Entanglement Swapping in Orbit: a Satellite Quantum Link Case Study
2405.07589

0
0
Abstract
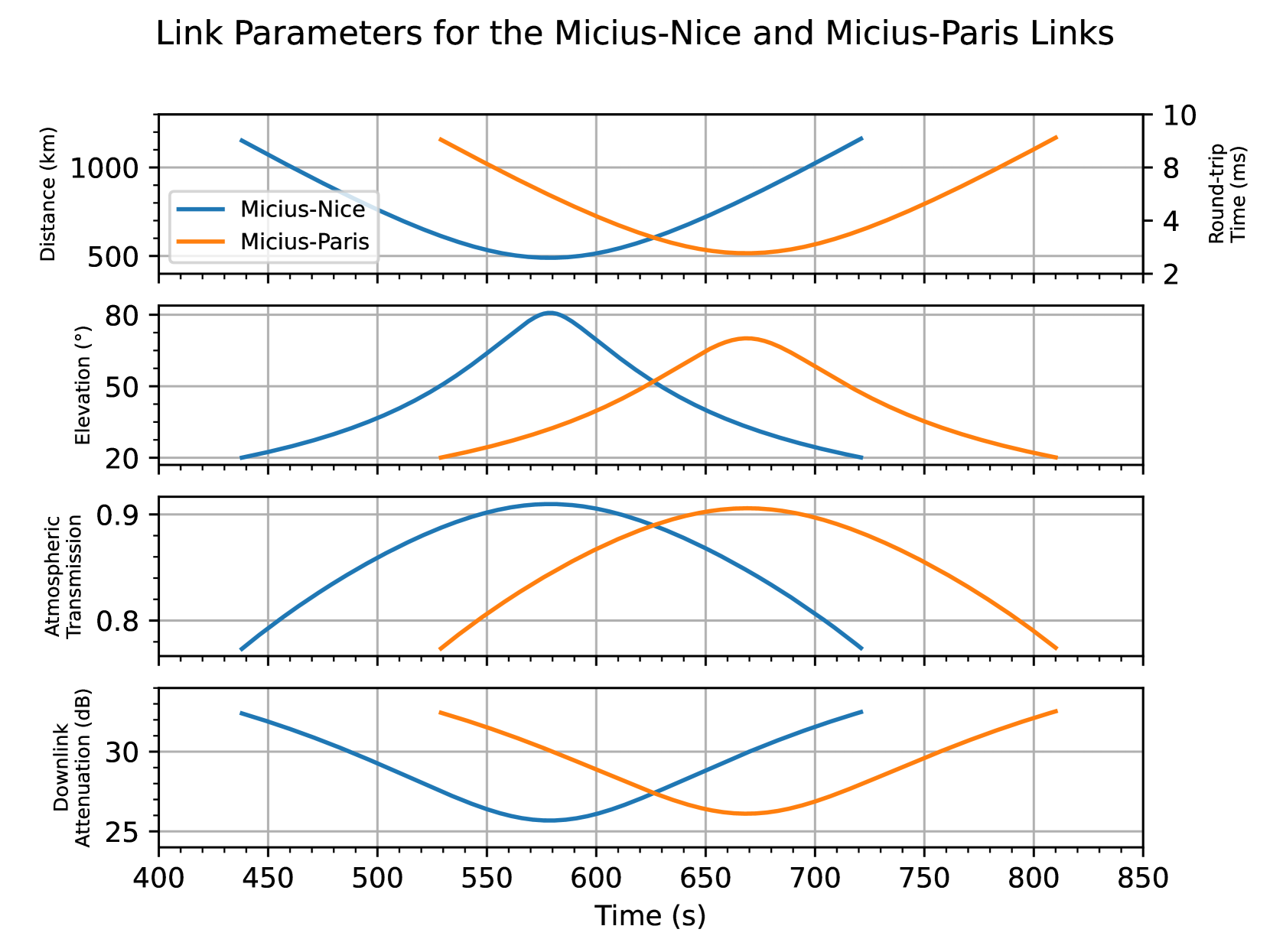
Satellite quantum communication is a promising way to build long distance quantum links, making it an essential complement to optical fiber for quantum internetworking beyond metropolitan scales. A satellite point to point optical link differs from the more common fiber links in many ways, both quantitative (higher latency, strong losses) and qualitative (nonconstant parameter values during satellite passage, intermittency of the link, impossibility to set repeaters between the satellite and the ground station). We study here the performance of a quantum link between two ground stations, using a quantum-memory-equipped satellite as a quantum repeater. In contrast with quantum key distribution satellite links, the number of available quantum memory slots m, together with the unavoidable round-trip communication latency t of at least a few milliseconds, severely reduces the effective average repetition rate to m/t -- at most a few kilohertz for foreseeable quantum memories. Our study uses two approaches, which validate each other: 1) a simple analytical model of the effective rate of the quantum link; 2) an event-based simulation using the open source Quantum Internet Simulation Package (QuISP). The important differences between satellite and fiber links led us to modify QuISP itself. This work paves the way to the study of hybrid satellite- and fiber-based quantum repeater networks interconnecting different metropolitan areas.
Create account to get full access
Overview
• This paper explores the concept of entanglement swapping, which is a fundamental technique in quantum networking, in the context of a satellite-based quantum link.
• The researchers demonstrate the successful implementation of entanglement swapping between a ground station and a satellite, enabling the establishment of long-distance quantum communication.
Plain English Explanation
• Entanglement is a unique quantum mechanical phenomenon where two or more particles become intrinsically linked, even over large distances. Entanglement swapping is a process that can be used to extend the range of entanglement-based communication.
• In this study, the researchers used a satellite in orbit to facilitate entanglement swapping between two ground stations. This allowed them to establish a quantum link over a much longer distance than would be possible with a direct connection between the two ground stations.
• The successful demonstration of this technique is an important step towards building a practical quantum internet, where information can be securely transmitted using the principles of quantum mechanics.
Technical Explanation
