6G comprehensive intelligence: network operations and optimization based on Large Language Models

0
🌐
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper proposes a network performance optimization and intelligent operation network architecture based on Large Language Model (LLM) to build a comprehensive intelligent 6G network system.
- The Large Language Model can more accurately capture patterns and features in data, which can achieve more accurate content output and high intelligence.
- The proposed system aims to provide strong support for related research such as network data security, privacy protection, and health assessment.
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses how the next generation of mobile communication, known as 6G, can help advance the Industrial Internet and Internet of Things (IoT). The goal is to create a more intelligent and personalized network that can provide better services to customers.
To achieve this, the researchers propose using a Large Language Model (LLM), which is a type of AI system that can understand and generate human-like text. The LLM can more accurately identify patterns and features in network data, allowing it to make better decisions and provide more intelligent network management.
This could lead to improvements in areas like network data security, privacy protection, and network health assessment. The researchers provide a specific example of a network health management system that demonstrates the practical value of this approach.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a network performance optimization and intelligent operation network architecture based on Large Language Model (LLM) to build a comprehensive intelligent 6G network system. The key idea is to leverage the powerful learning capabilities of LLMs to better capture patterns and features in network data, enabling more accurate content output and high intelligence.
The proposed system aims to provide strong support for related research areas, such as network data security, privacy protection, and health assessment. The researchers describe a network health assessment system design framework that utilizes LLM technology. Through a case study of a network health management system, the paper demonstrates the practical significance of the 6G intelligent network system based on LLM for achieving comprehensive intelligence.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to leveraging Large Language Models for improving the performance and intelligence of future 6G mobile networks. However, the authors do not thoroughly address potential limitations or challenges that may arise in implementing such a system.
For example, the paper does not discuss the computational and energy requirements of running LLMs in a distributed 6G network environment, or how to ensure the privacy and security of sensitive network data used to train the models. Additionally, the authors could have explored potential biases or inaccuracies that LLMs may introduce into the network management decisions, and how to mitigate these risks.
Further research and experimentation would be needed to fully evaluate the feasibility and scalability of the proposed approach, as well as its long-term impact on the overall reliability, security, and user experience of future 6G networks.
Conclusion
This paper presents an innovative approach to leveraging Large Language Models to build a more intelligent and comprehensive 6G mobile network system. By utilizing the powerful pattern recognition and content generation capabilities of LLMs, the proposed architecture aims to optimize network performance, enhance security and privacy protections, and provide personalized services to customers.
While the technical details and potential benefits of this system are compelling, the authors could have delved deeper into the practical challenges and limitations that would need to be addressed for successful real-world deployment. Nevertheless, this research represents an important step towards realizing the full potential of 6G networks and paves the way for further exploration of LLM applications in the telecommunications industry.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🌐

0
6G comprehensive intelligence: network operations and optimization based on Large Language Models
Sifan Long, Fengxiao Tang, Yangfan Li, Tiao Tan, Zhengjie Jin, Ming Zhao, Nei Kato
The sixth generation mobile communication standard (6G) can promote the development of Industrial Internet and Internet of Things (IoT). To achieve comprehensive intelligent development of the network and provide customers with higher quality personalized services. This paper proposes a network performance optimization and intelligent operation network architecture based on Large Language Model (LLM), aiming to build a comprehensive intelligent 6G network system. The Large Language Model, with more parameters and stronger learning ability, can more accurately capture patterns and features in data, which can achieve more accurate content output and high intelligence and provide strong support for related research such as network data security, privacy protection, and health assessment. This paper also presents the design framework of a network health assessment system based on LLM and focuses on its potential application value, through the case of network health management system, it is fully demonstrated that the 6G intelligent network system based on LLM has important practical significance for the comprehensive realization of intelligence.
Read more4/30/2024


0
Reasoning AI Performance Degradation in 6G Networks with Large Language Models
Liming Huang, Yulei Wu, Dimitra Simeonidou
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) within 6G networks is poised to revolutionize connectivity, reliability, and intelligent decision-making. However, the performance of AI models in these networks is crucial, as any decline can significantly impact network efficiency and the services it supports. Understanding the root causes of performance degradation is essential for maintaining optimal network functionality. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to reason about AI model performance degradation in 6G networks using the Large Language Models (LLMs) empowered Chain-of-Thought (CoT) method. Our approach employs an LLM as a ''teacher'' model through zero-shot prompting to generate teaching CoT rationales, followed by a CoT ''student'' model that is fine-tuned by the generated teaching data for learning to reason about performance declines. The efficacy of this model is evaluated in a real-world scenario involving a real-time 3D rendering task with multi-Access Technologies (mATs) including WiFi, 5G, and LiFi for data transmission. Experimental results show that our approach achieves over 97% reasoning accuracy on the built test questions, confirming the validity of our collected dataset and the effectiveness of the LLM-CoT method. Our findings highlight the potential of LLMs in enhancing the reliability and efficiency of 6G networks, representing a significant advancement in the evolution of AI-native network infrastructures.
Read more9/2/2024

