Human-Centered Automation
2405.15960

0
0
🏷️
Abstract
The rapid advancement of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI), such as Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLM), has the potential to revolutionize the way we work and interact with digital systems across various industries. However, the current state of software automation, such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA) frameworks, often requires domain expertise and lacks visibility and intuitive interfaces, making it challenging for users to fully leverage these technologies. This position paper argues for the emerging area of Human-Centered Automation (HCA), which prioritizes user needs and preferences in the design and development of automation systems. Drawing on empirical evidence from human-computer interaction research and case studies, we highlight the importance of considering user perspectives in automation and propose a framework for designing human-centric automation solutions. The paper discusses the limitations of existing automation approaches, the challenges in integrating AI and RPA, and the benefits of human-centered automation for productivity, innovation, and democratizing access to these technologies. We emphasize the importance of open-source solutions and provide examples of how HCA can empower individuals and organizations in the era of rapidly progressing AI, helping them remain competitive. The paper also explores pathways to achieve more advanced and context-aware automation solutions. We conclude with a call to action for researchers and practitioners to focus on developing automation technologies that adapt to user needs, provide intuitive interfaces, and leverage the capabilities of high-end AI to create a more accessible and user-friendly future of automation.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Discusses the current state of automation and the limitations of existing approaches
- Proposes a human-centered approach to automation that prioritizes collaboration between humans and machines
- Explores strategies for designing automation systems that enhance human agency and adaptability
Plain English Explanation
This paper explores the current state of automation and the limitations of existing approaches, such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA). The authors argue that these traditional automation methods often fail to effectively leverage human capabilities and can even undermine human agency.
To address these shortcomings, the paper advocates for a "human-centered" approach to automation, where the focus is on fostering collaboration between humans and machines. This involves designing automation systems that enhance human adaptability and decision-making, rather than simply replacing human workers with automated processes.
The paper examines strategies for creating automation that amplifies human skills and decision-making, rather than diminishing them. This could involve developing interactive visualization tools that allow humans to better understand and guide automated systems, or proactive conversational agents that can engage with humans in a more natural and adaptive way.
By prioritizing the human element in the design of automation systems, the authors believe it is possible to create technologies that enhance, rather than replace, human capabilities. This could lead to more effective and meaningful collaborations between humans and machines, ultimately benefiting both individuals and organizations.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by examining the current state of automation, with a focus on the limitations of Robotic Process Automation (RPA). The authors argue that while RPA has been widely adopted, it often fails to effectively leverage human capabilities and can even undermine human agency.
To address these shortcomings, the paper proposes a "human-centered" approach to automation, where the emphasis is on fostering collaboration between humans and machines. This involves designing automation systems that enhance human adaptability and decision-making, rather than simply replacing human workers with automated processes.
The authors explore various strategies for creating this type of human-centered automation, including the development of interactive visualization tools that allow humans to better understand and guide automated systems, and proactive conversational agents that can engage with humans in a more natural and adaptive way.
By prioritizing the human element in the design of automation systems, the authors believe it is possible to create technologies that amplify, rather than replace, human capabilities. This could lead to more effective and meaningful collaborations between humans and machines, ultimately benefiting both individuals and organizations.
Critical Analysis
The paper raises valid concerns about the limitations of existing automation approaches, such as RPA, and the potential for these technologies to undermine human agency and decision-making. The authors' proposal for a more human-centered approach to automation is an important contribution to the field, as it challenges the traditional focus on pure efficiency and productivity in favor of a more balanced and collaborative approach.
However, the paper does not delve deeply into the practical challenges of implementing this human-centered approach. It would be helpful to see more discussion of the specific design considerations and trade-offs involved, as well as potential barriers to adoption within organizations that may be more focused on cost savings and immediate efficiency gains.
Additionally, while the authors mention the potential for interactive visualization tools and proactive conversational agents to enhance human-machine collaboration, they do not provide a comprehensive review of the existing research and developments in these areas. A more thorough exploration of the state of the art in these related fields could strengthen the paper's overall argument and provide a clearer roadmap for future research and development.
Conclusion
This paper presents a compelling case for a more human-centered approach to automation, one that prioritizes collaboration between humans and machines rather than the simple replacement of human labor. By designing automation systems that enhance human agency, adaptability, and decision-making, the authors believe it is possible to create technologies that truly augment and empower human capabilities, rather than diminish them.
While the paper does not address all of the practical challenges involved in implementing this vision, it nonetheless offers a valuable contribution to the ongoing debate around the role of automation in society. As advances in AI and robotics continue to reshape the nature of work, it will be crucial to ensure that automation is designed and deployed in a way that supports, rather than undermines, human well-being and agency. The ideas presented in this paper provide a useful starting point for further exploration and innovation in this critical area.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Position: A Call to Action for a Human-Centered AutoML Paradigm
Marius Lindauer, Florian Karl, Anne Klier, Julia Moosbauer, Alexander Tornede, Andreas Mueller, Frank Hutter, Matthias Feurer, Bernd Bischl