• The researchers conducted an experiment where they generated entangled photon pairs on the ground and transmitted one photon from each pair to a satellite in orbit. The satellite then performed a measurement that "swapped" the entanglement, allowing the two ground stations to establish a shared entanglement.
• This entanglement swapping protocol was implemented using a low-Earth-orbit satellite and ground stations separated by hundreds of kilometers. The researchers carefully designed the experiment to overcome challenges posed by factors such as satellite motion, atmospheric turbulence, and loss of photons during transmission.
• The results show that the entanglement swapping was successful, enabling the ground stations to generate a shared quantum state. This represents an important milestone in the development of Efficient Quantum Network Communication Using Optimized Entanglement and Quantum Backbone Networks: Hybrid Quantum Dataframe Transmission.
Critical Analysis
• The paper acknowledges that the current experiment is limited in scale and details several areas for future improvement, such as increasing the entanglement generation rate, reducing photon losses, and extending the distance over which entanglement can be swapped.
• An important limitation is the relatively low success rate of the entanglement swapping process, which could hamper the practical implementation of this technique in a Quantum-Assisted Trustworthiness of Quantum Internet or Realization of Programmable Multi-Purpose Photonic Quantum Memory scenario. Further research is needed to optimize the entanglement swapping protocol.
• Additionally, the paper does not address potential challenges related to the Analysis of Asynchronous Protocols for Entanglement Distribution in Quantum Networks, such as timing synchronization and coordination between the satellite and ground stations.
Conclusion
• This study demonstrates the successful implementation of entanglement swapping in a satellite-based quantum link, which is a crucial step towards the realization of a practical quantum internet.
• The findings highlight the potential of using satellites to extend the reach of quantum communication networks, paving the way for Efficient Quantum Network Communication Using Optimized Entanglement and Quantum Backbone Networks: Hybrid Quantum Dataframe Transmission.
• While the current experiment has some limitations, the researchers have made significant progress in overcoming the technical challenges associated with Analysis of Asynchronous Protocols for Entanglement Distribution in Quantum Networks and Quantum-Assisted Trustworthiness of Quantum Internet. Further advancements in this area could lead to the Realization of Programmable Multi-Purpose Photonic Quantum Memory and the development of a robust and secure quantum communication infrastructure.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

