Generation and Detection of Sign Language Deepfakes - A Linguistic and Visual Analysis
2404.01438

0
0
🛸
Abstract
A question in the realm of deepfakes is slowly emerging pertaining to whether we can go beyond facial deepfakes and whether it would be beneficial to society. Therefore, this research presents a positive application of deepfake technology in upper body generation, while performing sign-language for the Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHoH) community. The resulting videos are later vetted with a sign language expert. This is particularly helpful, given the intricate nature of sign language, a scarcity of sign language experts, and potential benefits for health and education. The objectives of this work encompass constructing a reliable deepfake dataset, evaluating its technical and visual credibility through computer vision and natural language processing models, and assessing the plausibility of the generated content. With over 1200 videos, featuring both previously seen and unseen individuals for the generation model, using the help of a sign language expert, we establish a deepfake dataset in sign language that can further be utilized to detect fake videos that may target certain people of determination.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Researchers explore using deepfake technology to generate sign language videos, which could benefit the Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHoH) community.
- They create a dataset of over 1,200 sign language videos featuring both familiar and unfamiliar individuals.
- The generated videos are evaluated by a sign language expert to assess their technical and visual credibility.
- The goal is to develop a reliable deepfake dataset that could be used to detect fake sign language videos that may target people with disabilities.
Plain English Explanation
Deepfake technology has often been associated with concerns around misinformation and the creation of fake videos. However, this research explores a positive application of deepfakes - using them to generate sign language videos. This is particularly helpful for the Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHoH) community, as sign language can be a complex and intricate form of communication, and there is a scarcity of sign language experts available.
By creating a dataset of over 1,200 sign language videos featuring both familiar and unfamiliar people, the researchers aim to develop a reliable resource that can be used to detect fake sign language videos that may target individuals with disabilities. This is important because fake videos could potentially be used to mislead or manipulate the DHoH community.
The researchers work with a sign language expert to evaluate the technical and visual credibility of the generated videos, ensuring that they accurately represent the nuances of sign language. This step is crucial, as it helps validate the usefulness of the dataset for future applications, such as training models to detect fake sign language videos.
Overall, this research highlights how deepfake technology, when used responsibly, can be leveraged to create beneficial tools and resources for underserved communities, such as the DHoH population. By focusing on the potential positive impact, the researchers aim to shift the conversation around deepfakes towards more constructive applications.
Technical Explanation
The research presents a novel application of deepfake technology in the context of sign language generation. The primary objectives are to:
- Construct a reliable deepfake dataset of sign language videos.
- Evaluate the technical and visual credibility of the generated videos through computer vision and natural language processing models.
- Assess the plausibility of the generated content with the help of a sign language expert.
The dataset consists of over 1,200 sign language videos, featuring both previously seen and unseen individuals for the generation model. By involving a sign language expert in the evaluation process, the researchers ensure that the generated videos accurately represent the intricacies of sign language communication.
The technical approach involves training a deepfake model to generate realistic upper body movements and facial expressions that correspond to the sign language being performed. The researchers utilize computer vision and natural language processing techniques to assess the quality and coherence of the generated videos, ensuring that they are visually and linguistically credible.
The key insights from this research include the demonstration of a positive application of deepfake technology, the creation of a valuable dataset for the detection of fake sign language videos, and the importance of involving domain experts (in this case, sign language experts) in the evaluation process to ensure the practical relevance and utility of the generated content.
Critical Analysis
The research presents a thoughtful and responsible approach to exploring the potential benefits of deepfake technology. By focusing on sign language generation, the researchers address a specific need within the Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHoH) community, where the availability of sign language experts is limited.
However, the research does not delve into potential limitations or caveats that may arise when deploying such a system in real-world scenarios. For example, the impact of generated sign language videos on the trust and confidence of the DHoH community, or the potential for misuse of the technology to create false or misleading content, are not thoroughly discussed.
Additionally, while the involvement of a sign language expert in the evaluation process is commendable, the research could be strengthened by incorporating feedback and perspectives from a broader range of stakeholders within the DHoH community. This would help ensure that the generated content truly meets the needs and expectations of the intended users.
Further research could also explore the long-term implications of deepfake technology in the context of accessibility and inclusive communication, as well as the potential for adversarial attacks or malicious use of the generated sign language videos.
Conclusion
This research presents a promising application of deepfake technology in the context of sign language generation, which could significantly benefit the Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHoH) community. By creating a reliable dataset of sign language videos and involving a sign language expert in the evaluation process, the researchers demonstrate a responsible and thoughtful approach to leveraging this technology for positive impact.
The potential of this work lies in its ability to provide accessible and scalable sign language resources, which can help address the scarcity of sign language experts and improve communication and educational opportunities for the DHoH community. Additionally, the dataset developed in this research could be used to train models that can detect fake sign language videos, protecting the DHoH community from potential misinformation or manipulation.
While the research highlights the positive potential of deepfake technology, it also raises important questions about the long-term implications and the need for ongoing engagement with the DHoH community to ensure that the generated content truly meets their needs and expectations. As deepfake technology continues to evolve, it will be crucial to explore both its benefits and potential risks, with a focus on responsible and inclusive development.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
A real-time Artificial Intelligence system for learning Sign Language
Elisa Cabana

