Integrating A.I. in Higher Education: Protocol for a Pilot Study with 'SAMCares: An Adaptive Learning Hub'
2405.00330

0
0
🗣️
Abstract
Learning never ends, and there is no age limit to grow yourself. However, the educational landscape may face challenges in effectively catering to students' inclusion and diverse learning needs. These students should have access to state-of-the-art methods for lecture delivery, online resources, and technology needs. However, with all the diverse learning sources, it becomes harder for students to comprehend a large amount of knowledge in a short period of time. Traditional assistive technologies and learning aids often lack the dynamic adaptability required for individualized education plans. Large Language Models (LLM) have been used in language translation, text summarization, and content generation applications. With rapid growth in AI over the past years, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants have been developed. This research aims to bridge this gap by introducing an innovative study buddy we will be calling the 'SAMCares'. The system leverages a Large Language Model (LLM) (in our case, LLaMa-2 70B as the base model) and Retriever-Augmented Generation (RAG) to offer real-time, context-aware, and adaptive educational support. The context of the model will be limited to the knowledge base of Sam Houston State University (SHSU) course notes. The LLM component enables a chat-like environment to interact with it to meet the unique learning requirements of each student. For this, we will build a custom web-based GUI. At the same time, RAG enhances real-time information retrieval and text generation, in turn providing more accurate and context-specific assistance. An option to upload additional study materials in the web GUI is added in case additional knowledge support is required. The system's efficacy will be evaluated through controlled trials and iterative feedback mechanisms.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- Learning is a lifelong process, but the educational landscape faces challenges in effectively supporting diverse learning needs.
- Traditional assistive technologies often lack the dynamic adaptability required for personalized education.
- Large Language Models (LLMs) and AI-powered chatbots have potential to address these gaps.
Plain English Explanation
The research paper introduces an innovative "study buddy" system called "SAMCares" that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) and Retriever-Augmented Generation (RAG) to provide real-time, context-aware, and adaptive educational support. The system is designed to cater to the unique learning needs of each student, offering a chat-like environment powered by an LLM and enhanced by RAG for more accurate and relevant information retrieval and text generation.
The key idea is to create a virtual assistant that can adapt to the individual learning requirements of students, unlike traditional assistive technologies which often lack this dynamic capability. By leveraging advanced AI models like LLMs and RAG, the SAMCares system aims to bridge the gap between students' diverse needs and the educational resources available to them.
Technical Explanation
The research paper proposes the development of the "SAMCares" system, which utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) (specifically, the LLaMa-2 70B model) and Retriever-Augmented Generation (RAG) to provide real-time, context-aware, and adaptive educational support. The system's knowledge base is limited to the course notes of Sam Houston State University (SHSU).
The LLM component enables a chat-like environment for students to interact with the system and have their unique learning requirements met. The RAG mechanism enhances real-time information retrieval and text generation, leading to more accurate and context-specific assistance. Additionally, the system includes an option for students to upload their own study materials, which can further expand the knowledge base and personalize the support provided.
The effectiveness of the SAMCares system will be evaluated through controlled trials and iterative feedback mechanisms.
Critical Analysis
The research paper acknowledges the potential challenges of effectively catering to diverse learning needs in the educational landscape. While the proposed SAMCares system leverages advanced AI technologies like LLMs and RAG to address this issue, there may be limitations to the adaptability and generalizability of the system.
The paper focuses on the SHSU course notes as the knowledge base, which raises questions about the system's scalability and ability to cater to a broader range of educational contexts. Additionally, the evaluation methodology, involving controlled trials and iterative feedback, may provide insights, but further research is needed to assess the system's long-term efficacy and impact on student outcomes.
It would be valuable to explore the system's integration with automated generation of high-quality medical simulation scenarios or its effectiveness in introductory computer science education, as these domains may present different challenges and requirements.
Conclusion
The research paper presents an innovative approach to enhancing educational support through the development of the "SAMCares" system, which leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) and Retriever-Augmented Generation (RAG) to provide personalized, context-aware, and adaptive educational assistance. This system aims to bridge the gap between diverse student needs and the limitations of traditional assistive technologies.
While the proposed solution shows promise, further research and evaluation are necessary to assess its long-term effectiveness, scalability, and applicability across different educational contexts. As AI models continue to advance, the potential for AI-powered educational assistants to enhance learning experiences and outcomes remains an exciting area of exploration.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬
How Can Large Language Models Enable Better Socially Assistive Human-Robot Interaction: A Brief Survey
Zhonghao Shi, Ellen Landrum, Amy O' Connell, Mina Kian, Leticia Pinto-Alva, Kaleen Shrestha, Xiaoyuan Zhu, Maja J Matari'c

