Improved Emotional Alignment of AI and Humans: Human Ratings of Emotions Expressed by Stable Diffusion v1, DALL-E 2, and DALL-E 3
2405.18510

0
0
🤖
Abstract
Generative AI systems are increasingly capable of expressing emotions via text and imagery. Effective emotional expression will likely play a major role in the efficacy of AI systems -- particularly those designed to support human mental health and wellbeing. This motivates our present research to better understand the alignment of AI expressed emotions with the human perception of emotions. When AI tries to express a particular emotion, how might we assess whether they are successful? To answer this question, we designed a survey to measure the alignment between emotions expressed by generative AI and human perceptions. Three generative image models (DALL-E 2, DALL-E 3 and Stable Diffusion v1) were used to generate 240 examples of images, each of which was based on a prompt designed to express five positive and five negative emotions across both humans and robots. 24 participants recruited from the Prolific website rated the alignment of AI-generated emotional expressions with a text prompt used to generate the emotion (i.e., A robot expressing the emotion amusement). The results of our evaluation suggest that generative AI models are indeed capable of producing emotional expressions that are well-aligned with a range of human emotions; however, we show that the alignment significantly depends upon the AI model used and the emotion itself. We analyze variations in the performance of these systems to identify gaps for future improvement. We conclude with a discussion of the implications for future AI systems designed to support mental health and wellbeing.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Researchers explored how well generative AI models can express emotions in text and images, and how those emotional expressions align with human perceptions.
- They used three popular generative AI models (DALL-E 2, DALL-E 3, and Stable Diffusion v1) to create 240 images based on prompts designed to evoke positive and negative emotions in both humans and robots.
- 24 participants rated the alignment between the AI-generated emotional expressions and the prompts used to create them.
- The results show that generative AI can produce emotional expressions that are generally well-aligned with human perceptions, but the alignment varies depending on the model and the specific emotion.
Plain English Explanation
Generative AI systems like DALL-E 2, DALL-E 3, and Stable Diffusion are becoming increasingly skilled at creating text and images that convey emotions. This is an important capability, especially for AI systems designed to support human mental health and well-being, as emotional expression is crucial for effective communication and connection.
The researchers in this study wanted to understand how well the emotional expressions generated by these AI models align with how humans perceive those emotions. They created a variety of prompts intended to evoke both positive and negative emotions in both humans and robots, and then used the AI models to generate images based on those prompts. They then asked a group of people to rate how well the AI-generated emotional expressions matched the intended emotions.
