Measuring Online Emotional Reactions to Events
2307.10245

0
0
⚙️
Abstract
The rich and dynamic information environment of social media provides researchers, policy makers, and entrepreneurs with opportunities to learn about social phenomena in a timely manner. However, using this data to understand social behavior is difficult due heterogeneity of topics and events discussed in the highly dynamic online information environment. To address these challenges, we present a method for systematically detecting and measuring emotional reactions to offline events using change point detection on the time series of collective affect, and further explaining these reactions using a transformer-based topic model. We demonstrate the utility of the method on a corpus of tweets from a large US metropolitan area between January and August, 2020, covering a period of great social change. We demonstrate that our method is able to disaggregate topics to measure population's emotional and moral reactions. This capability allows for better monitoring of population's reactions during crises using online data.
Create account to get full access
The paper presents a method for detecting and measuring emotional reactions to offline events using social media data. The method employs change point detection on time series of collective affect and explains these reactions using a transformer-based topic model. The utility of the method is demonstrated on a corpus of tweets from a large US metropolitan area between January and August, 2020, a period of significant social change. The method can disaggregate topics to measure the population's emotional and moral reactions, enabling better monitoring of population reactions during crises using online data. The heterogeneity of topics and the highly dynamic nature of the online information environment make it challenging to use this data to understand social behavior.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Event Detection from Social Media for Epidemic Prediction
Tanmay Parekh, Anh Mac, Jiarui Yu, Yuxuan Dong, Syed Shahriar, Bonnie Liu, Eric Yang, Kuan-Hao Huang, Wei Wang, Nanyun Peng, Kai-Wei Chang

0
0
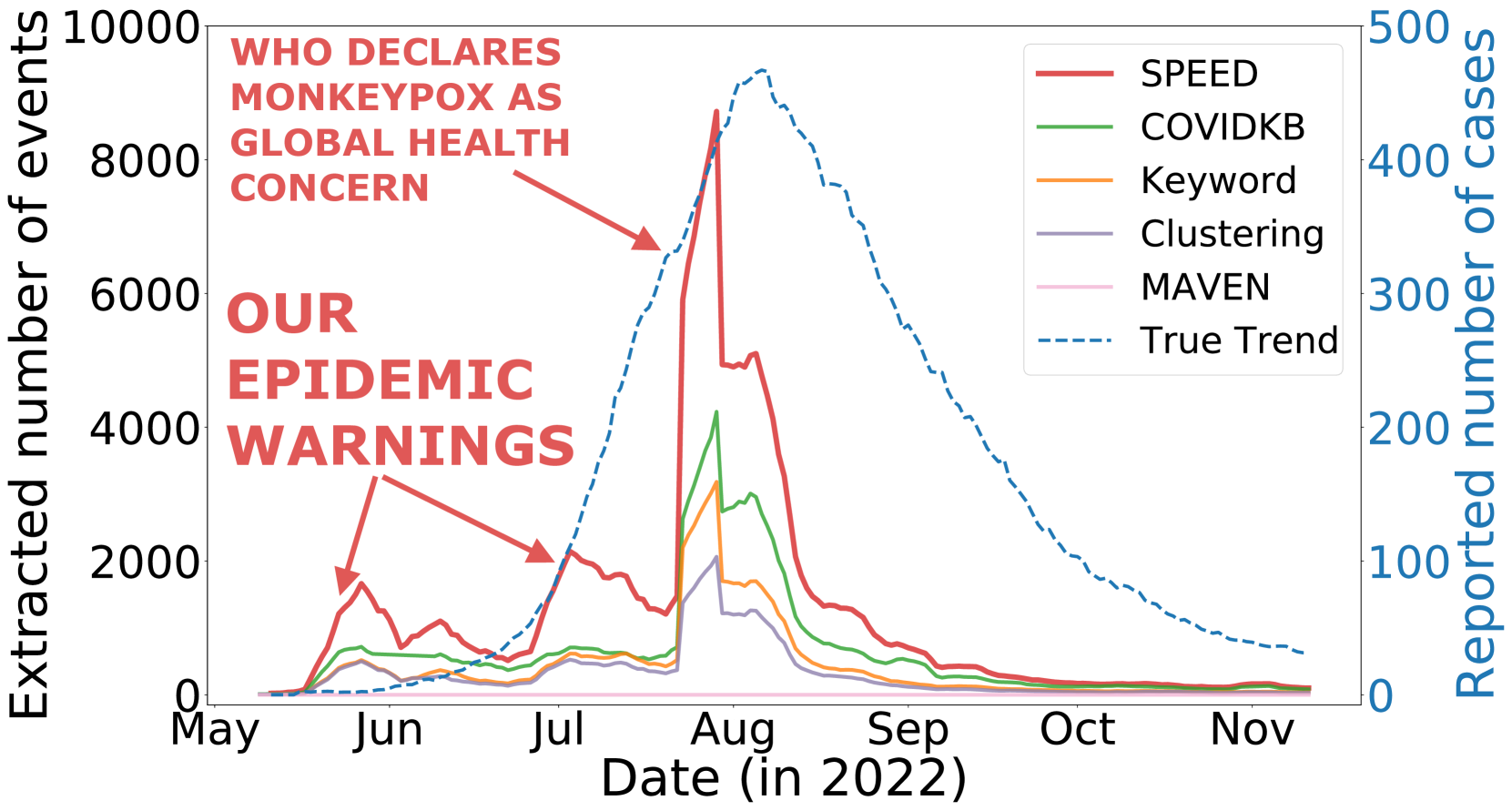
