Video Question Answering for People with Visual Impairments Using an Egocentric 360-Degree Camera
2405.19794

0
0
Abstract
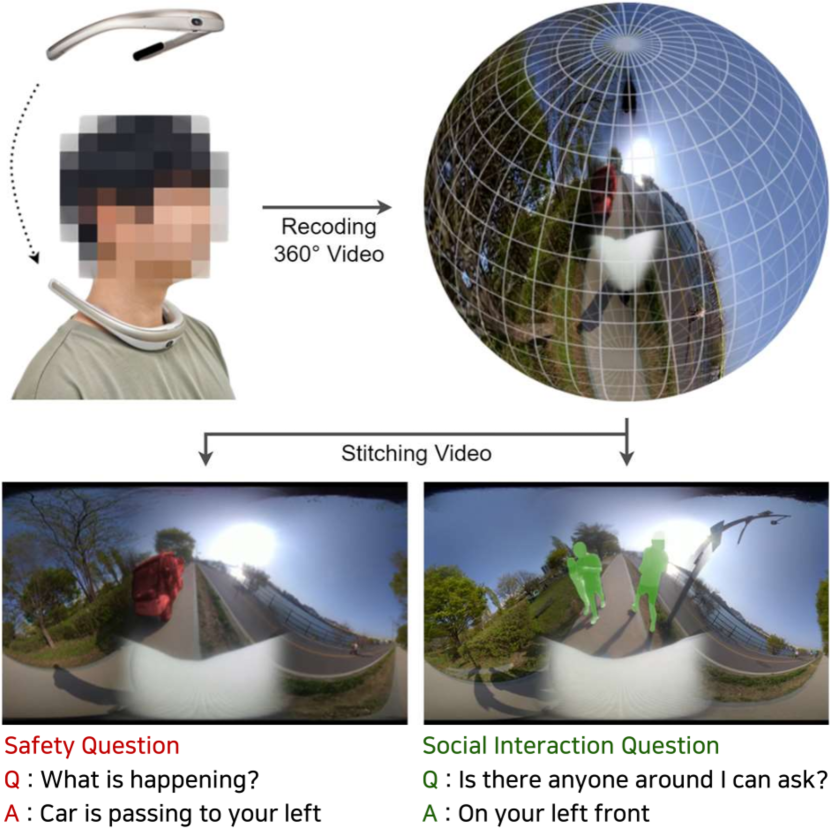
This paper addresses the daily challenges encountered by visually impaired individuals, such as limited access to information, navigation difficulties, and barriers to social interaction. To alleviate these challenges, we introduce a novel visual question answering dataset. Our dataset offers two significant advancements over previous datasets: Firstly, it features videos captured using a 360-degree egocentric wearable camera, enabling observation of the entire surroundings, departing from the static image-centric nature of prior datasets. Secondly, unlike datasets centered on singular challenges, ours addresses multiple real-life obstacles simultaneously through an innovative visual-question answering framework. We validate our dataset using various state-of-the-art VideoQA methods and diverse metrics. Results indicate that while progress has been made, satisfactory performance levels for AI-powered assistive services remain elusive for visually impaired individuals. Additionally, our evaluation highlights the distinctive features of the proposed dataset, featuring ego-motion in videos captured via 360-degree cameras across varied scenarios.
Create account to get full access
Overview
• This paper presents a video question answering system designed for people with visual impairments, using an egocentric 360-degree camera.
• The system aims to provide visually impaired users with the ability to independently understand and interact with their surrounding environment by answering questions about the video footage captured by the camera.
Plain English Explanation
• The researchers developed a technology that can help people who are blind or have low vision better understand their surroundings.
• They used a special 360-degree camera that can capture a full view of the environment from the user's perspective.
• The camera footage is then analyzed by an artificial intelligence (AI) system that can answer questions the user asks about what's happening in the video.
• This allows visually impaired individuals to get information about their environment and interact with it more independently, without relying as much on sighted assistance.
Technical Explanation
• The paper introduces a video question answering (VQA) system that leverages an egocentric 360-degree camera to assist people with visual impairments.
• The system comprises several key components:
- Retrieval-Augmented Egocentric Video Captioning: This component generates textual descriptions of the video content.
- 360-Degree Localization: This component determines the user's orientation and location within the 360-degree video.
- Multimodal Question Answering: This component uses the video descriptions and user location to answer questions about the environment.
• The system is evaluated on a new dataset of 360-degree videos and questions specifically designed for visually impaired users, called 360X.
• The researchers also propose a map-based modular approach to enable zero-shot generalization, allowing the system to answer questions about unseen environments.
Critical Analysis
• The paper highlights the importance of developing assistive technologies to improve the independence and quality of life for people with visual impairments.
• The use of an egocentric 360-degree camera is a novel approach that can capture a more comprehensive view of the user's surroundings compared to traditional camera setups.
• The modular design of the system allows for flexibility and potential improvements to individual components, such as the video captioning or question answering modules.
• However, the paper acknowledges the challenge of building a system that can accurately understand and interpret the complex and dynamic nature of real-world environments.
• Further research is needed to improve the system's robustness, generalization capabilities, and to address potential biases in the underlying AI models.
Conclusion
• This paper presents a promising approach to video question answering for people with visual impairments, leveraging an egocentric 360-degree camera and a modular AI system.
• The research highlights the potential of assistive technologies to enhance the independence and quality of life for individuals with visual disabilities, and it lays the groundwork for future advancements in this important field.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Identification of Conversation Partners from Egocentric Video
Tobias Dorszewski, S{o}ren A. Fuglsang, Jens Hjortkj{ae}r

