When `Computing follows Vehicles': Decentralized Mobility-Aware Resource Allocation in the Edge-to-Cloud Continuum
2404.13179

0
0
Abstract
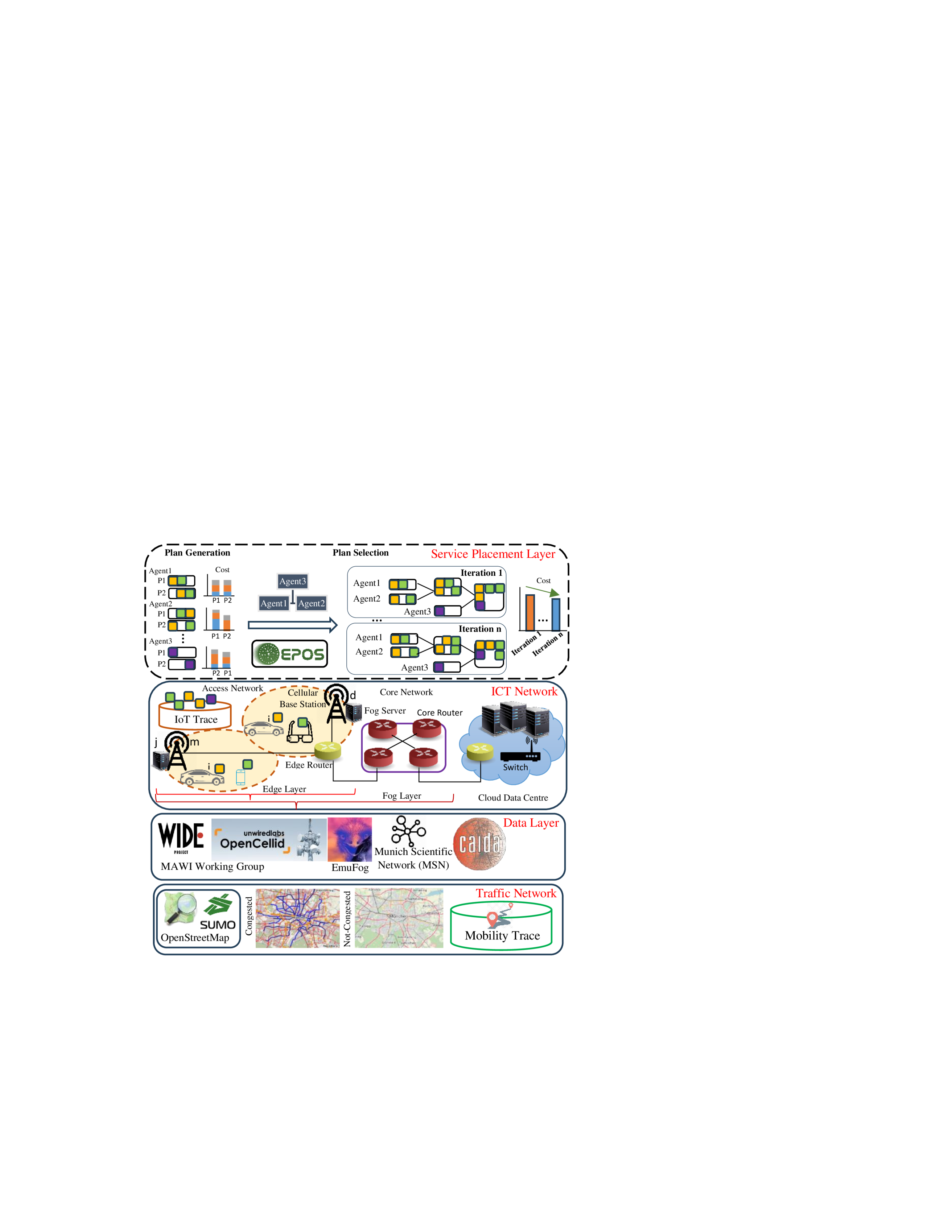
The transformation of smart mobility is unprecedented--Autonomous, shared and electric connected vehicles, along with the urgent need to meet ambitious net-zero targets by shifting to low-carbon transport modalities result in new traffic patterns and requirements for real-time computation at large-scale, for instance, augmented reality applications. The cloud computing paradigm can neither respond to such low-latency requirements nor adapt resource allocation to such dynamic spatio-temporal service requests. This paper addresses this grand challenge by introducing a novel decentralized optimization framework for mobility-aware edge-to-cloud resource allocation, service offloading, provisioning and load-balancing. In contrast to related work, this framework comes with superior efficiency and cost-effectiveness under evaluation in real-world traffic settings and mobility datasets. This breakthrough capability of 'computing follows vehicles' proves able to reduce utilization variance by more than 40 times, while preventing service deadline violations by 14%-34%.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores a decentralized approach to resource allocation in the edge-to-cloud computing continuum, with a focus on supporting smart mobility applications.
- The proposed system aims to dynamically allocate computing resources based on the mobility patterns of vehicles, ensuring efficient utilization of the available infrastructure.
- The research leverages multi-agent systems and distributed optimization techniques to enable autonomous decision-making and coordination among the various computing nodes.
Plain English Explanation
As the number of connected vehicles and smart mobility applications continues to grow, the demand for computing resources to process all the data generated by these vehicles is also increasing. Traditional cloud-based computing may not be able to handle this influx of data and the need for real-time processing.
The researchers in this paper propose a decentralized approach to managing computing resources, where the resources are distributed across the "edge" (closer to the vehicles) and the "cloud" (remote data centers). By understanding the movement and location of the vehicles, the system can dynamically allocate computing power to where it's needed most, rather than relying on a central authority to make all the decisions.
This is achieved through the use of multi-agent systems, where each computing node (whether at the edge or in the cloud) acts as an autonomous agent, making decisions on how to best utilize the resources it has available. These agents communicate and coordinate with each other to ensure that the overall system is operating efficiently and meeting the needs of the vehicles.
The key advantage of this approach is that it can adapt more quickly to changing conditions, such as vehicles entering or leaving a particular area, or spikes in data processing demands. By distributing the decision-making, the system becomes more resilient and flexible, which is important for supporting mission-critical smart mobility applications.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a decentralized mobility-aware resource allocation framework for the edge-to-cloud computing continuum. The system is designed to dynamically allocate computing resources based on the mobility patterns of vehicles, aiming to optimize resource utilization and meet the demands of smart mobility applications.