Social media is an easy-to-access platform providing timely updates about societal trends and events. Discussions regarding epidemic-related events such as infections, symptoms, and social interactions can be crucial for informing policymaking during epidemic outbreaks. In our work, we pioneer exploiting Event Detection (ED) for better preparedness and early warnings of any upcoming epidemic by developing a framework to extract and analyze epidemic-related events from social media posts. To this end, we curate an epidemic event ontology comprising seven disease-agnostic event types and construct a Twitter dataset SPEED with human-annotated events focused on the COVID-19 pandemic. Experimentation reveals how ED models trained on COVID-based SPEED can effectively detect epidemic events for three unseen epidemics of Monkeypox, Zika, and Dengue; while models trained on existing ED datasets fail miserably. Furthermore, we show that reporting sharp increases in the extracted events by our framework can provide warnings 4-9 weeks earlier than the WHO epidemic declaration for Monkeypox. This utility of our framework lays the foundations for better preparedness against emerging epidemics.
5/27/2024
🛠️
Grounding Toxicity in Real-World Events across Languages
Wondimagegnhue Tsegaye Tufa, Ilia Markov, Piek Vossen

0
0
Social media conversations frequently suffer from toxicity, creating significant issues for users, moderators, and entire communities. Events in the real world, like elections or conflicts, can initiate and escalate toxic behavior online. Our study investigates how real-world events influence the origin and spread of toxicity in online discussions across various languages and regions. We gathered Reddit data comprising 4.5 million comments from 31 thousand posts in six different languages (Dutch, English, German, Arabic, Turkish and Spanish). We target fifteen major social and political world events that occurred between 2020 and 2023. We observe significant variations in toxicity, negative sentiment, and emotion expressions across different events and language communities, showing that toxicity is a complex phenomenon in which many different factors interact and still need to be investigated. We will release the data for further research along with our code.
