A Simulation Study of Source Routing for Load Balancing in Software-Defined Satellite Networks
2405.16292

0
0

Abstract
In the next generation network, the satellite network will play a fundamental role, in overcoming the limitation of the terrestrial network. Nonetheless, the satellite-terrestrial network integration presents a number of problems due to the time-variant topology of the first. One of the most important is the routing process of such networks. Many solutions have been proposed in the literature since the 1990s, and in recent years, the development of modern technologies such as Software Defined Networking (SDN) led to new possible approaches to the routing of satellite network. In this paper, a graph-based, source routing algorithm is presented. The algorithm exploits reliability and flexibility of the SDN architecture and the simplicity of source routing to tackle the dynamic topology of the network, providing rerouting solutions when necessary.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a simulation study on the use of source routing for load balancing in software-defined satellite networks.
- The researchers explore the performance of source routing in managing traffic loads across a satellite network.
- The study aims to provide insights into how source routing can be leveraged to improve network efficiency and resilience in satellite-based communication systems.
Plain English Explanation
Satellite networks are an important part of modern communication infrastructure, providing connectivity to remote and hard-to-reach areas. However, managing the flow of data traffic across these networks can be challenging, especially when dealing with fluctuating demands and potential congestion.
The researchers in this study investigate the use of source routing as a technique to address these challenges. Source routing is a method where the path a data packet takes through the network is determined at the source, rather than being decided by the individual network nodes along the way. This approach can enable more deliberate control over traffic flow and load distribution.
By running simulations, the researchers evaluate how source routing performs in managing the traffic loads across a software-defined satellite network. They examine various metrics, such as network throughput, latency, and the distribution of load across different satellite nodes. The findings from this study can provide valuable insights for satellite network operators and designers looking to improve the efficiency and resilience of their systems.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a simulation-based analysis of source routing for load balancing in software-defined satellite networks. The researchers developed a simulation environment to model a satellite network with multiple satellites, ground stations, and user terminals. They implemented a source routing algorithm that allows the network controller to specify the exact path a data packet should take through the network.
Through the simulations, the team examined the performance of the source routing approach under various traffic patterns and network conditions. They measured metrics such as network throughput, end-to-end latency, and the distribution of load across the satellite nodes. The results were compared to a traditional routing approach, where the routing decisions are made independently by each network node.
The findings suggest that the source routing strategy can effectively balance the traffic loads across the satellite network, leading to improved overall throughput and reduced latency. The researchers also observed that source routing can enhance the network's resilience to congestion, as the centralized controller can dynamically adjust the routing paths to avoid overloaded satellite nodes.
The paper discusses the trade-offs and potential limitations of the source routing approach, including the increased signaling overhead and the need for tight synchronization between the network controller and the satellite nodes. The authors also highlight opportunities for further research, such as exploring more advanced routing algorithms and incorporating additional factors, like satellite mobility and environmental effects, into the simulation model.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a valuable contribution to the field of software-defined satellite networks by demonstrating the potential benefits of source routing for load balancing. The simulation-based approach allows the researchers to systematically evaluate the performance of this routing strategy under a range of network conditions, which is crucial given the complex and dynamic nature of satellite communication systems.
One potential limitation of the study is the use of a simplified simulation model that may not fully capture the real-world complexities of satellite networks, such as the impact of atmospheric conditions, satellite handovers, and the heterogeneity of user traffic patterns. Incorporating these factors into the simulation environment could lead to more realistic and nuanced insights.
Additionally, the paper focuses primarily on the performance metrics related to network throughput and latency, but it does not delve deeply into other important considerations, such as the energy efficiency of the satellite nodes or the impact of source routing on the overall system complexity and operational costs. These aspects could be valuable to explore in future research.
Another area for further investigation could be the development of more intelligent and adaptive source routing algorithms that can dynamically adjust the traffic paths based on real-time network conditions, user demands, and other contextual factors. This could help optimize the network's performance and resilience in an even more sophisticated manner.
Conclusion
This simulation study provides valuable insights into the potential benefits of source routing for load balancing in software-defined satellite networks. By enabling centralized control over the traffic paths, the source routing approach can enhance network throughput, reduce latency, and improve resilience to congestion. These findings have important implications for the design and management of satellite communication systems, which are becoming increasingly crucial for providing global connectivity and enabling various applications, from remote sensing to disaster response.
The researchers have laid the groundwork for further exploration of source routing and other advanced routing strategies in the context of satellite networks. Incorporating more realistic factors, expanding the performance metrics, and developing more sophisticated routing algorithms could lead to even more valuable insights and practical solutions for enhancing the efficiency and reliability of these crucial communication infrastructures.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🔍
Routing Algorithm for Software Defined Network Based on Boxcovering Algorithm
Dana Turlykozhayeva, Sayat Akhtanov, Nurzhan Ussipov, Almat Akhmetali, Aslan Bolysbay, Yerkin Shabdan