The researchers leverage multi-agent systems and distributed optimization techniques to enable autonomous decision-making and coordination among the various computing nodes, which can be located at the edge (e.g., roadside units) or in the cloud (remote data centers).
Each computing node acts as an agent, making decisions on how to best utilize the resources it has available. The agents communicate and coordinate with each other to ensure that the overall system is operating efficiently and meeting the needs of the vehicles. This decentralized approach allows the system to adapt more quickly to changing conditions, such as vehicles entering or leaving a particular area, or spikes in data processing demands.
The researchers evaluate their proposed framework through simulation experiments, comparing its performance to centralized and static resource allocation approaches. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the decentralized, mobility-aware resource allocation in improving resource utilization and supporting the quality of service requirements of smart mobility applications.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a well-designed and technically sound approach to addressing the challenges of resource allocation in the edge-to-cloud continuum for smart mobility applications. The use of multi-agent systems and distributed optimization techniques is a promising strategy to enable autonomous and adaptive decision-making.
However, the authors acknowledge that the proposed framework relies on accurate predictions of vehicle mobility patterns, which can be challenging in practice. Factors such as unexpected traffic conditions, driver behavior, and other environmental factors may introduce uncertainties that could impact the system's performance.
Additionally, the paper does not delve into the potential security and privacy concerns that may arise from the decentralized nature of the system. As computing resources are distributed across multiple nodes, there may be increased vulnerabilities that need to be addressed.
Further research could explore ways to make the system more robust to uncertainties, as well as investigate the security and privacy implications of the decentralized architecture. Experimental validation with real-world deployments would also help to assess the practical feasibility and scalability of the proposed framework.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel approach to resource allocation in the edge-to-cloud continuum, leveraging decentralized decision-making and mobility-awareness to support smart mobility applications. By empowering individual computing nodes to autonomously manage resources based on vehicle movement patterns, the system can adapt more quickly to changing conditions and optimize resource utilization.
The research highlights the potential benefits of incorporating distributed intelligence and contextual awareness into the design of edge-to-cloud computing systems, paving the way for more efficient and resilient infrastructure to meet the growing demands of emerging smart mobility technologies. As the field of edge computing continues to evolve, this work provides valuable insights and a promising direction for future research and development.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