5/24/2024
Multi-channel Emotion Analysis for Consensus Reaching in Group Movie Recommendation Systems
Adilet Yerkin, Elnara Kadyrgali, Yerdauit Torekhan, Pakizar Shamoi

0
0
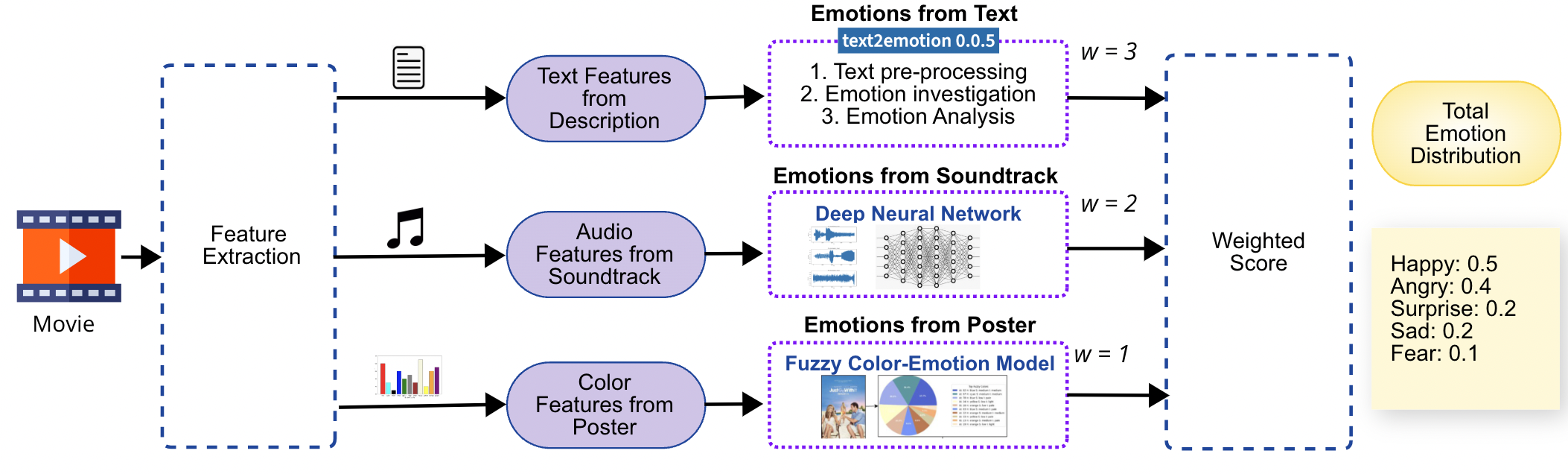
Watching movies is one of the social activities typically done in groups. Emotion is the most vital factor that affects movie viewers' preferences. So, the emotional aspect of the movie needs to be determined and analyzed for further recommendations. It can be challenging to choose a movie that appeals to the emotions of a diverse group. Reaching an agreement for a group can be difficult due to the various genres and choices. This paper proposes a novel approach to group movie suggestions by examining emotions from three different channels: movie descriptions (text), soundtracks (audio), and posters (image). We employ the Jaccard similarity index to match each participant's emotional preferences to prospective movie choices, followed by a fuzzy inference technique to determine group consensus. We use a weighted integration process for the fusion of emotion scores from diverse data types. Then, group movie recommendation is based on prevailing emotions and viewers' best-loved movies. After determining the recommendations, the group's consensus level is calculated using a fuzzy inference system, taking participants' feedback as input. Participants (n=130) in the survey were provided with different emotion categories and asked to select the emotions best suited for particular movies (n=12). Comparison results between predicted and actual scores demonstrate the efficiency of using emotion detection for this problem (Jaccard similarity index = 0.76). We explored the relationship between induced emotions and movie popularity as an additional experiment, analyzing emotion distribution in 100 popular movies from the TMDB database. Such systems can potentially improve the accuracy of movie recommendation systems and achieve a high level of consensus among participants with diverse preferences.
