3D Gaussian as a New Era: A Survey

0
👨🏫
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a comprehensive survey of recent advancements in the field of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS), a technique for explicit scene representation and novel view synthesis without relying on neural networks like Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF).
- 3D Gaussian Splatting has found applications in various domains, including robotics, urban mapping, autonomous navigation, and virtual/augmented reality.
- The paper aims to introduce new researchers to 3D Gaussian Splatting, provide a valuable reference for seminal works in the field, and inspire future research directions.
Plain English Explanation
3D Gaussian Splatting is a powerful technique in computer graphics that allows for the creation of detailed 3D scenes without the need for complex neural networks. Unlike neural-network-based approaches, 3D Gaussian Splatting provides an explicit representation of the scene, making it useful in applications where precise control and understanding of the 3D environment are essential, such as in robotics, autonomous vehicles, and virtual/augmented reality.
This paper reviews the latest advancements in 3D Gaussian Splatting, organizing them into different categories based on their characteristics and applications. The goal is to help new researchers understand this technology and inspire future work in the field. The paper covers the theoretical foundations of 3D Gaussian Splatting, as well as practical examples of how it is being used in various industries.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by introducing 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) as a significant advancement in computer graphics, offering an explicit scene representation and novel view synthesis without relying on neural networks like Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF).
The authors then organize the survey into taxonomies based on the characteristics and applications of 3D Gaussian Splatting, providing an introduction to the theoretical underpinnings of the technique. This includes discussions of 3D Half-Gaussian Splatting (3D-HGS) and RADE-GS, which are variations of the core 3D Gaussian Splatting approach.
The survey covers a wide range of applications for 3D Gaussian Splatting, highlighting its versatility in domains such as robotics, urban mapping, autonomous navigation, and virtual/augmented reality. The authors also discuss the advantages of 3D Gaussian Splatting over neural network-based methods, such as its explicit scene representation and improved performance in certain tasks.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements in 3D Gaussian Splatting, but it does not delve deeply into the technical details or limitations of the various approaches discussed. While the paper highlights the advantages of 3D Gaussian Splatting over neural network-based methods, it would be helpful to have a more nuanced discussion of the trade-offs and potential drawbacks of this technique.
Additionally, the paper could have explored the challenges and open research questions in the field of 3D Gaussian Splatting, such as the computational complexity of the algorithms, the handling of occlusions, and the integration of 3D Gaussian Splatting with other computer vision and graphics techniques.
Conclusion
This survey paper provides a valuable introduction to the field of 3D Gaussian Splatting, a powerful technique for explicit scene representation and novel view synthesis. By organizing the research into taxonomies and highlighting the diverse applications of 3D Gaussian Splatting, the authors have created a useful resource for both new and experienced researchers in the field of computer graphics.
The paper's emphasis on the advantages of 3D Gaussian Splatting over neural network-based methods suggests that this technique could play a significant role in the future development of 3D modeling, visualization, and interactive applications. As the field continues to evolve, further research and refinement of 3D Gaussian Splatting may lead to even more exciting advancements in the world of computer graphics.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
👨🏫

0
3D Gaussian as a New Era: A Survey
Ben Fei, Jingyi Xu, Rui Zhang, Qingyuan Zhou, Weidong Yang, Ying He
3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) has emerged as a significant advancement in the field of Computer Graphics, offering explicit scene representation and novel view synthesis without the reliance on neural networks, such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF). This technique has found diverse applications in areas such as robotics, urban mapping, autonomous navigation, and virtual reality/augmented reality, just name a few. Given the growing popularity and expanding research in 3D Gaussian Splatting, this paper presents a comprehensive survey of relevant papers from the past year. We organize the survey into taxonomies based on characteristics and applications, providing an introduction to the theoretical underpinnings of 3D Gaussian Splatting. Our goal through this survey is to acquaint new researchers with 3D Gaussian Splatting, serve as a valuable reference for seminal works in the field, and inspire future research directions, as discussed in our concluding section.
Read more7/11/2024