An Implementation and Analysis of a Practical Quantum Link Architecture Utilizing Entangled Photon Sources
Kento Samuel Soon, Michal Hajduv{s}ek, Shota Nagayama, Naphan Benchasattabuse, Kentaro Teramoto, Ryosuke Satoh, Rodney Van Meter

0
0
Quantum repeater networks play a crucial role in distributing entanglement. Various link architectures have been proposed to facilitate the creation of Bell pairs between distant nodes, with entangled photon sources emerging as a primary technology for building quantum networks. Our work advances the Memory-Source-Memory (MSM) link architecture, addressing the absence of practical implementation details. We conduct numerical simulations using the Quantum Internet Simulation Package (QuISP) to analyze the performance of the MSM link and contrast it with other link architectures. We observe a saturation effect in the MSM link, where additional quantum resources do not affect the Bell pair generation rate of the link. By introducing a theoretical model, we explain the origin of this effect and characterize the parameter region where it occurs. Our work bridges theoretical insights with practical implementation, which is crucial for robust and scalable quantum networks.
5/17/2024
🔄
Harnessing Quantum Entanglement: Comprehensive Strategies for Enhanced Communication and Beyond in Quantum Networks
Amit Kumar Bhuyan, Hrishikesh Dutta

0
0
Quantum communication represents a revolutionary advancement over classical information theory, which leverages unique quantum mechanics properties like entanglement to achieve unprecedented capabilities in secure and efficient information transmission. Unlike bits in classical communication, quantum communication utilizes qubits in superposition states, allowing for novel information storage and processing. Entanglement, a key quantum phenomenon, enables advanced protocols with enhanced security and processing power. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of quantum communication, emphasizing the role of entanglement in theoretical foundations, practical protocols, experimental progress, and security implications. It contrasts quantum communications potential applications with classical networks, identifying areas where entanglement offers significant advantages. The paper explores the fundamentals of quantum mechanics in communication, the physical realization of quantum information, and the formation of secure quantum networks through entanglement-based strategies like Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) and teleportation. It addresses the challenges of long-distance quantum communication, the role of quantum repeaters in scaling networks, and the conceptualization of interconnected quantum networks. Additionally, it discusses strides towards the Quantum Internet, Quantum Error-Correcting codes, and quantum cryptographys role in ensuring secure communication. By highlighting the role of entanglement, this paper aims to inspire further research and innovation in secure and efficient information exchange within quantum networks.
6/14/2024

Boosting end-to-end entanglement fidelity in quantum repeater networks via hybridized strategies
Poramet Pathumsoot, Theerapat Tansuwannont, Naphan Benchasattabuse, Ryosuke Satoh, Michal Hajduv{s}ek, Poompong Chaiwongkhot, Sujin Suwanna, Rodney Van Meter

0
0
Quantum networks are expected to enhance distributed quantum computing and quantum communication over long distances while providing security dependent upon physical effects rather than mathematical assumptions. Through simulation, we show that a quantum network utilizing only entanglement purification or only quantum error correction as error management strategies cannot create Bell pairs with fidelity that exceeds the requirement for a secured quantum key distribution protocol for a broad range of hardware parameters. We propose hybrid strategies utilizing quantum error correction on top of purification and show that they can produce Bell pairs of sufficiently high fidelity. We identify the error parameter regime for gate and measurement errors in which these hybrid strategies are applicable.
6/12/2024
Quantum Circuit Switching with One-Way Repeaters in Star Networks
'Alvaro G. I~nesta, Hyeongrak Choi, Dirk Englund, Stephanie Wehner

