Exploring Post Quantum Cryptography with Quantum Key Distribution for Sustainable Mobile Network Architecture Design
2404.10602

0
0
Abstract
The proliferation of mobile networks and their increasing importance to modern life, combined with the emerging threat of quantum computing, present new challenges and opportunities for cybersecurity. This paper addresses the complexity of protecting these critical infrastructures against future quantum attacks while considering operational sustainability. We begin with an overview of the current landscape, identify the main vulnerabilities in mobile networks, and evaluate existing security solutions with new post-quantum cryptography (PQC) methods. We then present a quantum-secure architecture with PQC and Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) tailored explicitly for sustainable mobile networks and illustrate its applicability with several use cases that emphasize the need for advanced protection measures in this new era. In addition, a comprehensive analysis of PQC algorithm families is presented, focusing on their suitability for integration in mobile environments, with particular attention to the trade-offs between energy consumption and security improvements. Finally, recommendations for strengthening mobile networks against quantum threats are provided through a detailed examination of current challenges and opportunities.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Explores the use of post-quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution to design a sustainable mobile network architecture
- Focuses on enhancing security and resilience of mobile networks against emerging quantum computing threats
- Proposes a framework that integrates post-quantum cryptographic algorithms and quantum key distribution protocols
Plain English Explanation
This research paper investigates ways to make mobile network architectures more secure and sustainable for the future. As quantum computing technology advances, current encryption methods used in mobile networks may become vulnerable. The researchers explore the use of post-quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution as potential solutions to address this emerging threat.
The researchers propose a framework that combines post-quantum cryptographic algorithms and quantum key distribution protocols to enhance the security and resilience of mobile network architectures. This approach aims to protect mobile networks against attacks enabled by powerful quantum computers, which could potentially break current encryption methods.
By integrating these advanced cryptographic techniques, the researchers hope to develop a more sustainable mobile network architecture that can withstand the challenges posed by the rise of quantum computing. This could help ensure the long-term security and reliability of mobile communication systems, which are increasingly vital for various applications, including IoT, smart cities, and remote healthcare.
Technical Explanation
The paper explores the integration of post-quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution to design a sustainable mobile network architecture. Post-quantum cryptography refers to cryptographic algorithms that are designed to be resistant to attacks by quantum computers, which could potentially break current encryption methods.
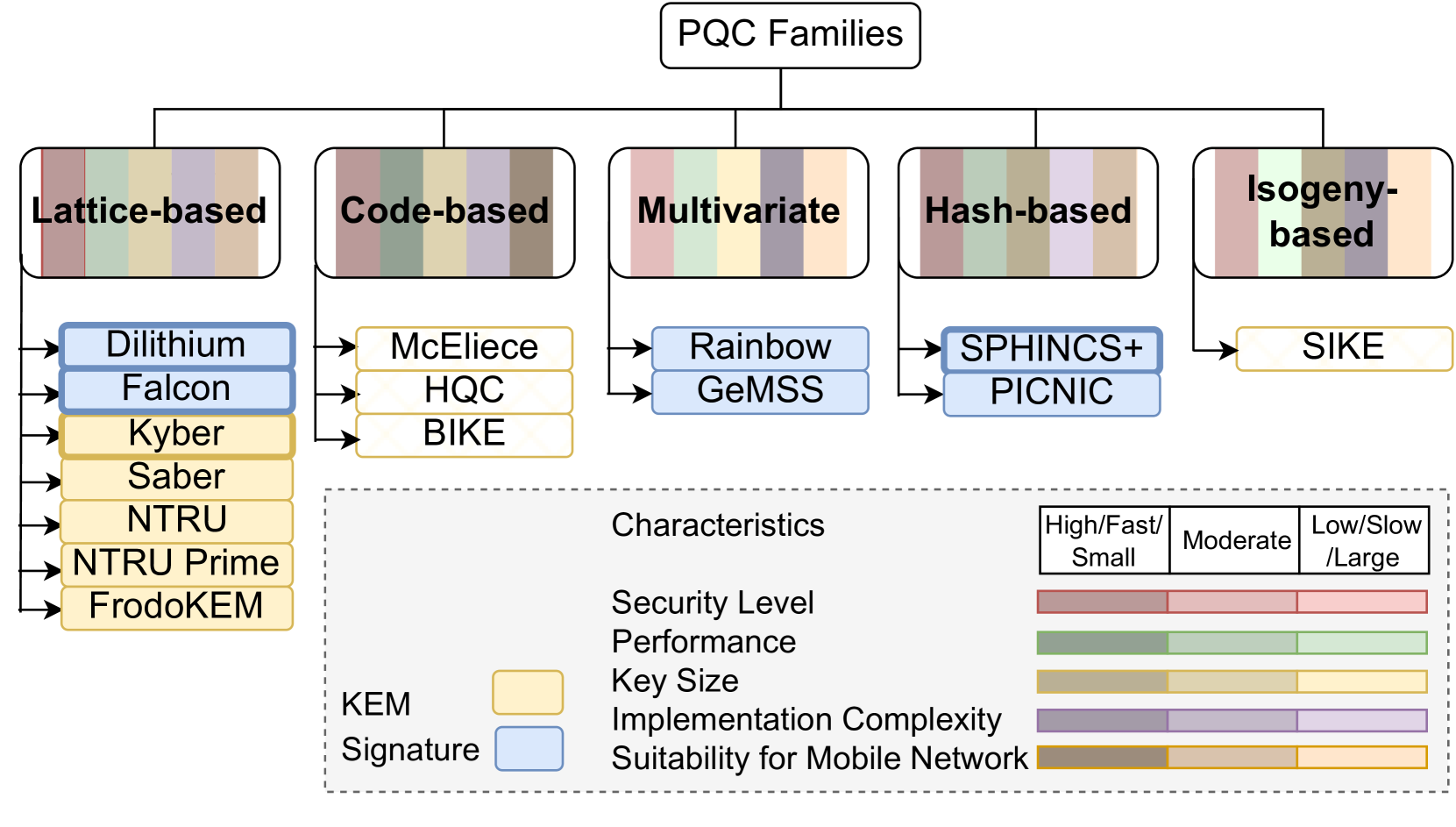
The researchers propose a framework that combines post-quantum cryptographic algorithms, such as lattice-based or code-based schemes, with quantum key distribution protocols. Quantum key distribution is a technique that allows two parties to produce a shared random secret key known only to them, which can then be used to encrypt and decrypt messages.
By integrating these advanced cryptographic techniques, the researchers aim to enhance the security and resilience of mobile network architectures against the threat of quantum computing. The proposed framework also considers factors such as energy efficiency, scalability, and adaptability to ensure the long-term sustainability of the mobile network infrastructure.
The researchers evaluate the performance and feasibility of their proposed approach through simulations and analytical modeling, considering various metrics like key generation rate, computational overhead, and energy consumption. The results suggest that the integration of post-quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution can provide a viable solution for securing mobile networks in the face of emerging quantum computing challenges.
Critical Analysis
The research paper presents a compelling approach to addressing the security challenges posed by the advent of quantum computing in the context of mobile network architectures. The integration of post-quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution is a promising direction, as it aims to future-proof mobile networks against the potential weaknesses of current encryption methods.
However, the paper does not fully address the practical challenges and limitations of implementing such a framework in real-world mobile network deployments. For instance, the availability and scalability of quantum key distribution infrastructure, as well as the performance and energy efficiency of post-quantum cryptographic algorithms, may pose significant challenges that require further investigation.
Additionally, the paper could have delved deeper into the potential trade-offs and design considerations involved in balancing security, performance, and sustainability in the proposed mobile network architecture. A more comprehensive analysis of the potential drawbacks, deployment barriers, and areas for further research would strengthen the critical evaluation of the proposed approach.
Conclusion
This research paper presents a novel framework that leverages post-quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution to design a sustainable mobile network architecture. By addressing the security vulnerabilities posed by the rise of quantum computing, the proposed approach aims to enhance the long-term resilience and reliability of mobile communication systems.
The integration of these advanced cryptographic techniques holds promise for securing mobile networks against emerging threats and ensuring their continued relevance in the face of technological advancements. However, the practical implementation challenges and trade-offs involved require further exploration to fully assess the feasibility and applicability of the proposed solution.
Overall, this research contributes to the ongoing efforts to future-proof mobile network infrastructures and highlight the importance of proactively addressing the security implications of quantum computing for critical communication systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🔮
Applications of Post-quantum Cryptography
Emils Bagirovs, Grigory Provodin, Tuomo Sipola, Jari Hautamaki

