Secure Link State Routing for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
2403.19859

0
0
🔗
Abstract
The secure operation of the routing protocol is one of the major challenges to be met for the proliferation of the Mobile Ad hoc Networking (MANET) paradigm. Nevertheless, security enhancements have been proposed mostly for reactive MANET protocols. The proposed here Secure Link State Routing Protocol (SLSP) provides secure proactive topology discovery, which can be multiply beneficial to the network operation. SLSP can be employed as a stand-alone protocol, or fit naturally into a hybrid routing framework, when combined with a reactive protocol. SLSP is robust against individual attackers, it is capable of adjusting its scope between local and network-wide topology discovery, and it is capable of operating in networks of frequently changing topology and membership.
Create account to get full access
The paper introduces the Secure Link State Routing Protocol (SLSP), a secure proactive routing protocol for Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANETs). SLSP aims to address the security challenges faced by MANETs, particularly in the area of routing protocols. While most security enhancements have focused on reactive MANET protocols, SLSP provides secure proactive topology discovery, which offers multiple benefits to network operation.
SLSP can function as a standalone protocol or integrate seamlessly into a hybrid routing framework when combined with a reactive protocol. The protocol is designed to be robust against individual attackers and capable of adjusting its scope between local and network-wide topology discovery. Additionally, SLSP can operate in networks with frequently changing topology and membership, making it suitable for dynamic MANET environments.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

A Lightweight Security Solution for Mitigation of Hatchetman Attack in RPL-based 6LoWPAN
Girish Sharma, Jyoti Grover, Abhishek Verma

0
0
In recent times, the Internet of Things (IoT) has a significant rise in industries, and we live in the era of Industry 4.0, where each device is connected to the Internet from small to big. These devices are Artificial Intelligence (AI) enabled and are capable of perspective analytics. By 2023, it's anticipated that over 14 billion smart devices will be available on the Internet. These applications operate in a wireless environment where memory, power, and other resource limitations apply to the nodes. In addition, the conventional routing method is ineffective in networks with limited resource devices, lossy links, and slow data rates. Routing Protocol for Low Power and Lossy Networks (RPL), a new routing protocol for such networks, was proposed by the IETF's ROLL group. RPL operates in two modes: Storing and Non-Storing. In Storing mode, each node have the information to reach to other node. In Non-Storing mode, the routing information lies with the root node only. The attacker may exploit the Non-Storing feature of the RPL. When the root node transmits User Datagram Protocol~(UDP) or control message packet to the child nodes, the routing information is stored in the extended header of the IPv6 packet. The attacker may modify the address from the source routing header which leads to Denial of Service (DoS) attack. This attack is RPL specific which is known as Hatchetman attack. This paper shows significant degradation in terms of network performance when an attacker exploits this feature. We also propose a lightweight mitigation of Hatchetman attack using game theoretic approach to detect the Hatchetman attack in IoT.
4/3/2024

Smart Routing with Precise Link Estimation: DSEE-Based Anypath Routing for Reliable Wireless Networking
Narjes Nourzad, Bhaskar Krishnamachari

