Paving the Way to Hybrid Quantum-Classical Scientific Workflows
2404.10389

0
0
🌀
Abstract
The increasing growth of data volume, and the consequent explosion in demand for computational power, are affecting scientific computing, as shown by the rise of extreme data scientific workflows. As the need for computing power increases, quantum computing has been proposed as a way to deliver it. It may provide significant theoretical speedups for many scientific applications (i.e., molecular dynamics, quantum chemistry, combinatorial optimization, and machine learning). Therefore, integrating quantum computers into the computing continuum constitutes a promising way to speed up scientific computation. However, the scientific computing community still lacks the necessary tools and expertise to fully harness the power of quantum computers in the execution of complex applications such as scientific workflows. In this work, we describe the main characteristics of quantum computing and its main benefits for scientific applications, then we formalize hybrid quantum-classic workflows, explore how to identify quantum components and map them onto resources. We demonstrate concepts on a real use case and define a software architecture for a hybrid workflow management system.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Data volume and computational demand are increasing, driving the need for new approaches like quantum computing.
- Quantum computing may provide significant speedups for scientific applications like molecular dynamics, quantum chemistry, combinatorial optimization, and machine learning.
- Integrating quantum computers into scientific workflows is a promising way to accelerate computation, but the scientific community lacks the necessary tools and expertise.
- This work explores formalizing hybrid quantum-classic workflows and mapping them onto quantum resources.
Plain English Explanation
As the amount of data we need to process continues to grow rapidly, the demand for powerful computing resources has skyrocketed. This is a major challenge for the scientific community, who rely on complex computational workflows to drive their research.
One potential solution that has been proposed is quantum computing. Quantum computers have the theoretical ability to perform certain calculations much faster than classical computers, especially for problems related to molecular dynamics, quantum chemistry, optimization, and machine learning. By integrating quantum computers into scientific workflows, researchers hope to dramatically accelerate their computations and unlock new discoveries.
However, the scientific community currently lacks the specific tools and knowledge needed to effectively harness the power of quantum computers for their complex applications. This paper aims to address that gap by formalizing the concept of "hybrid quantum-classic workflows" - computational pipelines that leverage both quantum and classical computing resources. The researchers explore how to identify which parts of a workflow could benefit from quantum acceleration and how to map those components onto actual quantum hardware.
Technical Explanation
The paper first provides an overview of quantum computing and its potential benefits for scientific applications. It highlights several areas, such as molecular dynamics, quantum chemistry, combinatorial optimization, and machine learning, where quantum computers could provide significant theoretical speedups compared to classical computers.
The core of the paper focuses on formalizing the concept of hybrid quantum-classic workflows. This involves identifying which components of a scientific workflow could be executed more efficiently on a quantum computer, and then mapping those quantum components onto the available quantum hardware resources. The researchers describe a software architecture for a hybrid workflow management system that could facilitate this integration of quantum and classical computing.
Finally, the paper demonstrates the concepts on a real-world use case, providing a concrete example of how hybrid quantum-classic workflows could be implemented and executed.
Critical Analysis
The paper makes a compelling case for the potential of quantum computing to accelerate scientific workflows, but it also acknowledges the significant challenges that remain. The scientific community currently lacks the necessary tools and expertise to fully harness quantum computers for complex applications like scientific workflows.
While the paper proposes a framework for formalizing hybrid quantum-classic workflows, it does not provide a complete solution. The mapping of quantum components onto available hardware resources is a non-trivial problem that requires further research and development, as highlighted in the discussion of hybrid quantum solvers.
Additionally, the paper does not address the significant practical and technical hurdles of actually building and maintaining reliable quantum computing hardware and software. Issues like quantum circuit imperfections and the complexities of quantum machine learning architectures will need to be solved before quantum computers can be seamlessly integrated into scientific workflows.
Overall, the paper provides a valuable roadmap for exploring the potential of quantum computing in scientific applications, but much more research and development will be needed to turn this vision into a practical reality.
Conclusion
This paper highlights the growing need for powerful computing resources to support the increasing volume and complexity of scientific data. It proposes quantum computing as a promising solution, with the potential to provide significant speedups for a range of scientific applications.
By formalizing the concept of hybrid quantum-classic workflows, the researchers have taken an important step towards enabling the integration of quantum computers into scientific computing. However, significant technical and practical challenges remain before this vision can be fully realized.
Nonetheless, this work represents an important contribution to the ongoing efforts to harness the power of emerging quantum technologies for the benefit of scientific research and discovery.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Quantum Computing: Vision and Challenges
Sukhpal Singh Gill, Oktay Cetinkaya, Stefano Marrone, Daniel Claudino, David Haunschild, Leon Schlote, Huaming Wu, Carlo Ottaviani, Xiaoyuan Liu, Sree Pragna Machupalli, Kamalpreet Kaur, Priyansh Arora, Ji Liu, Ahmed Farouk, Houbing Herbert Song, Steve Uhlig, Kotagiri Ramamohanarao

