360Loc: A Dataset and Benchmark for Omnidirectional Visual Localization with Cross-device Queries
2311.17389

0
0

Abstract
Portable 360$^circ$ cameras are becoming a cheap and efficient tool to establish large visual databases. By capturing omnidirectional views of a scene, these cameras could expedite building environment models that are essential for visual localization. However, such an advantage is often overlooked due to the lack of valuable datasets. This paper introduces a new benchmark dataset, 360Loc, composed of 360$^circ$ images with ground truth poses for visual localization. We present a practical implementation of 360$^circ$ mapping combining 360$^circ$ images with lidar data to generate the ground truth 6DoF poses. 360Loc is the first dataset and benchmark that explores the challenge of cross-device visual positioning, involving 360$^circ$ reference frames, and query frames from pinhole, ultra-wide FoV fisheye, and 360$^circ$ cameras. We propose a virtual camera approach to generate lower-FoV query frames from 360$^circ$ images, which ensures a fair comparison of performance among different query types in visual localization tasks. We also extend this virtual camera approach to feature matching-based and pose regression-based methods to alleviate the performance loss caused by the cross-device domain gap, and evaluate its effectiveness against state-of-the-art baselines. We demonstrate that omnidirectional visual localization is more robust in challenging large-scale scenes with symmetries and repetitive structures. These results provide new insights into 360-camera mapping and omnidirectional visual localization with cross-device queries.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper introduces 360Loc, a new dataset and benchmark for omnidirectional visual localization with cross-device queries.
- The dataset includes 360-degree images captured from multiple devices and locations, along with corresponding camera poses and other metadata.
- The benchmark evaluates the ability of visual localization algorithms to accurately estimate the camera pose from a query image, even when the query and reference images were captured on different devices.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers behind this paper have created a new dataset called 360Loc to help improve visual localization technology. Visual localization is the process of determining the position and orientation of a camera based on the images it captures. This is an important capability for applications like augmented reality, robotics, and autonomous vehicles.
The 360Loc dataset contains 360-degree panoramic images taken from various locations using different camera devices. These images are paired with information about the camera's position and orientation when each photo was taken. The researchers have designed a benchmark to evaluate how well visual localization algorithms can estimate the camera pose from a query image, even if that image was captured on a different device than the reference images in the dataset.
This benchmark is valuable because it mimics real-world scenarios where users might want to localize themselves using their own camera-equipped devices, rather than specialized equipment. The 360-degree panoramic views also provide a more comprehensive representation of the surroundings compared to traditional perspective images.
By providing this dataset and benchmark, the researchers hope to spur further advancements in omnidirectional visual localization that can work robustly across different devices and capture conditions. This could lead to improved navigation, mapping, and situational awareness for a variety of applications.
Technical Explanation
The 360Loc dataset contains 360-degree panoramic images captured from 1,128 distinct locations using a variety of consumer cameras and smartphones. Each image is paired with the corresponding 6-DoF camera pose (position and orientation) obtained from a high-precision inertial measurement unit (IMU) and global navigation satellite system (GNSS).
The researchers designed a benchmark task to evaluate the cross-device visual localization performance of algorithms on the 360Loc dataset. In this task, the algorithm is given a query image captured on an unknown device and must estimate the 6-DoF camera pose of that image based on the reference panoramic images and poses in the dataset. This simulates real-world scenarios where users would localize themselves using their personal devices rather than specialized equipment.
The benchmark includes two evaluation protocols: device-specific and device-agnostic. In the device-specific protocol, the algorithm is trained and tested on data from the same device. In the device-agnostic protocol, the algorithm must generalize to localize images from unseen devices during testing.
The researchers evaluated several state-of-the-art visual localization methods on the 360Loc benchmark, including [internal link: https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/fully-geometric-panoramic-localization] and [internal link: https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/omnicolor-global-camera-pose-optimization-approach-lidar]. They found that while the methods performed well on the device-specific protocol, they struggled with the more challenging device-agnostic protocol, highlighting the need for further research in cross-device visual localization.
Critical Analysis
The 360Loc dataset and benchmark represent an important step forward in evaluating the real-world performance of visual localization algorithms. By incorporating 360-degree panoramic images and cross-device queries, the researchers have created a more realistic and challenging evaluation scenario compared to traditional visual localization benchmarks.
However, the paper does not address several potential limitations of the dataset and benchmark. For example, the dataset only includes images from a relatively small number of locations, which may limit the diversity of environments represented. Additionally, the benchmark focuses solely on estimating camera pose, and does not evaluate other important aspects of visual localization such as semantic understanding or scene recognition.
Further research is also needed to develop more robust and generalizable visual localization algorithms that can handle the challenges posed by the 360Loc benchmark, such as variations in camera hardware, lighting conditions, and scene content. [Internal link: https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/360x-panoptic-multi-modal-scene-understanding-dataset] and [Internal link: https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/autoregressive-omni-aware-outpainting-open-vocabulary-360] are examples of related work that could provide insights for improving cross-device visual localization performance.
Conclusion
The 360Loc dataset and benchmark introduced in this paper represent an important contribution to the field of visual localization. By incorporating 360-degree panoramic images and cross-device queries, the researchers have created a more realistic and challenging evaluation scenario that better reflects real-world conditions.
The benchmark results highlight the need for further advancements in visual localization algorithms that can robustly handle variations in camera hardware, lighting, and scene content. Addressing these challenges could lead to significant improvements in applications such as augmented reality, robotics, and autonomous vehicles, where accurate and reliable visual localization is crucial.
Overall, the 360Loc dataset and benchmark provide a valuable new tool for the research community to drive progress in this important area of computer vision and spatial understanding.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