0
0
Automated machine learning (AutoML) was formed around the fundamental objectives of automatically and efficiently configuring machine learning (ML) workflows, aiding the research of new ML algorithms, and contributing to the democratization of ML by making it accessible to a broader audience. Over the past decade, commendable achievements in AutoML have primarily focused on optimizing predictive performance. This focused progress, while substantial, raises questions about how well AutoML has met its broader, original goals. In this position paper, we argue that a key to unlocking AutoML's full potential lies in addressing the currently underexplored aspect of user interaction with AutoML systems, including their diverse roles, expectations, and expertise. We envision a more human-centered approach in future AutoML research, promoting the collaborative design of ML systems that tightly integrates the complementary strengths of human expertise and AutoML methodologies.
6/6/2024
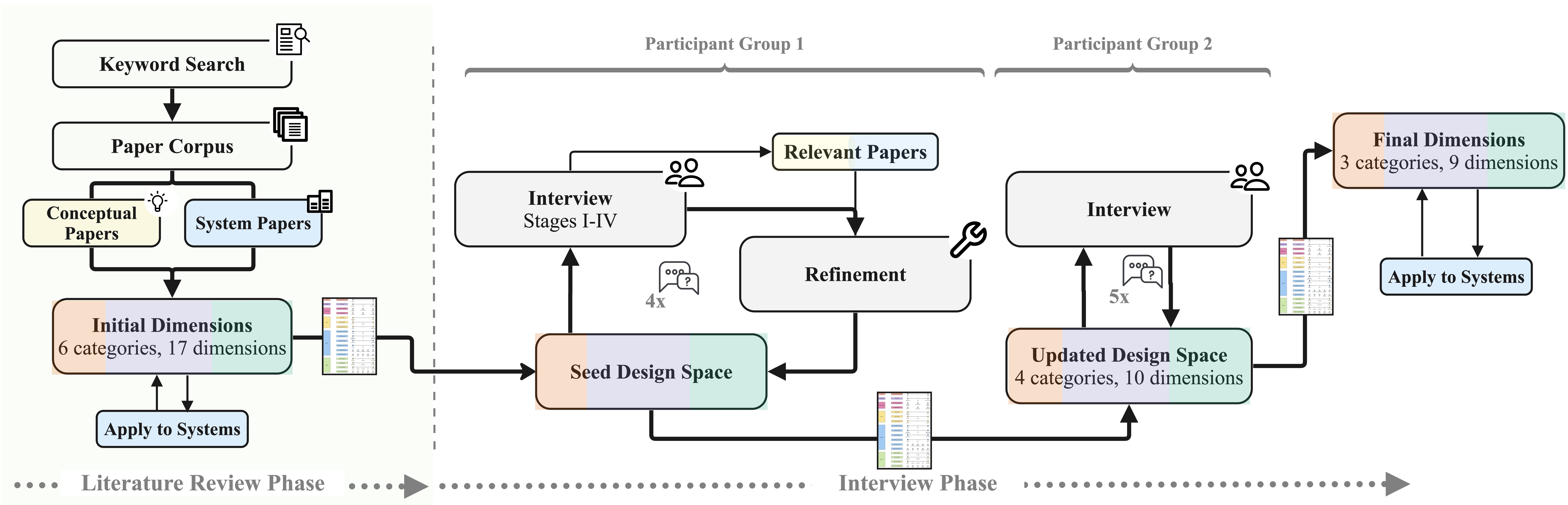
Deconstructing Human-AI Collaboration: Agency, Interaction, and Adaptation
Steffen Holter, Mennatallah El-Assady