0
0
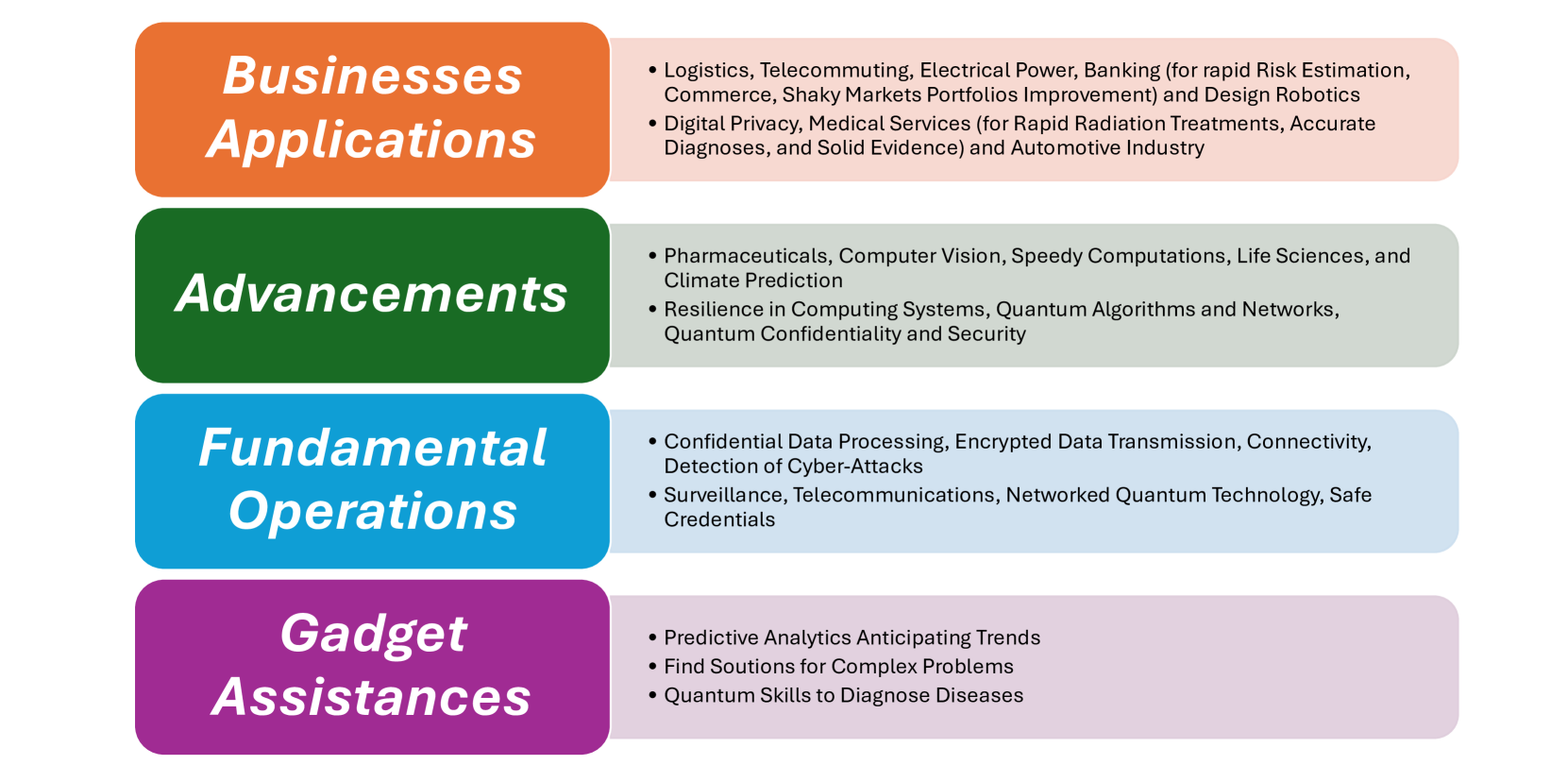
The recent development of quantum computing, which uses entanglement, superposition, and other quantum fundamental concepts, can provide substantial processing advantages over traditional computing. These quantum features help solve many complex problems that cannot be solved with conventional computing methods. These problems include modeling quantum mechanics, logistics, chemical-based advances, drug design, statistical science, sustainable energy, banking, reliable communication, and quantum chemical engineering. The last few years have witnessed remarkable advancements in quantum software and algorithm creation and quantum hardware research, which has significantly advanced the prospect of realizing quantum computers. It would be helpful to have comprehensive literature research on this area to grasp the current status and find outstanding problems that require considerable attention from the research community working in the quantum computing industry. To better understand quantum computing, this paper examines the foundations and vision based on current research in this area. We discuss cutting-edge developments in quantum computer hardware advancement and subsequent advances in quantum cryptography, quantum software, and high-scalability quantum computers. Many potential challenges and exciting new trends for quantum technology research and development are highlighted in this paper for a broader debate.
6/6/2024
🤖
Quantum computing with Qiskit
Ali Javadi-Abhari, Matthew Treinish, Kevin Krsulich, Christopher J. Wood, Jake Lishman, Julien Gacon, Simon Martiel, Paul D. Nation, Lev S. Bishop, Andrew W. Cross, Blake R. Johnson, Jay M. Gambetta