0
0
Socially assistive robots (SARs) have shown great success in providing personalized cognitive-affective support for user populations with special needs such as older adults, children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and individuals with mental health challenges. The large body of work on SAR demonstrates its potential to provide at-home support that complements clinic-based interventions delivered by mental health professionals, making these interventions more effective and accessible. However, there are still several major technical challenges that hinder SAR-mediated interactions and interventions from reaching human-level social intelligence and efficacy. With the recent advances in large language models (LLMs), there is an increased potential for novel applications within the field of SAR that can significantly expand the current capabilities of SARs. However, incorporating LLMs introduces new risks and ethical concerns that have not yet been encountered, and must be carefully be addressed to safely deploy these more advanced systems. In this work, we aim to conduct a brief survey on the use of LLMs in SAR technologies, and discuss the potentials and risks of applying LLMs to the following three major technical challenges of SAR: 1) natural language dialog; 2) multimodal understanding; 3) LLMs as robot policies.
4/9/2024
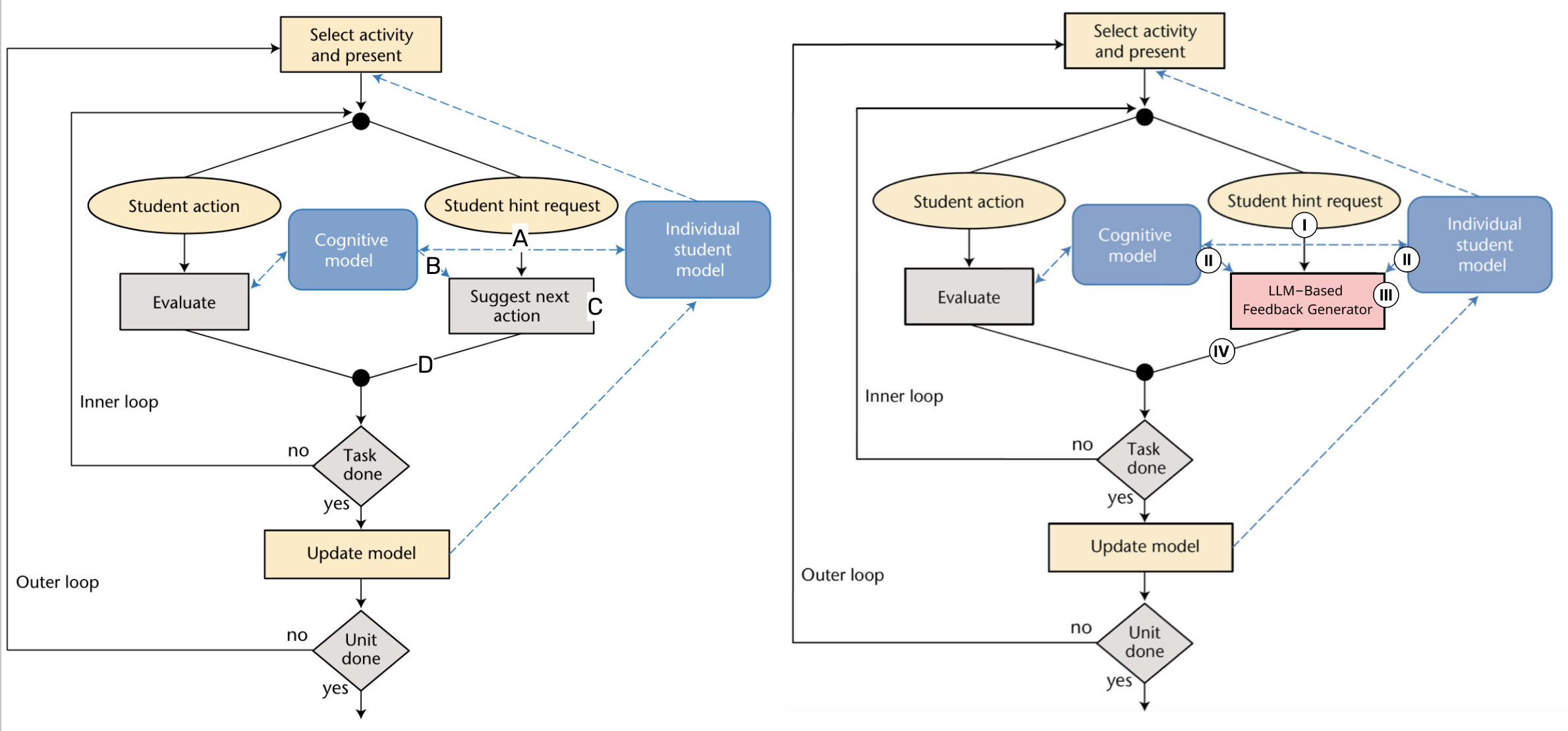
Enhancing LLM-Based Feedback: Insights from Intelligent Tutoring Systems and the Learning Sciences
John Stamper, Ruiwei Xiao, Xinying Hou