0
0
Communicating in noisy, multi-talker environments is challenging, especially for people with hearing impairments. Egocentric video data can potentially be used to identify a user's conversation partners, which could be used to inform selective acoustic amplification of relevant speakers. Recent introduction of datasets and tasks in computer vision enable progress towards analyzing social interactions from an egocentric perspective. Building on this, we focus on the task of identifying conversation partners from egocentric video and describe a suitable dataset. Our dataset comprises 69 hours of egocentric video of diverse multi-conversation scenarios where each individual was assigned one or more conversation partners, providing the labels for our computer vision task. This dataset enables the development and assessment of algorithms for identifying conversation partners and evaluating related approaches. Here, we describe the dataset alongside initial baseline results of this ongoing work, aiming to contribute to the exciting advancements in egocentric video analysis for social settings.
6/13/2024

Retrieval-Augmented Egocentric Video Captioning
Jilan Xu, Yifei Huang, Junlin Hou, Guo Chen, Yuejie Zhang, Rui Feng, Weidi Xie

0
0
Understanding human actions from videos of first-person view poses significant challenges. Most prior approaches explore representation learning on egocentric videos only, while overlooking the potential benefit of exploiting existing large-scale third-person videos. In this paper, (1) we develop EgoInstructor, a retrieval-augmented multimodal captioning model that automatically retrieves semantically relevant third-person instructional videos to enhance the video captioning of egocentric videos. (2) For training the cross-view retrieval module, we devise an automatic pipeline to discover ego-exo video pairs from distinct large-scale egocentric and exocentric datasets. (3) We train the cross-view retrieval module with a novel EgoExoNCE loss that pulls egocentric and exocentric video features closer by aligning them to shared text features that describe similar actions. (4) Through extensive experiments, our cross-view retrieval module demonstrates superior performance across seven benchmarks. Regarding egocentric video captioning, EgoInstructor exhibits significant improvements by leveraging third-person videos as references. Project page is available at: https://jazzcharles.github.io/Egoinstructor/
6/21/2024

A Human-Annotated Video Dataset for Training and Evaluation of 360-Degree Video Summarization Methods
Ioannis Kontostathis, Evlampios Apostolidis, Vasileios Mezaris

0
0
In this paper we introduce a new dataset for 360-degree video summarization: the transformation of 360-degree video content to concise 2D-video summaries that can be consumed via traditional devices, such as TV sets and smartphones. The dataset includes ground-truth human-generated summaries, that can be used for training and objectively evaluating 360-degree video summarization methods. Using this dataset, we train and assess two state-of-the-art summarization methods that were originally proposed for 2D-video summarization, to serve as a baseline for future comparisons with summarization methods that are specifically tailored to 360-degree video. Finally, we present an interactive tool that was developed to facilitate the data annotation process and can assist other annotation activities that rely on video fragment selection.
6/6/2024

360Loc: A Dataset and Benchmark for Omnidirectional Visual Localization with Cross-device Queries
Huajian Huang, Changkun Liu, Yipeng Zhu, Hui Cheng, Tristan Braud, Sai-Kit Yeung

0
0
Portable 360$^circ$ cameras are becoming a cheap and efficient tool to establish large visual databases. By capturing omnidirectional views of a scene, these cameras could expedite building environment models that are essential for visual localization. However, such an advantage is often overlooked due to the lack of valuable datasets. This paper introduces a new benchmark dataset, 360Loc, composed of 360$^circ$ images with ground truth poses for visual localization. We present a practical implementation of 360$^circ$ mapping combining 360$^circ$ images with lidar data to generate the ground truth 6DoF poses. 360Loc is the first dataset and benchmark that explores the challenge of cross-device visual positioning, involving 360$^circ$ reference frames, and query frames from pinhole, ultra-wide FoV fisheye, and 360$^circ$ cameras. We propose a virtual camera approach to generate lower-FoV query frames from 360$^circ$ images, which ensures a fair comparison of performance among different query types in visual localization tasks. We also extend this virtual camera approach to feature matching-based and pose regression-based methods to alleviate the performance loss caused by the cross-device domain gap, and evaluate its effectiveness against state-of-the-art baselines. We demonstrate that omnidirectional visual localization is more robust in challenging large-scale scenes with symmetries and repetitive structures. These results provide new insights into 360-camera mapping and omnidirectional visual localization with cross-device queries.
6/3/2024