Position: Categorical Deep Learning is an Algebraic Theory of All Architectures
2402.15332

3
0
🤿
Abstract
We present our position on the elusive quest for a general-purpose framework for specifying and studying deep learning architectures. Our opinion is that the key attempts made so far lack a coherent bridge between specifying constraints which models must satisfy and specifying their implementations. Focusing on building a such a bridge, we propose to apply category theory -- precisely, the universal algebra of monads valued in a 2-category of parametric maps -- as a single theory elegantly subsuming both of these flavours of neural network design. To defend our position, we show how this theory recovers constraints induced by geometric deep learning, as well as implementations of many architectures drawn from the diverse landscape of neural networks, such as RNNs. We also illustrate how the theory naturally encodes many standard constructs in computer science and automata theory.
Create account to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Categorical semiotics: Foundations for Knowledge Integration
Carlos Leandro

0
0
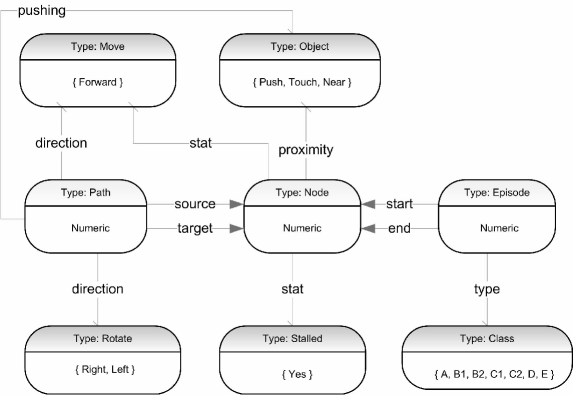
The integration of knowledge extracted from diverse models, whether described by domain experts or generated by machine learning algorithms, has historically been challenged by the absence of a suitable framework for specifying and integrating structures, learning processes, data transformations, and data models or rules. In this work, we extend algebraic specification methods to address these challenges within such a framework. In our work, we tackle the challenging task of developing a comprehensive framework for defining and analyzing deep learning architectures. We believe that previous efforts have fallen short by failing to establish a clear connection between the constraints a model must adhere to and its actual implementation. Our methodology employs graphical structures that resemble Ehresmann's sketches, interpreted within a universe of fuzzy sets. This approach offers a unified theory that elegantly encompasses both deterministic and non-deterministic neural network designs. Furthermore, we highlight how this theory naturally incorporates fundamental concepts from computer science and automata theory. Our extended algebraic specification framework, grounded in graphical structures akin to Ehresmann's sketches, offers a promising solution for integrating knowledge across disparate models and domains. By bridging the gap between domain-specific expertise and machine-generated insights, we pave the way for more comprehensive, collaborative, and effective approaches to knowledge integration and modeling.
4/3/2024
🤖
Token Space: A Category Theory Framework for AI Computations
Wuming Pan

0
0
This paper introduces the Token Space framework, a novel mathematical construct designed to enhance the interpretability and effectiveness of deep learning models through the application of category theory. By establishing a categorical structure at the Token level, we provide a new lens through which AI computations can be understood, emphasizing the relationships between tokens, such as grouping, order, and parameter types. We explore the foundational methodologies of the Token Space, detailing its construction, the role of construction operators and initial categories, and its application in analyzing deep learning models, specifically focusing on attention mechanisms and Transformer architectures. The integration of category theory into AI research offers a unified framework to describe and analyze computational structures, enabling new research paths and development possibilities. Our investigation reveals that the Token Space framework not only facilitates a deeper theoretical understanding of deep learning models but also opens avenues for the design of more efficient, interpretable, and innovative models, illustrating the significant role of category theory in advancing computational models.
4/19/2024
🤿
Cellular automata, many-valued logic, and deep neural networks
Yani Zhang, Helmut Bolcskei

0
0
We develop a theory characterizing the fundamental capability of deep neural networks to learn, from evolution traces, the logical rules governing the behavior of cellular automata (CA). This is accomplished by first establishing a novel connection between CA and Lukasiewicz propositional logic. While binary CA have been known for decades to essentially perform operations in Boolean logic, no such relationship exists for general CA. We demonstrate that many-valued (MV) logic, specifically Lukasiewicz propositional logic, constitutes a suitable language for characterizing general CA as logical machines. This is done by interpolating CA transition functions to continuous piecewise linear functions, which, by virtue of the McNaughton theorem, yield formulae in MV logic characterizing the CA. Recognizing that deep rectified linear unit (ReLU) networks realize continuous piecewise linear functions, it follows that these formulae are naturally extracted from CA evolution traces by deep ReLU networks. A corresponding algorithm together with a software implementation is provided. Finally, we show that the dynamical behavior of CA can be realized by recurrent neural networks.
4/9/2024
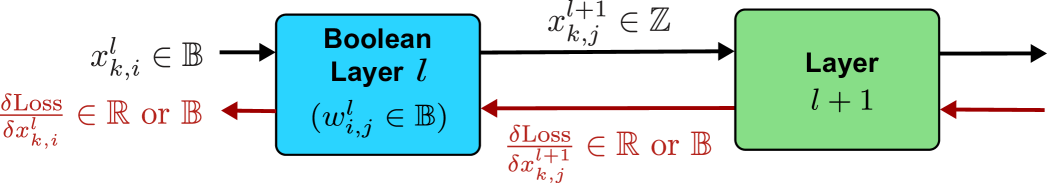
BOLD: Boolean Logic Deep Learning
Van Minh Nguyen, Cristian Ocampo, Aymen Askri, Louis Leconte, Ba-Hien Tran

0
0
Deep learning is computationally intensive, with significant efforts focused on reducing arithmetic complexity, particularly regarding energy consumption dominated by data movement. While existing literature emphasizes inference, training is considerably more resource-intensive. This paper proposes a novel mathematical principle by introducing the notion of Boolean variation such that neurons made of Boolean weights and inputs can be trained -- for the first time -- efficiently in Boolean domain using Boolean logic instead of gradient descent and real arithmetic. We explore its convergence, conduct extensively experimental benchmarking, and provide consistent complexity evaluation by considering chip architecture, memory hierarchy, dataflow, and arithmetic precision. Our approach achieves baseline full-precision accuracy in ImageNet classification and surpasses state-of-the-art results in semantic segmentation, with notable performance in image super-resolution, and natural language understanding with transformer-based models. Moreover, it significantly reduces energy consumption during both training and inference.
5/28/2024