Orbital Facility Location Problem for Satellite Constellation Servicing Depots
2302.12191

0
0
👨🏫
Abstract
This work proposes an adaptation of the Facility Location Problem for the optimal placement of on-orbit servicing depots for satellite constellations in high-altitude orbit. The high-altitude regime, such as Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), is a unique dynamical environment where existing low-thrust propulsion systems can provide the necessary thrust to conduct plane-change maneuvers between the various orbital planes of the constellation. As such, on-orbit servicing architectures involving servicer spacecraft that conduct round-trips between servicing depots and the client satellites of the constellation may be conceived. To this end, orbital facility location problem is a binary linear program, where the costs of operating and allocating the facility(ies) to satellites are considered in terms of the sum of Equivalent Mass to Low Earth Orbit (EMLEO), is proposed. The low-thrust transfers between the facilities and the clients are computed using a parallel implementation of a Lyapunov feedback controller. The total launch cost of the depot along with its servicers, propellant, and payload are taken into account as the cost to establish a given depot. The proposed approach is applied to designing on-orbit servicing depots for the Galileo and the GPS constellations.
Create account to get full access
This paper proposes an adaptation of the Facility Location Problem to determine the optimal placement of on-orbit servicing depots for satellite constellations in high-altitude orbits like Medium Earth Orbit (MEO). In this environment, low-thrust propulsion systems can provide the necessary thrust for maneuvers between the orbital planes of the constellation. The paper formulates the orbital facility location problem as a binary linear program, where the costs of operating and allocating the facility(ies) to satellites are considered in terms of the Equivalent Mass to Low Earth Orbit (EMLEO).
The low-thrust transfers between the facilities and the client satellites are computed using a parallel implementation of a Lyapunov feedback controller. The total launch cost of the depot, including the servicers, propellant, and payload, is taken into account as the cost to establish a given depot.
The proposed approach is applied to designing on-orbit servicing depots for the Galileo and the GPS constellations.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤷
End-to-End Delivery in LEO Mega-constellations and the Reordering Problem
Rasmus Sibbern Frederiksen, Thomas Gundgaard Mulvad, Israel Leyva-Mayorga, Tatiana Kozlova Madsen, Federico Chiariotti

0
0
Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite mega-constellations with hundreds or thousands of satellites and inter-satellite links (ISLs) have the potential to provide global end-to-end connectivity. Furthermore, if the physical distance between source and destination is sufficiently long, end-to-end routing over the LEO constellation can provide lower latency when compared to the terrestrial infrastructure due to the faster propagation of electromagnetic waves in space than in optic fiber. However, the frequent route changes due to the movement of the satellites result in the out-of-order delivery of packets, causing sudden changes to the Round-Trip Time (RTT) that can be misinterpreted as congestion by congestion control algorithms. In this paper, the performance of three widely used congestion control algorithms, Cubic, Reno, and BBR, is evaluated in an emulated LEO satellite constellation with Free-Space Optical (FSO) ISLs. Furthermore, we perform a sensitivity analysis for Cubic by changing the satellite constellation parameters, length of the routes, and the positions of the source and destination to identify problematic routing scenarios. The results show that route changes can have profound transient effects on the goodput of the connection, posing problems for typical broadband applications.
5/14/2024
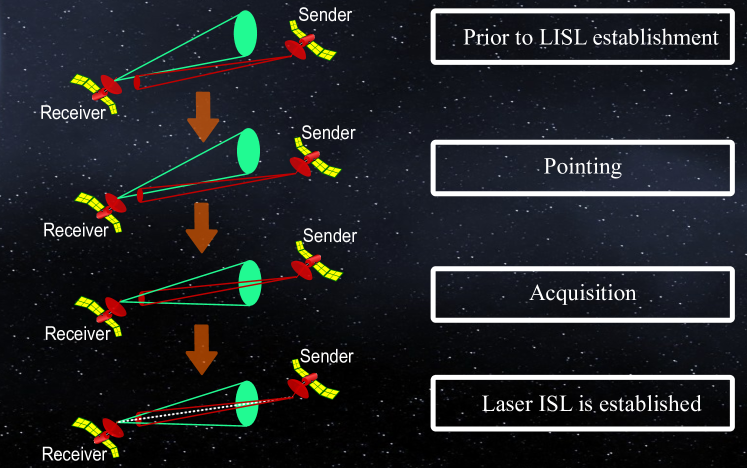
On-Demand Routing in LEO Mega-Constellations with Dynamic Laser Inter-Satellite Links
Dhiraj Bhattacharjee, Pablo G. Madoery, Aizaz U. Chaudhry, Halim Yanikomeroglu, Gunes Karabulut Kurt, Peng Hu, Khaled Ahmed, Stephane Martel