0
0
With the constantly advancing capabilities of quantum computers, conventional cryptographic systems relying on complex math problems may encounter unforeseen vulnerabilities. Unlike regular computers, which are often deemed cost-ineffective in cryptographic attacks, quantum computers have a significant advantage in calculation speed. This distinction potentially makes currently used algorithms less secure or even completely vulnerable, compelling the exploration of post-quantum cryptography (PQC) as the most reasonable solution to quantum threats. This review aims to provide current information on applications, benefits, and challenges associated with the PQC. The review employs a systematic scoping review with the scope restricted to the years 2022 and 2023; only articles that were published in scientific journals were used in this paper. The review examined the articles on the applications of quantum computing in various spheres. However, the scope of this paper was restricted to the domain of the PQC because most of the analyzed articles featured this field. Subsequently, the paper is analyzing various PQC algorithms, including lattice-based, hash-based, code-based, multivariate polynomial, and isogeny-based cryptography. Each algorithm is being judged based on its potential applications, robustness, and challenges. All the analyzed algorithms are promising for the post-quantum era in such applications as digital signatures, communication channels, and IoT. Moreover, some of the algorithms are already implemented in the spheres of banking transactions, communication, and intellectual property. Meanwhile, despite their potential, these algorithms face serious challenges since they lack standardization, require vast amounts of storage and computation power, and might have unknown vulnerabilities that can be discovered only with years of cryptanalysis.
6/26/2024
Quantum-safe Edge Applications: How to Secure Computation in Distributed Computing Systems
Claudio Cicconetti, Dario Sabella, Pietro Noviello, Gennaro Davide Paduanelli