0
Recent Advances in 3D Gaussian Splatting
Tong Wu, Yu-Jie Yuan, Ling-Xiao Zhang, Jie Yang, Yan-Pei Cao, Ling-Qi Yan, Lin Gao
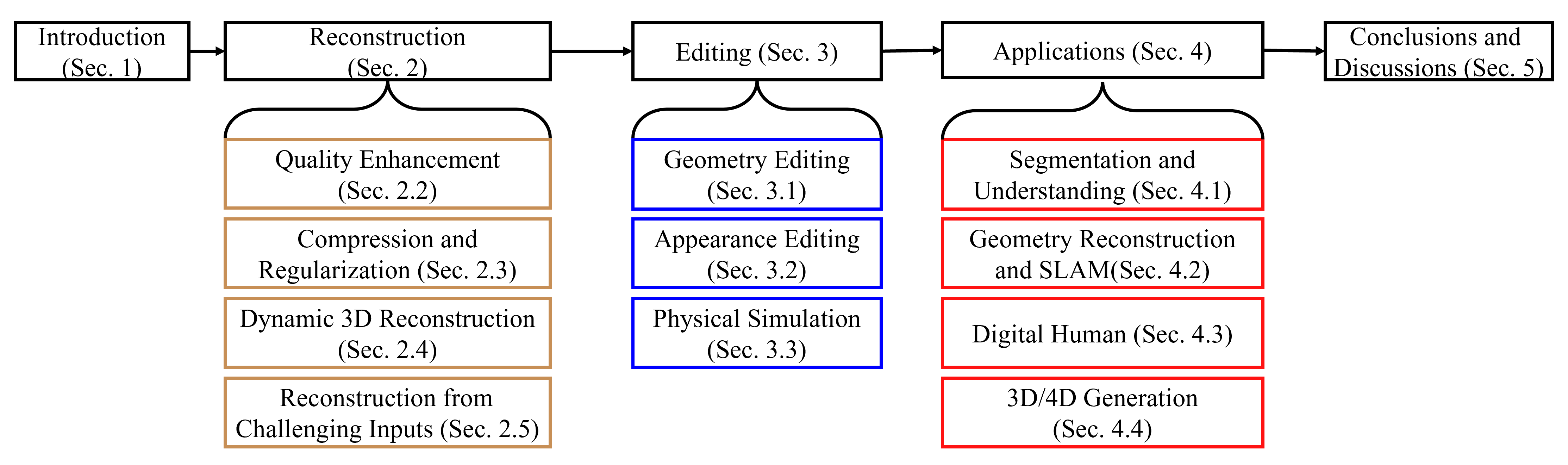
The emergence of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has greatly accelerated the rendering speed of novel view synthesis. Unlike neural implicit representations like Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) that represent a 3D scene with position and viewpoint-conditioned neural networks, 3D Gaussian Splatting utilizes a set of Gaussian ellipsoids to model the scene so that efficient rendering can be accomplished by rasterizing Gaussian ellipsoids into images. Apart from the fast rendering speed, the explicit representation of 3D Gaussian Splatting facilitates editing tasks like dynamic reconstruction, geometry editing, and physical simulation. Considering the rapid change and growing number of works in this field, we present a literature review of recent 3D Gaussian Splatting methods, which can be roughly classified into 3D reconstruction, 3D editing, and other downstream applications by functionality. Traditional point-based rendering methods and the rendering formulation of 3D Gaussian Splatting are also illustrated for a better understanding of this technique. This survey aims to help beginners get into this field quickly and provide experienced researchers with a comprehensive overview, which can stimulate the future development of the 3D Gaussian Splatting representation.
Read more4/16/2024
↗️

0
A Survey on 3D Gaussian Splatting
Guikun Chen, Wenguan Wang
3D Gaussian splatting (GS) has recently emerged as a transformative technique in the realm of explicit radiance field and computer graphics. This innovative approach, characterized by the utilization of millions of learnable 3D Gaussians, represents a significant departure from mainstream neural radiance field approaches, which predominantly use implicit, coordinate-based models to map spatial coordinates to pixel values. 3D GS, with its explicit scene representation and differentiable rendering algorithm, not only promises real-time rendering capability but also introduces unprecedented levels of editability. This positions 3D GS as a potential game-changer for the next generation of 3D reconstruction and representation. In the present paper, we provide the first systematic overview of the recent developments and critical contributions in the domain of 3D GS. We begin with a detailed exploration of the underlying principles and the driving forces behind the emergence of 3D GS, laying the groundwork for understanding its significance. A focal point of our discussion is the practical applicability of 3D GS. By enabling unprecedented rendering speed, 3D GS opens up a plethora of applications, ranging from virtual reality to interactive media and beyond. This is complemented by a comparative analysis of leading 3D GS models, evaluated across various benchmark tasks to highlight their performance and practical utility. The survey concludes by identifying current challenges and suggesting potential avenues for future research in this domain. Through this survey, we aim to provide a valuable resource for both newcomers and seasoned researchers, fostering further exploration and advancement in applicable and explicit radiance field representation.
Read more7/23/2024


0
3D Gaussian Splatting: Survey, Technologies, Challenges, and Opportunities
Yanqi Bao, Tianyu Ding, Jing Huo, Yaoli Liu, Yuxin Li, Wenbin Li, Yang Gao, Jiebo Luo
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a prominent technique with the potential to become a mainstream method for 3D representations. It can effectively transform multi-view images into explicit 3D Gaussian representations through efficient training, and achieve real-time rendering of novel views. This survey aims to analyze existing 3DGS-related works from multiple intersecting perspectives, including related tasks, technologies, challenges, and opportunities. The primary objective is to provide newcomers with a rapid understanding of the field and to assist researchers in methodically organizing existing technologies and challenges. Specifically, we delve into the optimization, application, and extension of 3DGS, categorizing them based on their focuses or motivations. Additionally, we summarize and classify nine types of technical modules and corresponding improvements identified in existing works. Based on these analyses, we further examine the common challenges and technologies across various tasks, proposing potential research opportunities.
Read more7/25/2024