0
0
As full AI-based automation remains out of reach in most real-world applications, the focus has instead shifted to leveraging the strengths of both human and AI agents, creating effective collaborative systems. The rapid advances in this area have yielded increasingly more complex systems and frameworks, while the nuance of their characterization has gotten more vague. Similarly, the existing conceptual models no longer capture the elaborate processes of these systems nor describe the entire scope of their collaboration paradigms. In this paper, we propose a new unified set of dimensions through which to analyze and describe human-AI systems. Our conceptual model is centered around three high-level aspects - agency, interaction, and adaptation - and is developed through a multi-step process. Firstly, an initial design space is proposed by surveying the literature and consolidating existing definitions and conceptual frameworks. Secondly, this model is iteratively refined and validated by conducting semi-structured interviews with nine researchers in this field. Lastly, to illustrate the applicability of our design space, we utilize it to provide a structured description of selected human-AI systems.
4/19/2024
🤖
AI Robots and Humanoid AI: Review, Perspectives and Directions
Longbing Cao

0
0
In the approximately century-long journey of robotics, humanoid robots made their debut around six decades ago. The rapid advancements in generative AI, large language models (LLMs), and large multimodal models (LMMs) have reignited interest in humanoids, steering them towards real-time, interactive, and multimodal designs and applications. This resurgence unveils boundless opportunities for AI robotics and novel applications, paving the way for automated, real-time and humane interactions with humanoid advisers, educators, medical professionals, caregivers, and receptionists. However, while current humanoid robots boast human-like appearances, they have yet to embody true humaneness, remaining distant from achieving human-like intelligence. In our comprehensive review, we delve into the intricate landscape of AI robotics and AI humanoid robots in particular, exploring the challenges, perspectives and directions in transitioning from human-looking to humane humanoids and fostering human-like robotics. This endeavour synergizes the advancements in LLMs, LMMs, generative AI, and human-level AI with humanoid robotics, omniverse, and decentralized AI, ushering in the era of AI humanoids and humanoid AI.
5/28/2024
From Explainable to Interactive AI: A Literature Review on Current Trends in Human-AI Interaction
Muhammad Raees, Inge Meijerink, Ioanna Lykourentzou, Vassilis-Javed Khan, Konstantinos Papangelis

0
0
AI systems are increasingly being adopted across various domains and application areas. With this surge, there is a growing research focus and societal concern for actively involving humans in developing, operating, and adopting these systems. Despite this concern, most existing literature on AI and Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) primarily focuses on explaining how AI systems operate and, at times, allowing users to contest AI decisions. Existing studies often overlook more impactful forms of user interaction with AI systems, such as giving users agency beyond contestability and enabling them to adapt and even co-design the AI's internal mechanics. In this survey, we aim to bridge this gap by reviewing the state-of-the-art in Human-Centered AI literature, the domain where AI and HCI studies converge, extending past Explainable and Contestable AI, delving into the Interactive AI and beyond. Our analysis contributes to shaping the trajectory of future Interactive AI design and advocates for a more user-centric approach that provides users with greater agency, fostering not only their understanding of AI's workings but also their active engagement in its development and evolution.
5/27/2024