0
0
The field of Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED) focuses on the intersection of technology, education, and psychology, placing a strong emphasis on supporting learners' needs with compassion and understanding. The growing prominence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has led to the development of scalable solutions within educational settings, including generating different types of feedback in Intelligent Tutoring Systems. However, the approach to utilizing these models often involves directly formulating prompts to solicit specific information, lacking a solid theoretical foundation for prompt construction and empirical assessments of their impact on learning. This work advocates careful and caring AIED research by going through previous research on feedback generation in ITS, with emphasis on the theoretical frameworks they utilized and the efficacy of the corresponding design in empirical evaluations, and then suggesting opportunities to apply these evidence-based principles to the design, experiment, and evaluation phases of LLM-based feedback generation. The main contributions of this paper include: an avocation of applying more cautious, theoretically grounded methods in feedback generation in the era of generative AI; and practical suggestions on theory and evidence-based feedback design for LLM-powered ITS.
5/14/2024
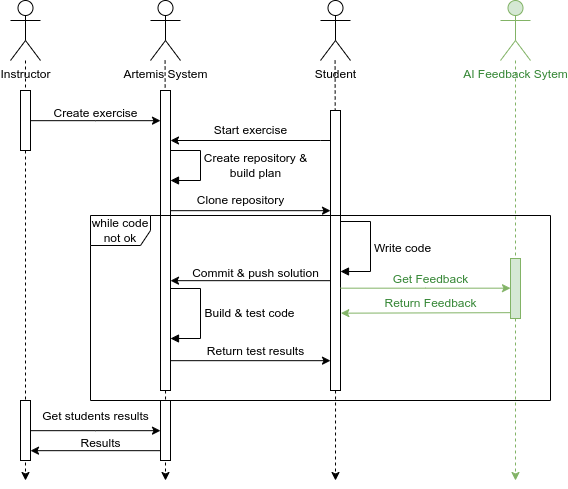
AI-Tutoring in Software Engineering Education
Eduard Frankford, Clemens Sauerwein, Patrick Bassner, Stephan Krusche, Ruth Breu

0
0
With the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) in various domains, the education sector is set for transformation. The potential of AI-driven tools in enhancing the learning experience, especially in programming, is immense. However, the scientific evaluation of Large Language Models (LLMs) used in Automated Programming Assessment Systems (APASs) as an AI-Tutor remains largely unexplored. Therefore, there is a need to understand how students interact with such AI-Tutors and to analyze their experiences. In this paper, we conducted an exploratory case study by integrating the GPT-3.5-Turbo model as an AI-Tutor within the APAS Artemis. Through a combination of empirical data collection and an exploratory survey, we identified different user types based on their interaction patterns with the AI-Tutor. Additionally, the findings highlight advantages, such as timely feedback and scalability. However, challenges like generic responses and students' concerns about a learning progress inhibition when using the AI-Tutor were also evident. This research adds to the discourse on AI's role in education.
4/8/2024
🤖
Developing generative AI chatbots conceptual framework for higher education
Joshua Ebere Chukwuere

0
0
This research explores the quickly changing field of generative artificial intelligence (GAI) chatbots in higher education, an industry that is undergoing major technological changes. AI chatbots, such as ChatGPT, HuggingChat, and Google Bard, are becoming more and more common in a variety of sectors, including education. Their acceptance is still in its early phases, with a variety of prospects and obstacles. However, their potential in higher education is particularly noteworthy, providing lecturers and students with affordable, individualized support. Creating a comprehensive framework to aid the usage of generative AI chatbots in higher education institutions (HEIs) is the aim of this project. The Generative AI Chatbots Acceptance Model (GAICAM) is the result of this study's synthesis of elements from well-known frameworks, including the TAM, UTAUT2, TPB, and others along with variables like optimism, innovativeness, discomfort, insecurity, and others. Using a research method that encompasses a comprehensive analysis of extant literature from databases such as IEEE, ACM, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar, the study aims to comprehend the implications of AI Chatbots on higher education and pinpoint critical elements for their efficacious implementation. Peer-reviewed English-language publications published between 2020 and 2023 with a focus on the use of AI chatbots in higher education were the main focus of the search criteria. The results demonstrate how much AI chatbots can do to improve student engagement, streamline the educational process, and support administrative and research duties. But there are also clear difficulties, such as unfavorable student sentiments, doubts about the veracity of material produced by AI, and unease and nervousness with new technologies.
5/14/2024