0
0
The advent of distributed computing systems will offer great flexibility for application workloads, while also imposing more attention to security, where the future advent and adoption of quantum technology can introduce new security threats. For this reason, the Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) working group at ETSI has recently started delving into security aspects, especially motivated by the upcoming reality of the MEC federation, which involves services made of application instances belonging to different systems (thus, different trust domains). On the other side, Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) can help strengthen the level of security by enabling the exchange of secure keys through an unconditionally secure protocol, e.g., to secure communication between REST clients and servers in distributed computing systems at the edge. In this paper, we propose a technical solution to achieve this goal, building on standard specifications, namely ETSI MEC and ETSI QKD, and discussing the gaps and limitations of current technology, which hamper full-fledged in-field deployment and mass adoption. Furthermore, we provide our look-ahead view on the future of secure distributed computing through the enticing option of federating edge computing domains.
5/28/2024
🚀
The Security Performance Analysis of Blockchain System Based on Post-Quantum Cryptography -- A Case Study of Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Abel C. H. Chen

0
0
The current blockchain system for cryptocurrency exchanges primarily employs elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) for generating key pairs in wallets, and elliptic curve digital signature algorithms (ECDSA) for generating signatures in transactions. Consequently, with the maturation of quantum computing technology, the current blockchain system faces the risk of quantum computing attacks. Quantum computers may potentially counterfeit signatures produced by ECDSA. Therefore, this study analyzes the vulnerabilities of the current blockchain system to quantum computing attacks and proposes a post-quantum cryptography (PQC)-based blockchain system to enhance security by addressing and improving each identified weakness. Furthermore, this study proposes PQC-based wallets and PQC-based transactions, utilizing PQC digital signature algorithms to generate PQC-based signatures for the inputs in PQC-based transactions, thereby preventing signatures from being counterfeited by quantum computing. Experimental results demonstrate that the efficiency of the Dilithium algorithm, a PQC digital signature algorithm, in producing wallets, generating signatures, and verifying signatures surpasses that of ECDSA in the current blockchain system. Furthermore, the Dilithium algorithm also exhibits a higher security level.
4/29/2024

Quantum Secure Anonymous Communication Networks
Mohammad Saidur Rahman, Stephen DiAdamo, Miralem Mehic, Charles Fleming

0
0
Anonymous communication networks (ACNs) enable Internet browsing in a way that prevents the accessed content from being traced back to the user. This allows a high level of privacy, protecting individuals from being tracked by advertisers or governments, for example. The Tor network, a prominent example of such a network, uses a layered encryption scheme to encapsulate data packets, using Tor nodes to obscure the routing process before the packets enter the public Internet. While Tor is capable of providing substantial privacy, its encryption relies on schemes, such as RSA and Diffie-Hellman for distributing symmetric keys, which are vulnerable to quantum computing attacks and are currently in the process of being phased out. To overcome the threat, we propose a quantum-resistant alternative to RSA and Diffie-Hellman for distributing symmetric keys, namely, quantum key distribution (QKD). Standard QKD networks depend on trusted nodes to relay keys across long distances, however, reliance on trusted nodes in the quantum network does not meet the criteria necessary for establishing a Tor circuit in the ACN. We address this issue by developing a protocol and network architecture that integrates QKD without the need for trusted nodes, thus meeting the requirements of the Tor network and creating a quantum-secure anonymous communication network.
5/13/2024