New!Koopman based trajectory model and computation offloading for high mobility paradigm in ISAC enabled IoT system
Minh-Tuan Tran

0
0
User experience on mobile devices is constrained by limited battery capacity and processing power, but 6G technology advancements are diving rapidly into mobile technical evolution. Mobile edge computing (MEC) offers a solution, offloading computationally intensive tasks to edge cloud servers, reducing battery drain compared to local processing. The upcoming integrated sensing and communication in mobile communication may improve the trajectory prediction and processing delays. This study proposes a greedy resource allocation optimization strategy for multi-user networks to minimize aggregate energy usage. Numerical results show potential improvement at 33% for every 1000 iteration. Addressing prediction model division and velocity accuracy issues is crucial for better results. A plan for further improvement and achieving objectives is outlined for the upcoming work phase.
7/1/2024
Multi-Objective Offloading Optimization in MEC and Vehicular-Fog Systems: A Distributed-TD3 Approach
Frezer Guteta Wakgra, Binayak Kar, Seifu Birhanu Tadele, Shan-Hsiang Shen, Asif Uddin Khan

0
0
The emergence of 5G networks has enabled the deployment of a two-tier edge and vehicular-fog network. It comprises Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) and Vehicular-Fogs (VFs), strategically positioned closer to Internet of Things (IoT) devices, reducing propagation latency compared to cloud-based solutions and ensuring satisfactory quality of service (QoS). However, during high-traffic events like concerts or athletic contests, MEC sites may face congestion and become overloaded. Utilizing offloading techniques, we can transfer computationally intensive tasks from resource-constrained devices to those with sufficient capacity, for accelerating tasks and extending device battery life. In this research, we consider offloading within a two-tier MEC and VF architecture, involving offloading from MEC to MEC and from MEC to VF. The primary objective is to minimize the average system cost, considering both latency and energy consumption. To achieve this goal, we formulate a multi-objective optimization problem aimed at minimizing latency and energy while considering given resource constraints. To facilitate decision-making for nearly optimal computational offloading, we design an equivalent reinforcement learning environment that accurately represents the network architecture and the formulated problem. To accomplish this, we propose a Distributed-TD3 (DTD3) approach, which builds on the TD3 algorithm. Extensive simulations, demonstrate that our strategy achieves faster convergence and higher efficiency compared to other benchmark solutions.
4/22/2024
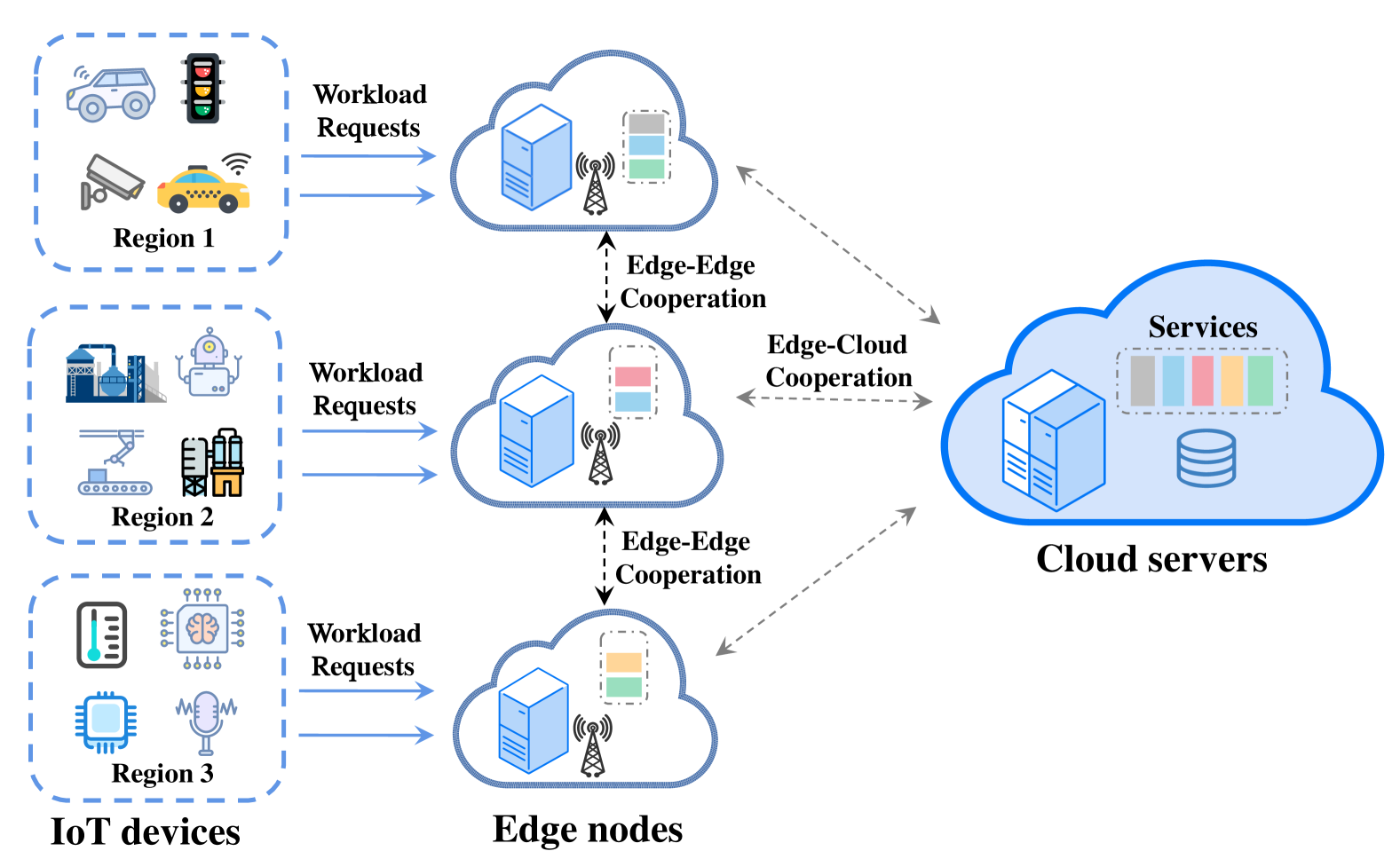
Collaborative Resource Management and Workloads Scheduling in Cloud-Assisted Mobile Edge Computing across Timescales
Lujie Tang, Minxian Xu, Chengzhong Xu, Kejiang Ye