0
0
A primary challenge for the deaf and hearing-impaired community stems from the communication gap with the hearing society, which can greatly impact their daily lives and result in social exclusion. To foster inclusivity in society, our endeavor focuses on developing a cost-effective, resource-efficient, and open technology based on Artificial Intelligence, designed to assist people in learning and using Sign Language for communication. The analysis presented in this research paper intends to enrich the recent academic scientific literature on Sign Language solutions based on Artificial Intelligence, with a particular focus on American Sign Language (ASL). This research has yielded promising preliminary results and serves as a basis for further development.
4/12/2024

Neural Sign Actors: A diffusion model for 3D sign language production from text
Vasileios Baltatzis, Rolandos Alexandros Potamias, Evangelos Ververas, Guanxiong Sun, Jiankang Deng, Stefanos Zafeiriou

0
0
Sign Languages (SL) serve as the primary mode of communication for the Deaf and Hard of Hearing communities. Deep learning methods for SL recognition and translation have achieved promising results. However, Sign Language Production (SLP) poses a challenge as the generated motions must be realistic and have precise semantic meaning. Most SLP methods rely on 2D data, which hinders their realism. In this work, a diffusion-based SLP model is trained on a curated large-scale dataset of 4D signing avatars and their corresponding text transcripts. The proposed method can generate dynamic sequences of 3D avatars from an unconstrained domain of discourse using a diffusion process formed on a novel and anatomically informed graph neural network defined on the SMPL-X body skeleton. Through quantitative and qualitative experiments, we show that the proposed method considerably outperforms previous methods of SLP. This work makes an important step towards realistic neural sign avatars, bridging the communication gap between Deaf and hearing communities.
4/8/2024
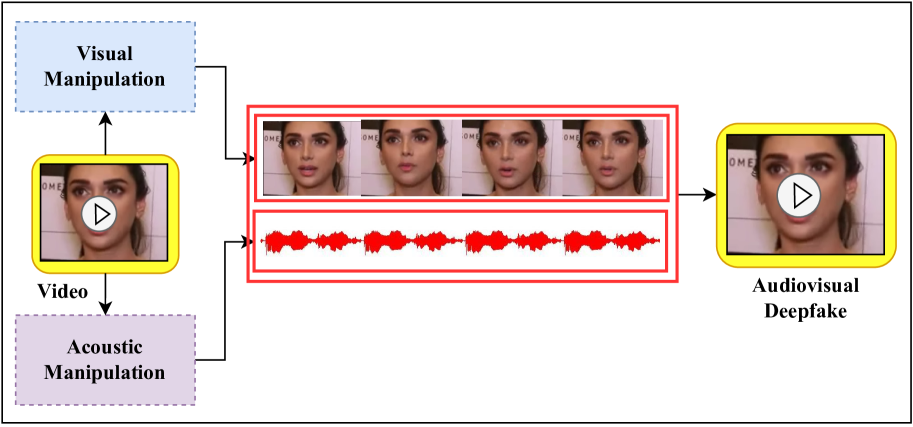
Unmasking Illusions: Understanding Human Perception of Audiovisual Deepfakes
Ammarah Hashmi, Sahibzada Adil Shahzad, Chia-Wen Lin, Yu Tsao, Hsin-Min Wang

0
0
The emergence of contemporary deepfakes has attracted significant attention in machine learning research, as artificial intelligence (AI) generated synthetic media increases the incidence of misinterpretation and is difficult to distinguish from genuine content. Currently, machine learning techniques have been extensively studied for automatically detecting deepfakes. However, human perception has been less explored. Malicious deepfakes could ultimately cause public and social problems. Can we humans correctly perceive the authenticity of the content of the videos we watch? The answer is obviously uncertain; therefore, this paper aims to evaluate the human ability to discern deepfake videos through a subjective study. We present our findings by comparing human observers to five state-ofthe-art audiovisual deepfake detection models. To this end, we used gamification concepts to provide 110 participants (55 native English speakers and 55 non-native English speakers) with a webbased platform where they could access a series of 40 videos (20 real and 20 fake) to determine their authenticity. Each participant performed the experiment twice with the same 40 videos in different random orders. The videos are manually selected from the FakeAVCeleb dataset. We found that all AI models performed better than humans when evaluated on the same 40 videos. The study also reveals that while deception is not impossible, humans tend to overestimate their detection capabilities. Our experimental results may help benchmark human versus machine performance, advance forensics analysis, and enable adaptive countermeasures.
5/8/2024

Bridging the Communication Gap: Artificial Agents Learning Sign Language through Imitation
Federico Tavella, Aphrodite Galata, Angelo Cangelosi

0
0
Artificial agents, particularly humanoid robots, interact with their environment, objects, and people using cameras, actuators, and physical presence. Their communication methods are often pre-programmed, limiting their actions and interactions. Our research explores acquiring non-verbal communication skills through learning from demonstrations, with potential applications in sign language comprehension and expression. In particular, we focus on imitation learning for artificial agents, exemplified by teaching a simulated humanoid American Sign Language. We use computer vision and deep learning to extract information from videos, and reinforcement learning to enable the agent to replicate observed actions. Compared to other methods, our approach eliminates the need for additional hardware to acquire information. We demonstrate how the combination of these different techniques offers a viable way to learn sign language. Our methodology successfully teaches 5 different signs involving the upper body (i.e., arms and hands). This research paves the way for advanced communication skills in artificial agents.
6/17/2024