The results showed that the generative AI models were generally successful at producing emotional expressions that aligned with human perceptions. However, the researchers also found that the degree of alignment varied depending on the specific AI model used and the emotion being expressed. This suggests that there is still room for improvement in this area, and the researchers hope their findings will help guide future developments in emotionally expressive AI systems.
Technical Explanation
The researchers designed a survey to measure the alignment between emotions expressed by generative AI and human perceptions of those emotions. They used three popular generative image models - DALL-E 2, DALL-E 3, and Stable Diffusion v1 - to generate 240 images based on prompts designed to express five positive and five negative emotions in both humans and robots.
For example, a prompt might be "a robot expressing the emotion of amusement." The researchers then recruited 24 participants from the Prolific website to rate the alignment of the AI-generated emotional expressions with the text prompts used to create them.
The results of the evaluation suggest that these generative AI models are indeed capable of producing emotional expressions that are well-aligned with a range of human emotions. However, the researchers found that the alignment varied significantly depending on the AI model used and the specific emotion being expressed.
Critical Analysis
The researchers acknowledge several limitations and areas for future research in their paper. For example, they note that their study only examined emotional expressions in the visual domain, and that further research is needed to understand how well generative AI models can convey emotions through text or other modalities.
Additionally, the researchers point out that their study used a relatively small sample size of participants, and that future work could explore how the alignment between AI-expressed emotions and human perceptions might vary across different cultural or demographic groups.
One potential concern that the researchers do not address is the potential for AI-generated emotional expressions to be used in manipulative or deceptive ways, such as in the context of large language models or multimodal systems. As these technologies become more advanced, it will be important to consider the ethical implications of their use, especially in applications that involve human-AI interaction and emotional connection.
Conclusion
The findings of this research suggest that generative AI models are capable of producing emotional expressions that are well-aligned with human perceptions, but the degree of alignment varies depending on the specific model and emotion. This has important implications for the development of AI systems designed to support human mental health and well-being, as effective emotional expression is crucial for building trust, empathy, and connection.
However, as these technologies continue to advance, it will be important to carefully consider the ethical implications of their use, particularly in applications that involve human-AI interaction and emotional engagement. By continuing to explore the capabilities and limitations of emotionally expressive AI, researchers can help guide the development of systems that are not only technically impressive, but also socially responsible and aligned with human values.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
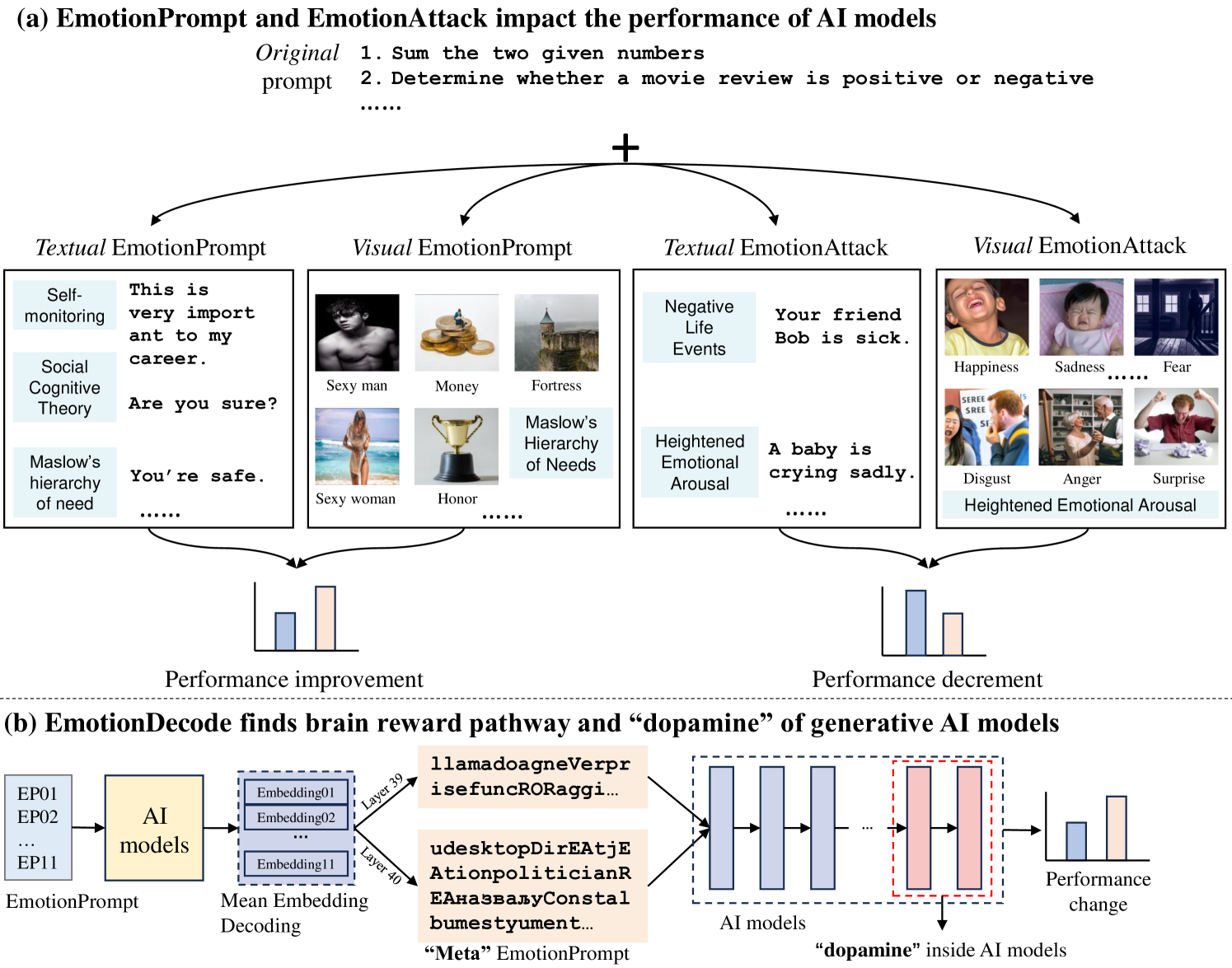
The Good, The Bad, and Why: Unveiling Emotions in Generative AI
Cheng Li, Jindong Wang, Yixuan Zhang, Kaijie Zhu, Xinyi Wang, Wenxin Hou, Jianxun Lian, Fang Luo, Qiang Yang, Xing Xie