0
0
In dynamic and resource-constrained environments, such as multi-hop wireless mesh networks, traditional routing protocols often falter by relying on predetermined paths that prove ineffective in unpredictable link conditions. Shortest Anypath routing offers a solution by adapting routing decisions based on real-time link conditions. However, the effectiveness of such routing is fundamentally dependent on the quality and reliability of the available links, and predicting these variables with certainty is challenging. This paper introduces a novel approach that leverages the Deterministic Sequencing of Exploration and Exploitation (DSEE), a multi-armed bandit algorithm, to address the need for accurate and real-time estimation of link delivery probabilities. This approach augments the reliability and resilience of the Shortest Anypath routing in the face of fluctuating link conditions. By coupling DSEE with Anypath routing, this algorithm continuously learns and ensures accurate delivery probability estimation and selects the most suitable way to efficiently route packets while maintaining a provable near-logarithmic regret bound. We also theoretically prove that our proposed scheme offers better regret scaling with respect to the network size than the previously proposed Thompson Sampling-based Opportunistic Routing (TSOR).
5/20/2024
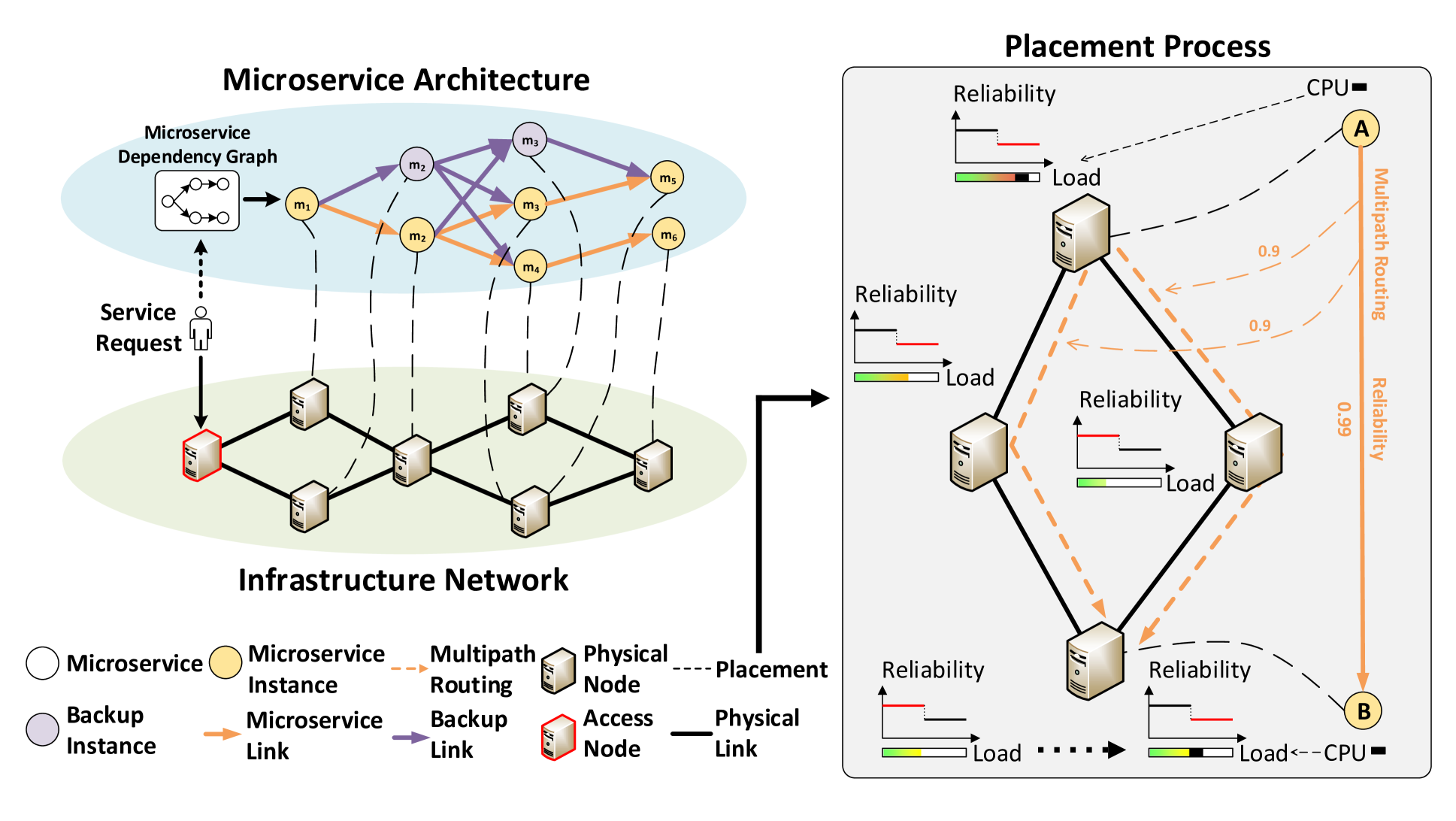
Network-Aware Reliability Modeling and Optimization for Microservice Placement
Fangyu Zhang, Yuang Chen, Hancheng Lu, Yongsheng Huang