0
0
A routing algorithm is the most fundamental problem in complex network communication. In complex networks, the amount of computation increases as the number of nodes increases which reduces routing performance. In this paper, we propose a routing algorithm for software-defined networking (SDN) based on a box-covering (BC) algorithm. It is known that using the BC algorithm it is possible to increase performance in complex SDN. We partition the entire SDN network into subnets using three existing box-covering methods such as MEMB, GC, and CIEA, then we use Dijkstratextquotesingle s algorithm to find the shortest path between subnets and within each subnet. We compared all box-covering algorithms and found that the GC algorithm has the highest performance for SDN routing.
6/11/2024

Throughput and Link Utilization Improvement in Satellite Networks: A Learning-Enabled Approach
Hao Wu

0
0
Satellite networks provide communication services to global users with an uneven geographical distribution. In densely populated regions, Inter-satellite links (ISLs) often experience congestion, blocking traffic from other links and leading to low link utilization and throughput. In such cases, delay-tolerant traffic can be withheld by moving satellites and carried to navigate congested areas, thereby mitigating link congestion in densely populated regions. Through rational store-and-forward decision-making, link utilization and throughput can be improved. Building on this foundation, this letter centers its focus on learning-based decision-making for satellite traffic. First, a link load prediction method based on topology isomorphism is proposed. Then, a Markov decision process (MDP) is formulated to model store-and-forward decision-making. To generate store-and-forward policies, we propose reinforcement learning algorithms based on value iteration and Q-Learning. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method improves throughput and link utilization while consuming less than 20$%$ of the time required by constraint-based routing.
6/4/2024

Quality of Service-Constrained Online Routing in High Throughput Satellites
Olivier B'elanger, Olfa Ben Yahia, St'ephane Martel, Antoine Lesage-Landry, Gunes Karabulut Kurt