360 in the Wild: Dataset for Depth Prediction and View Synthesis
Kibaek Park, Francois Rameau, Jaesik Park, In So Kweon

0
0
The large abundance of perspective camera datasets facilitated the emergence of novel learning-based strategies for various tasks, such as camera localization, single image depth estimation, or view synthesis. However, panoramic or omnidirectional image datasets, including essential information, such as pose and depth, are mostly made with synthetic scenes. In this work, we introduce a large scale 360$^{circ}$ videos dataset in the wild. This dataset has been carefully scraped from the Internet and has been captured from various locations worldwide. Hence, this dataset exhibits very diversified environments (e.g., indoor and outdoor) and contexts (e.g., with and without moving objects). Each of the 25K images constituting our dataset is provided with its respective camera's pose and depth map. We illustrate the relevance of our dataset for two main tasks, namely, single image depth estimation and view synthesis.
6/28/2024

360VOTS: Visual Object Tracking and Segmentation in Omnidirectional Videos
Yinzhe Xu, Huajian Huang, Yingshu Chen, Sai-Kit Yeung

0
0
Visual object tracking and segmentation in omnidirectional videos are challenging due to the wide field-of-view and large spherical distortion brought by 360{deg} images. To alleviate these problems, we introduce a novel representation, extended bounding field-of-view (eBFoV), for target localization and use it as the foundation of a general 360 tracking framework which is applicable for both omnidirectional visual object tracking and segmentation tasks. Building upon our previous work on omnidirectional visual object tracking (360VOT), we propose a comprehensive dataset and benchmark that incorporates a new component called omnidirectional video object segmentation (360VOS). The 360VOS dataset includes 290 sequences accompanied by dense pixel-wise masks and covers a broader range of target categories. To support both the development and evaluation of algorithms in this domain, we divide the dataset into a training subset with 170 sequences and a testing subset with 120 sequences. Furthermore, we tailor evaluation metrics for both omnidirectional tracking and segmentation to ensure rigorous assessment. Through extensive experiments, we benchmark state-of-the-art approaches and demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed 360 tracking framework and training dataset. Homepage: https://360vots.hkustvgd.com/
4/23/2024

360+x: A Panoptic Multi-modal Scene Understanding Dataset
Hao Chen, Yuqi Hou, Chenyuan Qu, Irene Testini, Xiaohan Hong, Jianbo Jiao