0
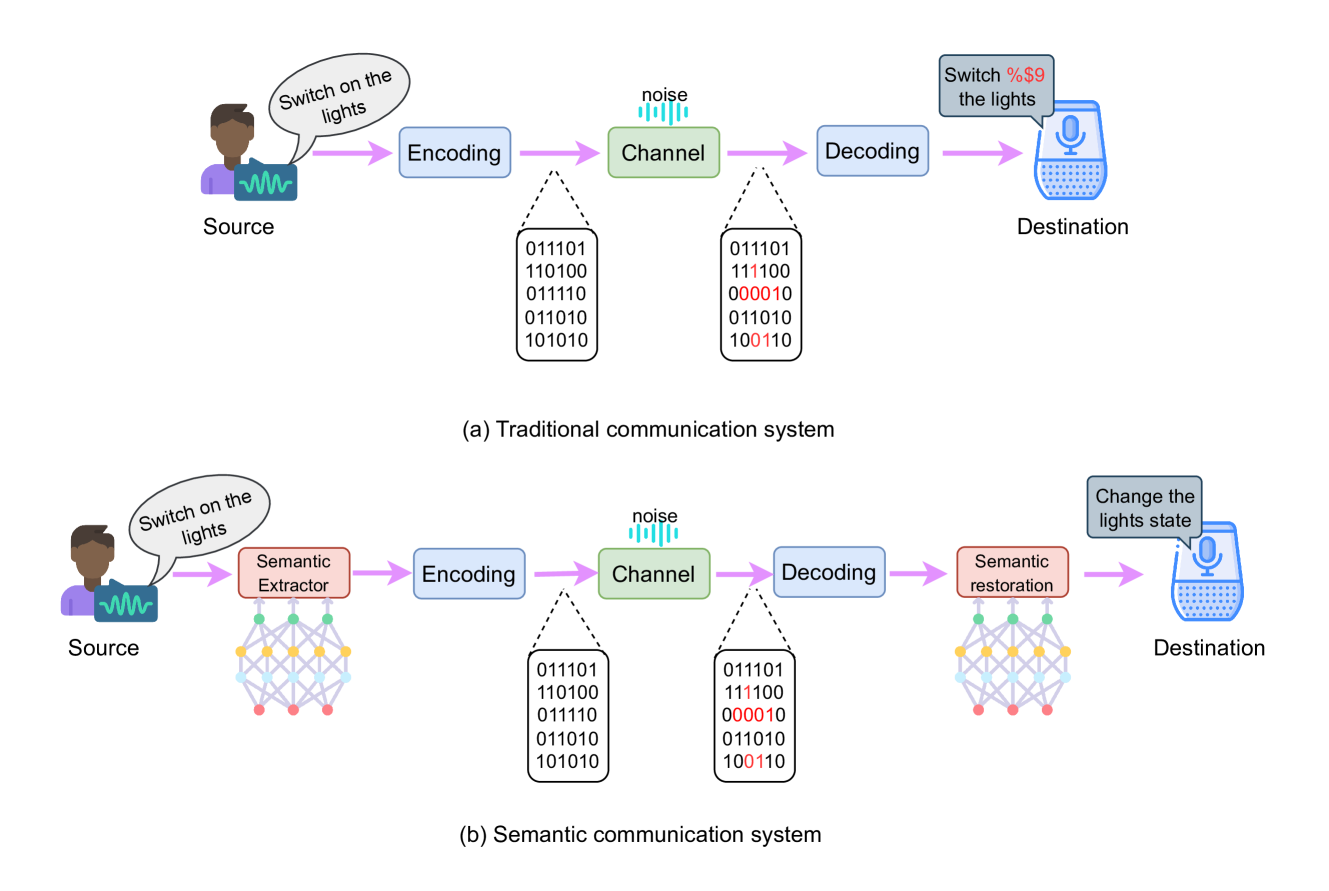
Large Language Models (LLMs) for Semantic Communication in Edge-based IoT Networks
Alakesh Kalita
With the advent of Fifth Generation (5G) and Sixth Generation (6G) communication technologies, as well as the Internet of Things (IoT), semantic communication is gaining attention among researchers as current communication technologies are approaching Shannon's limit. On the other hand, Large Language Models (LLMs) can understand and generate human-like text, based on extensive training on diverse datasets with billions of parameters. Considering the recent near-source computational technologies like Edge, in this article, we give an overview of a framework along with its modules, where LLMs can be used under the umbrella of semantic communication at the network edge for efficient communication in IoT networks. Finally, we discuss a few applications and analyze the challenges and opportunities to develop such systems.
Read more7/31/2024


0
Towards Intent-Based Network Management: Large Language Models for Intent Extraction in 5G Core Networks
Dimitrios Michael Manias, Ali Chouman, Abdallah Shami
The integration of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence (ML/AI) into fifth-generation (5G) networks has made evident the limitations of network intelligence with ever-increasing, strenuous requirements for current and next-generation devices. This transition to ubiquitous intelligence demands high connectivity, synchronicity, and end-to-end communication between users and network operators, and will pave the way towards full network automation without human intervention. Intent-based networking is a key factor in the reduction of human actions, roles, and responsibilities while shifting towards novel extraction and interpretation of automated network management. This paper presents the development of a custom Large Language Model (LLM) for 5G and next-generation intent-based networking and provides insights into future LLM developments and integrations to realize end-to-end intent-based networking for fully automated network intelligence.
Read more5/24/2024