0
0
We describe Qiskit, a software development kit for quantum information science. We discuss the key design decisions that have shaped its development, and examine the software architecture and its core components. We demonstrate an end-to-end workflow for solving a problem in condensed matter physics on a quantum computer that serves to highlight some of Qiskit's capabilities, for example the representation and optimization of circuits at various abstraction levels, its scalability and retargetability to new gates, and the use of quantum-classical computations via dynamic circuits. Lastly, we discuss some of the ecosystem of tools and plugins that extend Qiskit for various tasks, and the future ahead.
6/21/2024
👁️
Cyber Protection Applications of Quantum Computing: A Review
Ummar Ahmed, Tuomo Sipola, Jari Hautamaki

0
0
Quantum computing is a cutting-edge field of information technology that harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform computations. It has major implications for the cyber security industry. Existing cyber protection applications are working well, but there are still challenges and vulnerabilities in computer networks. Sometimes data and privacy are also compromised. These complications lead to research questions asking what kind of cyber protection applications of quantum computing are there and what potential methods or techniques can be used for cyber protection? These questions will reveal how much power quantum computing has and to what extent it can outperform the conventional computing systems. This scoping review was conducted by considering 815 papers. It showed the possibilities that can be achievedif quantum technologies are implemented in cyber environments. This scoping review discusses various domains such as algorithms and applications, bioinformatics, cloud and edge computing, the organization of complex systems, application areas focused on security and threats, and the broader quantum computing ecosystem. In each of these areas, there is significant scope for quantum computing to be implemented and to revolutionize the working environment. Numerous quantum computing applications for cyber protection and a number of techniques to protect our data and privacy were identified. The results are not limited to network security but also include data security. This paper also discusses societal aspects, e.g., the applications of quantum computing in the social sciences. This scoping review discusses how to enhance the efficiency and security of quantum computing in various cyber security domains. Additionally, it encourages the reader to think about what kind of techniques and methods can be deployed to secure the cyber world.
6/26/2024
📶
Quantum Cloud Computing: Trends and Challenges
Muhammed Golec, Emir Sahin Hatay, Mustafa Golec, Murat Uyar, Merve Golec, Sukhpal Singh Gill

0
0
Quantum computing (QC) is a new paradigm that will revolutionize various areas of computing, especially cloud computing. QC, still in its infancy, is a costly technology capable of operating in highly isolated environments due to its rapid response to environmental factors. For this reason, it is still a challenging technology for researchers to reach. Integrating QC into an isolated remote server, like a cloud, and making it available to users can overcome these problems. Furthermore, experts predict that QC, with its ability to swiftly resolve complex and computationally intensive operations, will offer significant benefits in systems that process large amounts of data, like cloud computing. This article presents the vision and challenges for the quantum cloud computing (QCC) paradigm that will emerge with the integration of quantum and cloud computing. Next, we present the advantages of QC over classical computing applications. We analyze the effects of QC on cloud systems, such as cost, security, and scalability. Besides all of these advantages, we highlight research gaps in QCC, such as qubit stability and efficient resource allocation. This article identifies QCC's advantages and challenges for future research, highlighting research gaps.
5/1/2024