0
0
Human perception of the world is shaped by a multitude of viewpoints and modalities. While many existing datasets focus on scene understanding from a certain perspective (e.g. egocentric or third-person views), our dataset offers a panoptic perspective (i.e. multiple viewpoints with multiple data modalities). Specifically, we encapsulate third-person panoramic and front views, as well as egocentric monocular/binocular views with rich modalities including video, multi-channel audio, directional binaural delay, location data and textual scene descriptions within each scene captured, presenting comprehensive observation of the world. Figure 1 offers a glimpse of all 28 scene categories of our 360+x dataset. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first database that covers multiple viewpoints with multiple data modalities to mimic how daily information is accessed in the real world. Through our benchmark analysis, we presented 5 different scene understanding tasks on the proposed 360+x dataset to evaluate the impact and benefit of each data modality and perspective in panoptic scene understanding. We hope this unique dataset could broaden the scope of comprehensive scene understanding and encourage the community to approach these problems from more diverse perspectives.
4/9/2024
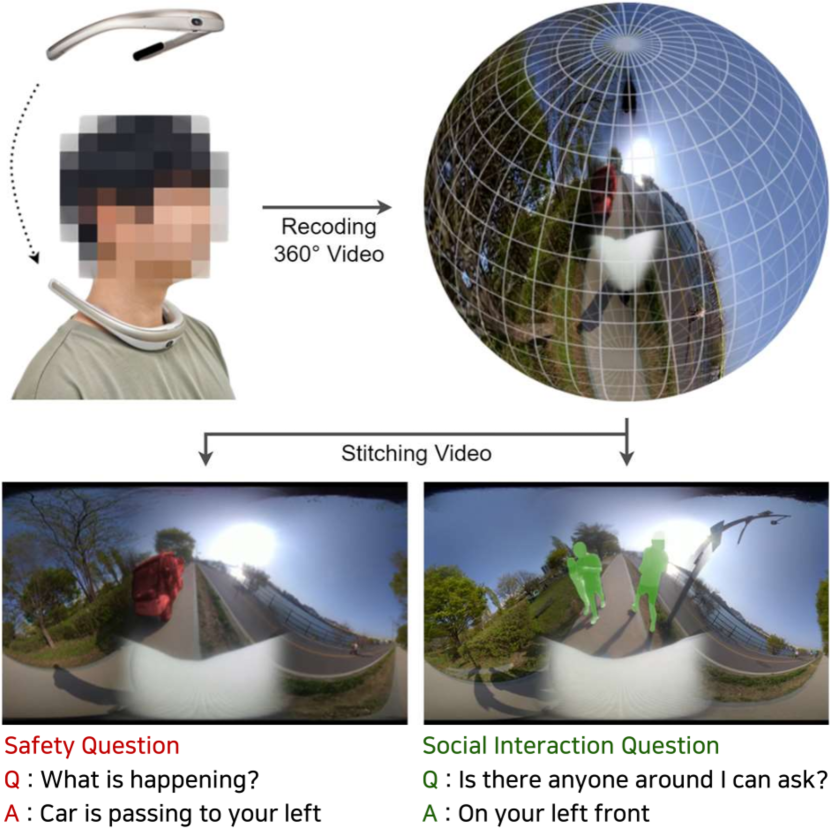
Video Question Answering for People with Visual Impairments Using an Egocentric 360-Degree Camera
Inpyo Song, Minjun Joo, Joonhyung Kwon, Jangwon Lee

0
0
This paper addresses the daily challenges encountered by visually impaired individuals, such as limited access to information, navigation difficulties, and barriers to social interaction. To alleviate these challenges, we introduce a novel visual question answering dataset. Our dataset offers two significant advancements over previous datasets: Firstly, it features videos captured using a 360-degree egocentric wearable camera, enabling observation of the entire surroundings, departing from the static image-centric nature of prior datasets. Secondly, unlike datasets centered on singular challenges, ours addresses multiple real-life obstacles simultaneously through an innovative visual-question answering framework. We validate our dataset using various state-of-the-art VideoQA methods and diverse metrics. Results indicate that while progress has been made, satisfactory performance levels for AI-powered assistive services remain elusive for visually impaired individuals. Additionally, our evaluation highlights the distinctive features of the proposed dataset, featuring ego-motion in videos captured via 360-degree cameras across varied scenarios.
5/31/2024