0
0
Optimizing microservice placement to enhance the reliability of services is crucial for improving the service level of microservice architecture-based mobile networks and Internet of Things (IoT) networks. Despite extensive research on service reliability, the impact of network load and routing on service reliability remains understudied, leading to suboptimal models and unsatisfactory performance. To address this issue, we propose a novel network-aware service reliability model that effectively captures the correlation between network state changes and reliability. Based on this model, we formulate the microservice placement problem as an integer nonlinear programming problem, aiming to maximize service reliability. Subsequently, a service reliability-aware placement (SRP) algorithm is proposed to solve the problem efficiently. To reduce bandwidth consumption, we further discuss the microservice placement problem with the shared backup path mechanism and propose a placement algorithm based on the SRP algorithm using shared path reliability calculation, known as the SRP-S algorithm. Extensive simulations demonstrate that the SRP algorithm reduces service failures by up to 29% compared to the benchmark algorithms. By introducing the shared backup path mechanism, the SRP-S algorithm reduces bandwidth consumption by up to 62% compared to the SRP algorithm with the fully protected path mechanism. It also reduces service failures by up to 21% compared to the SRP algorithm with the shared backup mechanism.
5/29/2024
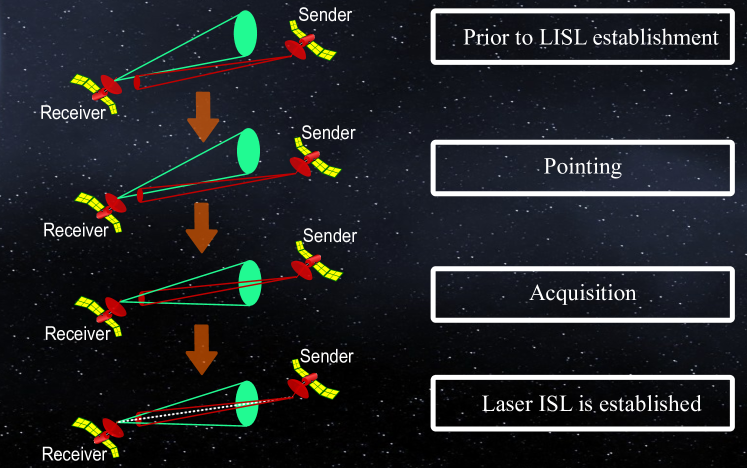
On-Demand Routing in LEO Mega-Constellations with Dynamic Laser Inter-Satellite Links
Dhiraj Bhattacharjee, Pablo G. Madoery, Aizaz U. Chaudhry, Halim Yanikomeroglu, Gunes Karabulut Kurt, Peng Hu, Khaled Ahmed, Stephane Martel

0
0
Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite mega constellations are beginning to include laser inter-satellite links (LISLs) to extend the Internet to the most remote locations on Earth. Since the process of establishing these links incurs a setup delay on the order of seconds, a static network topology is generally established well in advance, which is then used for the routing calculations. However, this involves keeping links active even when they are not being used to forward traffic, leading to poor energy efficiency. Motivated by technological advances that are gradually decreasing the LISL setup delays, we foresee scenarios where it will be possible to compute routes and establish dynamic LISLs on demand. This will require considering setup delays as penalties that will affect the end-to-end latency. In this paper, we present a nonlinear optimization model that considers these penalties in the cost function and propose three heuristic algorithms that solve the problem in a tractable way. The algorithms establish different trade-offs in terms of performance and computational complexity. We extensively analyze metrics including average latency, route change rate, outage probability, and jitter in Starlink's Phase I version 2 constellation. The results show the benefit of adaptive routing schemes according to the link setup delay. In particular, more complex schemes can decrease the average end-to-end latency in exchange for an increase in execution time. On the other hand, depending on the maximum tolerated latency, it is possible to use less computationally complex schemes which will be more scalable for the satellite mega constellations of the future.
6/5/2024