0
0
Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite mega constellations are beginning to include laser inter-satellite links (LISLs) to extend the Internet to the most remote locations on Earth. Since the process of establishing these links incurs a setup delay on the order of seconds, a static network topology is generally established well in advance, which is then used for the routing calculations. However, this involves keeping links active even when they are not being used to forward traffic, leading to poor energy efficiency. Motivated by technological advances that are gradually decreasing the LISL setup delays, we foresee scenarios where it will be possible to compute routes and establish dynamic LISLs on demand. This will require considering setup delays as penalties that will affect the end-to-end latency. In this paper, we present a nonlinear optimization model that considers these penalties in the cost function and propose three heuristic algorithms that solve the problem in a tractable way. The algorithms establish different trade-offs in terms of performance and computational complexity. We extensively analyze metrics including average latency, route change rate, outage probability, and jitter in Starlink's Phase I version 2 constellation. The results show the benefit of adaptive routing schemes according to the link setup delay. In particular, more complex schemes can decrease the average end-to-end latency in exchange for an increase in execution time. On the other hand, depending on the maximum tolerated latency, it is possible to use less computationally complex schemes which will be more scalable for the satellite mega constellations of the future.
6/5/2024
Instability of Self-Driving Satellite Mega-Constellation: From Theory to Practical Impacts on Network Lifetime and Capacity
Yimei Chen, Yuanjie Li, Hewu Li, Lixin Liu, Li Ouyang, Jiabo Yang, Junyi Li, Jianping Wu, Qian Wu, Jun Liu, Zeqi Lai