4/23/2024
Targeted aspect-based emotion analysis to detect opportunities and precaution in financial Twitter messages
Silvia Garc'ia-M'endez, Francisco de Arriba-P'erez, Ana Barros-Vila, Francisco J. Gonz'alez-Casta~no

0
0
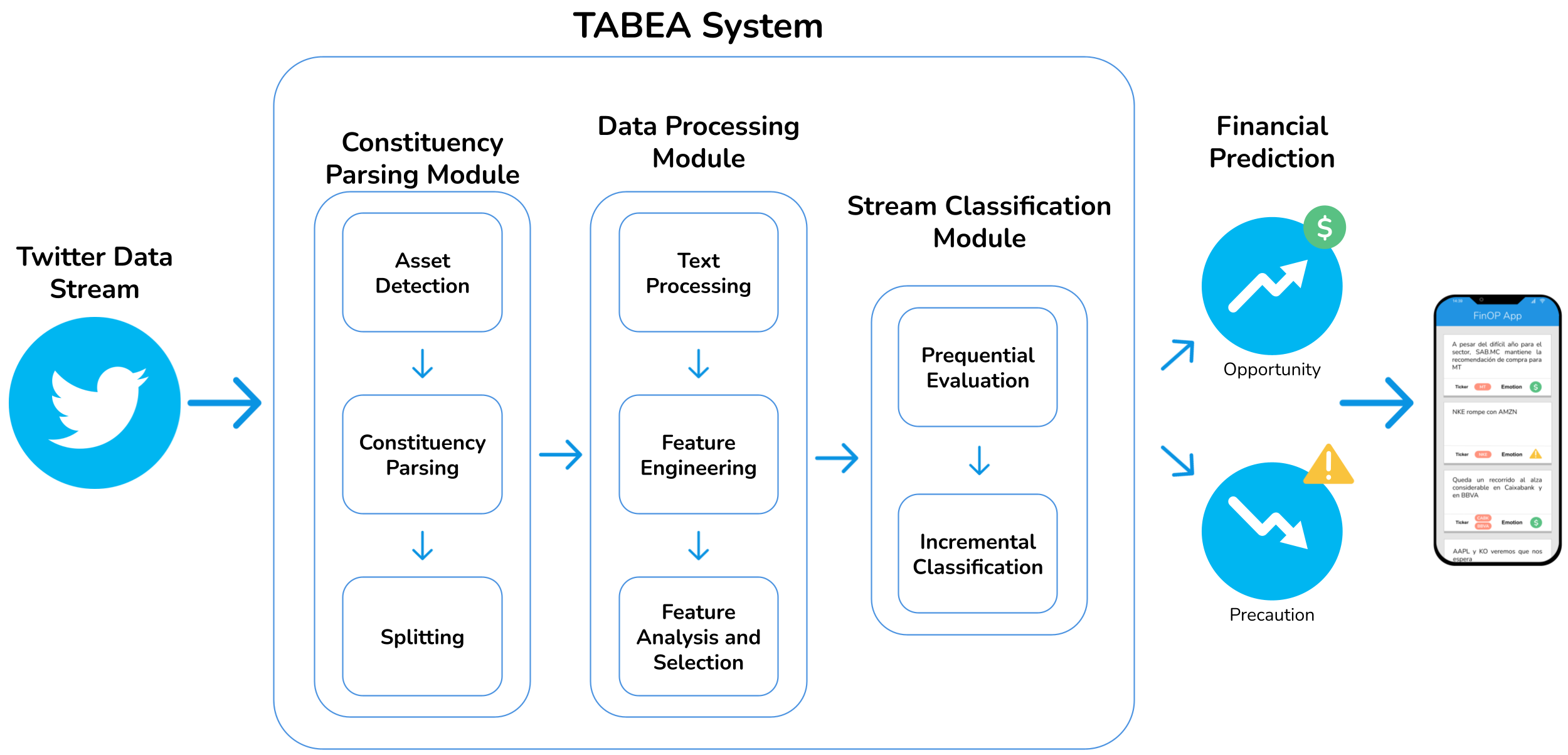
Microblogging platforms, of which Twitter is a representative example, are valuable information sources for market screening and financial models. In them, users voluntarily provide relevant information, including educated knowledge on investments, reacting to the state of the stock markets in real-time and, often, influencing this state. We are interested in the user forecasts in financial, social media messages expressing opportunities and precautions about assets. We propose a novel Targeted Aspect-Based Emotion Analysis (TABEA) system that can individually discern the financial emotions (positive and negative forecasts) on the different stock market assets in the same tweet (instead of making an overall guess about that whole tweet). It is based on Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques and Machine Learning streaming algorithms. The system comprises a constituency parsing module for parsing the tweets and splitting them into simpler declarative clauses; an offline data processing module to engineer textual, numerical and categorical features and analyse and select them based on their relevance; and a stream classification module to continuously process tweets on-the-fly. Experimental results on a labelled data set endorse our solution. It achieves over 90% precision for the target emotions, financial opportunity, and precaution on Twitter. To the best of our knowledge, no prior work in the literature has addressed this problem despite its practical interest in decision-making, and we are not aware of any previous NLP nor online Machine Learning approaches to TABEA.
4/16/2024