0
0
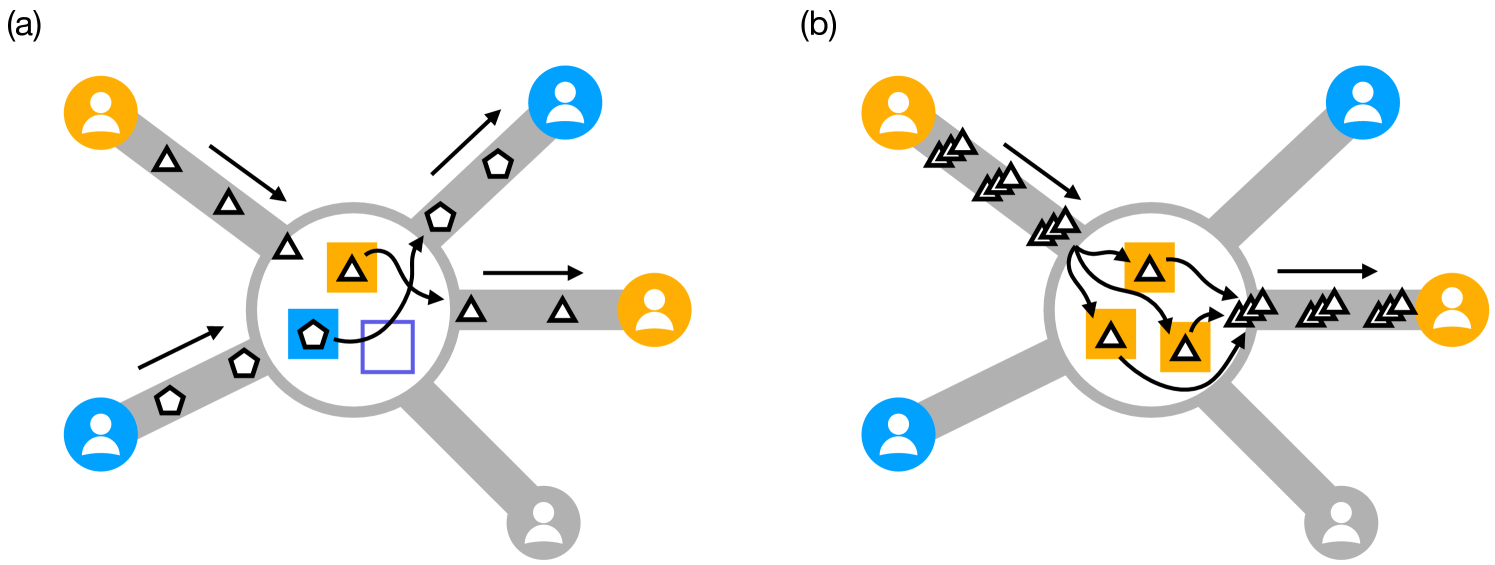
Distributing quantum states reliably among distant locations is a key challenge in the field of quantum networks. One-way quantum networks address this by using one-way communication and quantum error correction. Here, we analyze quantum circuit switching as a protocol to distribute quantum states in one-way quantum networks. In quantum circuit switching, pairs of users can request the delivery of multiple quantum states from one user to the other. After waiting for approval from the network, the states can be distributed either sequentially, forwarding one at a time along a path of quantum repeaters, or in parallel, sending batches of quantum states from repeater to repeater. Since repeaters can only forward a finite number of quantum states at a time, a pivotal question arises: is it advantageous to send them sequentially (allowing for multiple requests simultaneously) or in parallel (reducing processing time but handling only one request at a time)? We compare both approaches in a quantum network with a star topology. Using tools from queuing theory, we show that requests are met at a higher rate when packets are distributed in parallel, although sequential distribution can generally provide service to a larger number of users simultaneously. We also show that using a large number of quantum repeaters to combat channel losses limits the maximum distance between users, as each repeater introduces additional processing delays. These findings provide insight into the design of protocols for distributing quantum states in one-way quantum networks.
5/30/2024