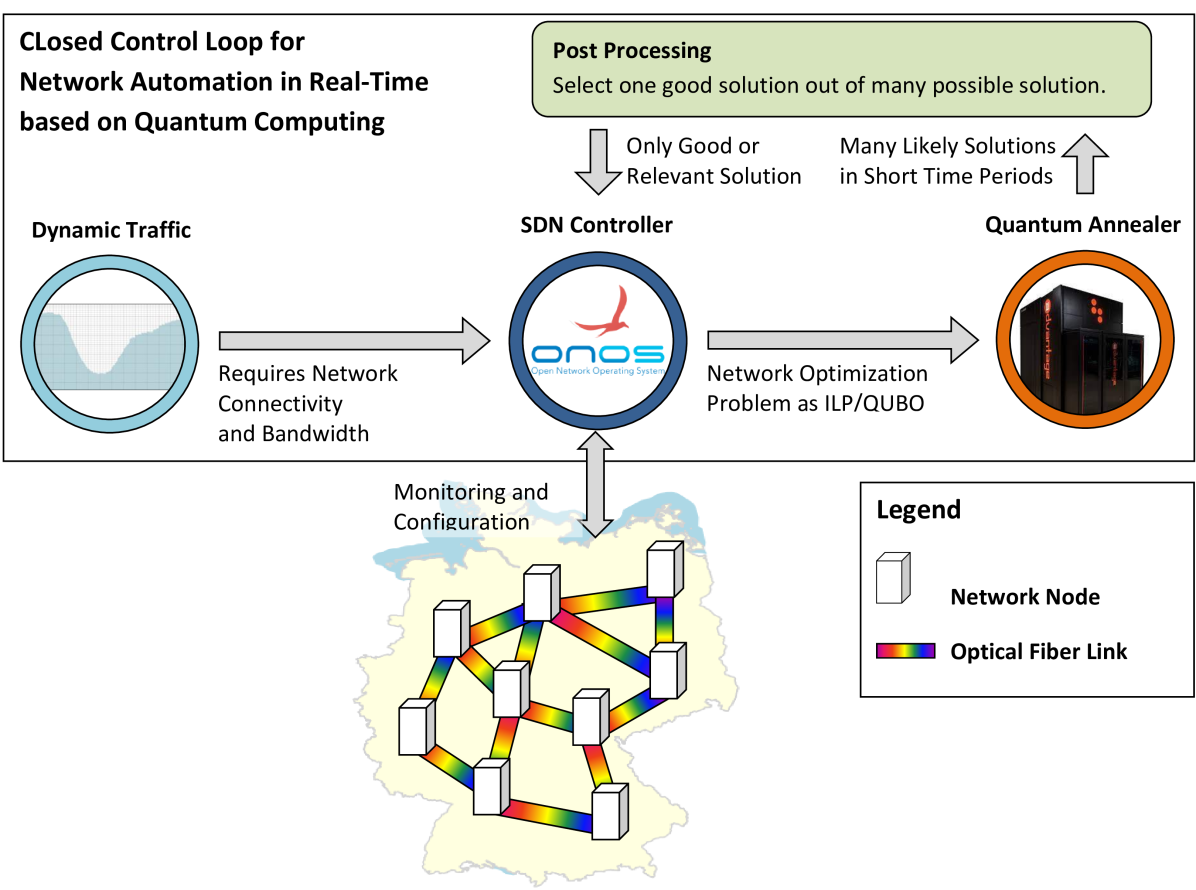
Queue-aware Network Control Algorithm with a High Quantum Computing Readiness-Evaluated in Discrete-time Flow Simulator for Fat-Pipe Networks
Arthur Witt

0
0
The emerging technology of quantum computing has the potential to change the way how problems will be solved in the future. This work presents a centralized network control algorithm executable on already existing quantum computer which are based on the principle of quantum annealing like the D-Wave Advantage. We introduce a resource reoccupation algorithm for traffic engineering in wide-area networks. The proposed optimization algorithm changes traffic steering and resource allocation in case of overloaded transceivers. Settings of active components like fiber amplifiers and transceivers are not changed for the reason of stability. This algorithm is beneficial in situations when the network traffic is fluctuating in time scales of seconds or spontaneous bursts occur. Further, we developed a discrete-time flow simulator to study the algorithm's performance in wide-area networks. Our network simulator considers backlog and loss modeling of buffered transmission lines. Concurring flows are handled equally in case of a backlog. This work provides an ILP-based network configuring algorithm that is applicable on quantum annealing computers. We showcase, that traffic losses can be reduced significantly by a factor of 2 if a resource reoccupation algorithm is applied in a network with bursty traffic. As resources are used more efficiently by reoccupation in heavy load situations, overprovisioning of networks can be reduced. Thus, this new form of network operation leads toward a zero-margin network. We show that our newly introduced network simulator enables analyses of short-time effects like buffering within fat-pipe networks. As the calculation of network configurations in real-sized networks is typically time-consuming, quantum computing can enable the proposed network configuration algorithm for application in real-sized wide-area networks.
5/21/2024
🏅
Dynamic Inhomogeneous Quantum Resource Scheduling with Reinforcement Learning
Linsen Li, Pratyush Anand, Kaiming He, Dirk Englund

0
0
A central challenge in quantum information science and technology is achieving real-time estimation and feedforward control of quantum systems. This challenge is compounded by the inherent inhomogeneity of quantum resources, such as qubit properties and controls, and their intrinsically probabilistic nature. This leads to stochastic challenges in error detection and probabilistic outcomes in processes such as heralded remote entanglement. Given these complexities, optimizing the construction of quantum resource states is an NP-hard problem. In this paper, we address the quantum resource scheduling issue by formulating the problem and simulating it within a digitized environment, allowing the exploration and development of agent-based optimization strategies. We employ reinforcement learning agents within this probabilistic setting and introduce a new framework utilizing a Transformer model that emphasizes self-attention mechanisms for pairs of qubits. This approach facilitates dynamic scheduling by providing real-time, next-step guidance. Our method significantly improves the performance of quantum systems, achieving more than a 3$times$ improvement over rule-based agents, and establishes an innovative framework that improves the joint design of physical and control systems for quantum applications in communication, networking, and computing.
5/28/2024