0
0
High throughput satellites (HTSs) outpace traditional satellites due to their multi-beam transmission. The rise of low Earth orbit mega constellations amplifies HTS data rate demands to terabits/second with acceptable latency. This surge in data rate necessitates multiple modems, often exceeding single device capabilities. Consequently, satellites employ several processors, forming a complex packet-switch network. This can lead to potential internal congestion and challenges in adhering to strict quality of service (QoS) constraints. While significant research exists on constellation-level routing, a literature gap remains on the internal routing within a single HTS. The intricacy of this internal network architecture presents a significant challenge to achieve high data rates. This paper introduces an online optimal flow allocation and scheduling method for HTSs. The problem is presented as a multi-commodity flow instance with different priority data streams. An initial full time horizon model is proposed as a benchmark. We apply a model predictive control (MPC) approach to enable adaptive routing based on current information and the forecast within the prediction time horizon while allowing for deviation of the latter. Importantly, MPC is inherently suited to handle uncertainty in incoming flows. Our approach minimizes the packet loss by optimally and adaptively managing the priority queue schedulers and flow exchanges between satellite processing modules. Central to our method is a routing model focusing on optimal priority scheduling to enhance data rates and maintain QoS. The model's stages are critically evaluated, and results are compared to traditional methods via numerical simulations. Through simulations, our method demonstrates performance nearly on par with the hindsight optimum, showcasing its efficiency and adaptability in addressing satellite communication challenges.
6/3/2024
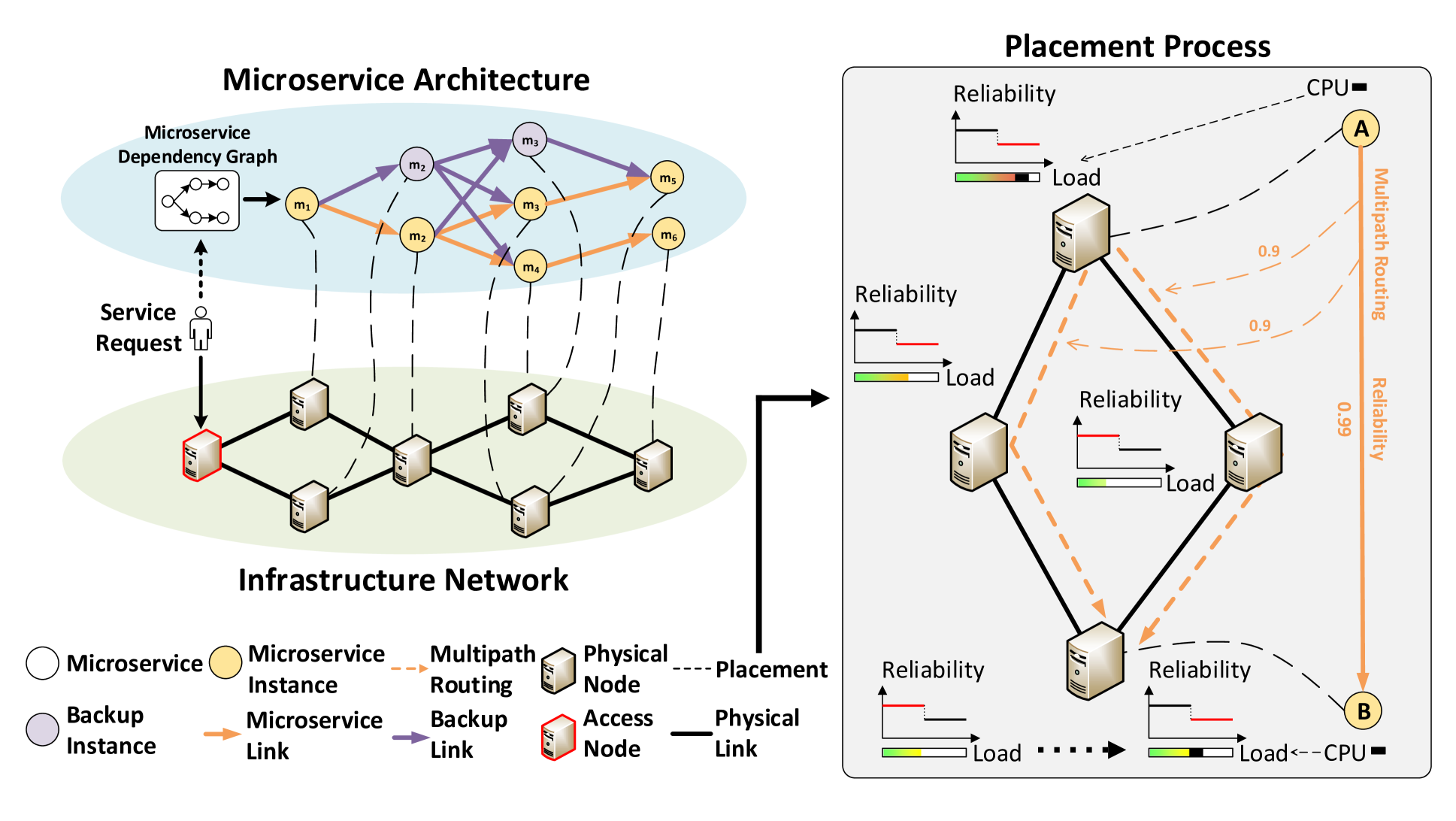
Network-Aware Reliability Modeling and Optimization for Microservice Placement
Fangyu Zhang, Yuang Chen, Hancheng Lu, Yongsheng Huang

0
0
Optimizing microservice placement to enhance the reliability of services is crucial for improving the service level of microservice architecture-based mobile networks and Internet of Things (IoT) networks. Despite extensive research on service reliability, the impact of network load and routing on service reliability remains understudied, leading to suboptimal models and unsatisfactory performance. To address this issue, we propose a novel network-aware service reliability model that effectively captures the correlation between network state changes and reliability. Based on this model, we formulate the microservice placement problem as an integer nonlinear programming problem, aiming to maximize service reliability. Subsequently, a service reliability-aware placement (SRP) algorithm is proposed to solve the problem efficiently. To reduce bandwidth consumption, we further discuss the microservice placement problem with the shared backup path mechanism and propose a placement algorithm based on the SRP algorithm using shared path reliability calculation, known as the SRP-S algorithm. Extensive simulations demonstrate that the SRP algorithm reduces service failures by up to 29% compared to the benchmark algorithms. By introducing the shared backup path mechanism, the SRP-S algorithm reduces bandwidth consumption by up to 62% compared to the SRP algorithm with the fully protected path mechanism. It also reduces service failures by up to 21% compared to the SRP algorithm with the shared backup mechanism.
5/29/2024