0
0
Due to the limited resource capacity of edge servers and the high purchase costs of edge resources, service providers are facing the new challenge of how to take full advantage of the constrained edge resources for Internet of Things (IoT) service hosting and task scheduling to maximize system performance. In this paper, we study the joint optimization problem on service placement, resource provisioning, and workloads scheduling under resource and budget constraints, which is formulated as a mixed integer non-linear programming problem. Given that the frequent service placement and resource provisioning will significantly increase system configuration costs and instability, we propose a two-timescale framework for resource management and workloads scheduling, named RMWS. RMWS consists of a Gibbs sampling algorithm and an alternating minimization algorithm to determine the service placement and resource provisioning on large timescales. And a sub-gradient descent method has been designed to solve the workload scheduling challenge on small timescales.We conduct comprehensive experiments under different parameter settings. The RMWS consistently ensures a minimum 10% performance enhancement compared to other algorithms, showcasing its superiority. Theoretical proofs are also provided accordingly.
6/3/2024

Computation Offloading for Multi-server Multi-access Edge Vehicular Networks: A DDQN-based Method
Siyu Wang, Bo Yang, Zhiwen Yu, Xuelin Cao, Yan Zhang, Chau Yuen

0
0
In this paper, we investigate a multi-user offloading problem in the overlapping domain of a multi-server mobile edge computing system. We divide the original problem into two stages: the offloading decision making stage and the request scheduling stage. To prevent the terminal from going out of service area during offloading, we consider the mobility parameter of the terminal according to the human behaviour model when making the offloading decision, and then introduce a server evaluation mechanism based on both the mobility parameter and the server load to select the optimal offloading server. In order to fully utilise the server resources, we design a double deep Q-network (DDQN)-based reward evaluation algorithm that considers the priority of tasks when scheduling offload requests. Finally, numerical simulations are conducted to verify that our proposed method outperforms traditional mathematical computation methods as well as the DQN algorithm.
4/12/2024