0
0
Emotion significantly impacts our daily behaviors and interactions. While recent generative AI models, such as large language models, have shown impressive performance in various tasks, it remains unclear whether they truly comprehend emotions. This paper aims to address this gap by incorporating psychological theories to gain a holistic understanding of emotions in generative AI models. Specifically, we propose three approaches: 1) EmotionPrompt to enhance AI model performance, 2) EmotionAttack to impair AI model performance, and 3) EmotionDecode to explain the effects of emotional stimuli, both benign and malignant. Through extensive experiments involving language and multi-modal models on semantic understanding, logical reasoning, and generation tasks, we demonstrate that both textual and visual EmotionPrompt can boost the performance of AI models while EmotionAttack can hinder it. Additionally, EmotionDecode reveals that AI models can comprehend emotional stimuli akin to the mechanism of dopamine in the human brain. Our work heralds a novel avenue for exploring psychology to enhance our understanding of generative AI models.
6/10/2024

The ethical situation of DALL-E 2
Eduard Hogea, Josem Rocafortf

0
0
A hot topic of Artificial Intelligence right now is image generation from prompts. DALL-E 2 is one of the biggest names in this domain, as it allows people to create images from simple text inputs, to even more complicated ones. The company that made this possible, OpenAI, has assured everyone that visited their website that their mission is to ensure that artificial general intelligence benefits all humanity. A noble idea in our opinion, that also stood as the motive behind us choosing this subject. This paper analyzes the ethical implications of an AI image generative system, with an emphasis on how society is responding to it, how it probably will and how it should if all the right measures are taken.
5/30/2024
🔎
Towards ethical multimodal systems
Alexis Roger, Esma Aimeur, Irina Rish

0
0
Generative AI systems (ChatGPT, DALL-E, etc) are expanding into multiple areas of our lives, from art Rombach et al. [2021] to mental health Rob Morris and Kareem Kouddous [2022]; their rapidly growing societal impact opens new opportunities, but also raises ethical concerns. The emerging field of AI alignment aims to make AI systems reflect human values. This paper focuses on evaluating the ethics of multimodal AI systems involving both text and images - a relatively under-explored area, as most alignment work is currently focused on language models. We first create a multimodal ethical database from human feedback on ethicality. Then, using this database, we develop algorithms, including a RoBERTa-large classifier and a multilayer perceptron, to automatically assess the ethicality of system responses.
5/21/2024
💬
Modeling Emotions and Ethics with Large Language Models
Edward Y. Chang

0
0
This paper explores the integration of human-like emotions and ethical considerations into Large Language Models (LLMs). We first model eight fundamental human emotions, presented as opposing pairs, and employ collaborative LLMs to reinterpret and express these emotions across a spectrum of intensity. Our focus extends to embedding a latent ethical dimension within LLMs, guided by a novel self-supervised learning algorithm with human feedback (SSHF). This approach enables LLMs to perform self-evaluations and adjustments concerning ethical guidelines, enhancing their capability to generate content that is not only emotionally resonant but also ethically aligned. The methodologies and case studies presented herein illustrate the potential of LLMs to transcend mere text and image generation, venturing into the realms of empathetic interaction and principled decision-making, thereby setting a new precedent in the development of emotionally aware and ethically conscious AI systems.
4/23/2024