0
0
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite mega-constellations aim to enable high-speed Internet for numerous users anywhere on Earth. To safeguard their network infrastructure in congested outer space, they perform automatic orbital maneuvers to avoid collisions with external debris and satellites. However, our control-theoretic analysis and empirical validation using Starlink's space situational awareness datasets discover that, these safety-oriented maneuvers themselves can threaten safety and networking via cascaded collision avoidance inside the mega-constellation. This domino effect forces a dilemma between long-term LEO network lifetime and short-term LEO network capacity. Its root cause is that, the decades-old local pairwise maneuver paradigm for standalone satellites is inherently unstable if scaled out to recent mega-constellation networks. We thus propose an alternative bilateral maneuver control that stabilizes self-driving mega-constellations for concurrent network lifetime and capacity boosts. Our operational trace-driven emulation shows a 8$times$ network lifetime extension in Starlink without limiting its network capacity.
6/11/2024
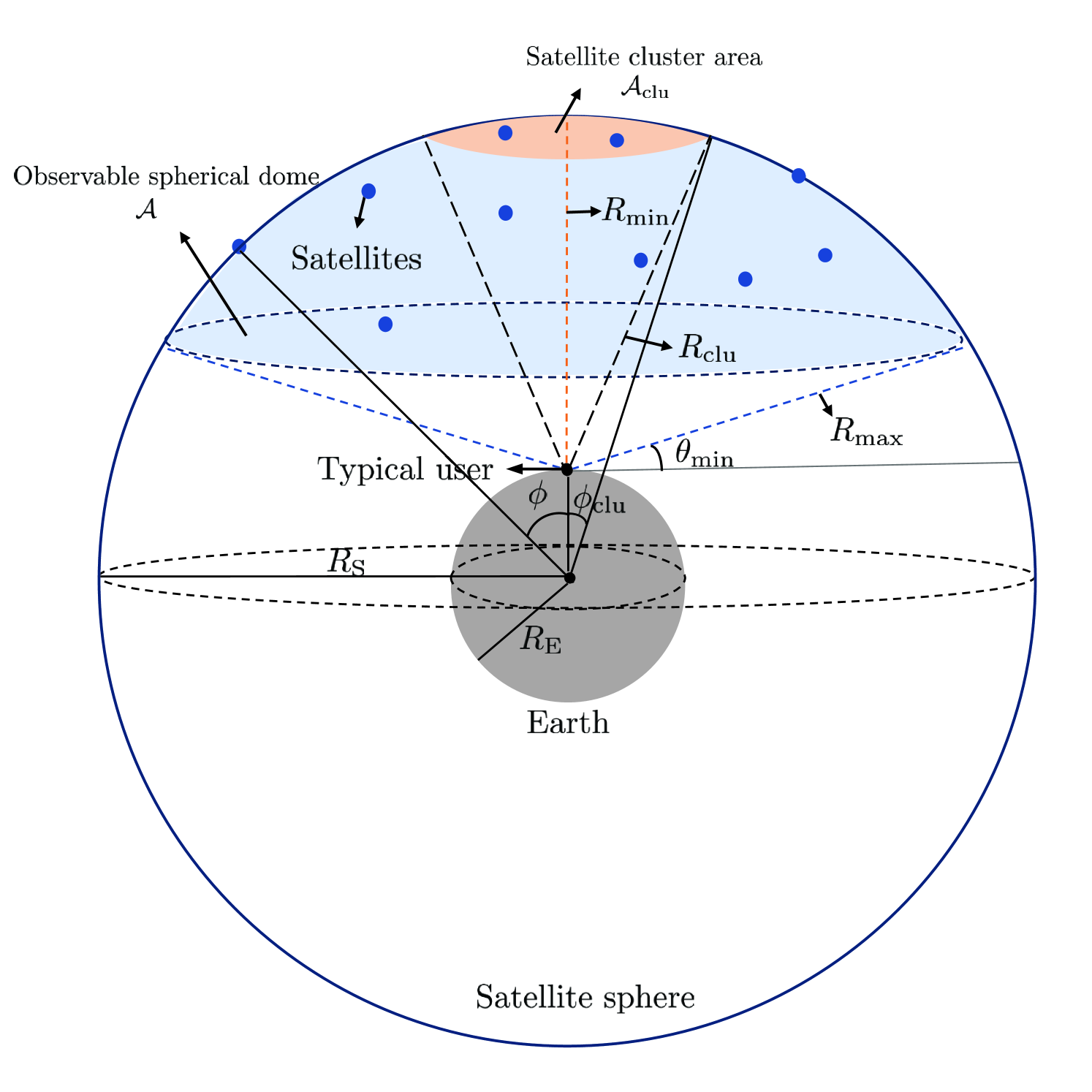
Analyzing Downlink Coverage in Clustered Low Earth Orbit Satellite Constellations: A Stochastic Geometry Approach
Miyeon Lee, Sucheol Kim, Minje Kim, Dong-Hyun Jung, Junil Choi

0
0
Satellite networks are emerging as vital solutions for global connectivity beyond 5G. As companies such as SpaceX, OneWeb, and Amazon are poised to launch a large number of satellites in low Earth orbit, the heightened inter-satellite interference caused by mega-constellations has become a significant concern. To address this challenge, recent works have introduced the concept of satellite cluster networks where multiple satellites in a cluster collaborate to enhance the network performance. In order to investigate the performance of these networks, we propose mathematical analyses by modeling the locations of satellites and users using Poisson point processes, building on the success of stochastic geometry-based analyses for satellite networks. In particular, we suggest the lower and upper bounds of the coverage probability as functions of the system parameters, including satellite density, satellite altitude, satellite cluster area, path loss exponent, and Nakagami parameter $m$. We validate the analytical expressions by comparing them with simulation results. Our analyses can be used to design reliable satellite cluster networks by effectively estimating the impact of system parameters on the coverage performance.
4/1/2024