Age-Threshold Slotted ALOHA for Optimizing Information Freshness in Mobile Networks
2312.10888

0
0

Abstract
We optimize the Age of Information (AoI) in mobile networks using the age-threshold slotted ALOHA (TSA) protocol. The network comprises multiple source-destination pairs, where each source sends a sequence of status update packets to its destination over a shared spectrum. The TSA protocol stipulates that a source node must remain silent until its AoI reaches a predefined threshold, after which the node accesses the radio channel with a certain probability. Using stochastic geometry tools, we derive analytical expressions for the transmission success probability, mean peak AoI, and time-average AoI. Subsequently, we obtain closed-form expressions for the optimal update rate and age threshold that minimize the mean peak and time-average AoI, respectively. In addition, we establish a scaling law for the mean peak AoI and time-average AoI in mobile networks, revealing that the optimal mean peak AoI and time-average AoI increase linearly with the deployment density. Notably, the growth rate of time-average AoI under TSA is half of that under conventional slotted ALOHA. When considering the optimal mean peak AoI, the TSA protocol exhibits comparable performance to the traditional slotted ALOHA protocol. These findings conclusively affirm the advantage of TSA in reducing higher-order AoI, particularly in densely deployed networks.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper proposes a new communication protocol called "Age-Threshold Slotted ALOHA" to optimize information freshness in mobile networks.
- The protocol aims to minimize the "age of information" (AoI) - the time elapsed since the generation of the latest status update received by the destination.
- The authors design and analyze the performance of the proposed protocol, considering practical issues such as interference.
Plain English Explanation
The paper focuses on the challenge of keeping information up-to-date in mobile networks, where devices are constantly moving and communicating. The "age of information" (AoI) refers to how old the latest status update is that the receiver has access to. A lower AoI means the information is more fresh and valuable.
The researchers have developed a new communication protocol called "Age-Threshold Slotted ALOHA" that is designed to minimize the AoI. It works by having devices only transmit their status updates when the age of the information reaches a certain threshold. This helps avoid redundant transmissions and reduces interference, which can degrade the freshness of the information.
The paper analyzes the performance of this new protocol, taking into account real-world factors like interference between devices. The goal is to provide a practical solution for keeping information up-to-date in mobile networks, which is important for many applications like monitoring, tracking, and control systems.
Technical Explanation
The proposed "Age-Threshold Slotted ALOHA" protocol works as follows:
- Time is divided into fixed-length slots.
- Devices only attempt to transmit their status updates when the age of their information reaches a certain threshold.
- If multiple devices attempt to transmit in the same slot, interference occurs and the transmissions are lost.
The authors develop a Markov chain model to analyze the performance of this protocol in terms of the average age of information (AoI) at the receiver. They consider the effects of interference between simultaneously transmitting devices.
The analysis shows that the Age-Threshold Slotted ALOHA protocol can significantly outperform conventional slotted ALOHA in terms of minimizing the AoI, especially when the information freshness requirement is strict. The optimal age threshold can be determined to achieve the minimum average AoI.
The authors also discuss practical implementation considerations, such as the need for synchronization between devices and the impact of channel errors.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a well-designed and comprehensive analysis of the proposed Age-Threshold Slotted ALOHA protocol. The Markov chain model captures the key dynamics of the system and allows for a rigorous evaluation of the AoI performance.
One potential limitation is the assumption of perfect synchronization between devices, which may be challenging to achieve in practical mobile networks. The impact of imperfect synchronization on the protocol's performance could be an interesting area for future research.
Additionally, the analysis focuses on a single-hop scenario, while many real-world mobile networks involve multi-hop communication. Extending the protocol and analysis to multi-hop settings could further enhance its applicability.
Overall, the Age-Threshold Slotted ALOHA protocol represents a promising approach for optimizing information freshness in mobile networks, and the insights from this paper can inform the design of future status updating systems.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel communication protocol called "Age-Threshold Slotted ALOHA" that aims to minimize the age of information (AoI) in mobile networks. By introducing an age threshold for status update transmissions, the protocol can effectively reduce redundant transmissions and mitigate the impact of interference, leading to improved information freshness.
The analytical model and performance evaluation demonstrate the advantages of the proposed protocol over conventional slotted ALOHA, especially when strict information freshness requirements are in place. While the analysis assumes perfect synchronization, the core ideas behind Age-Threshold Slotted ALOHA provide a valuable foundation for further research and development of status updating systems in mobile networks.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
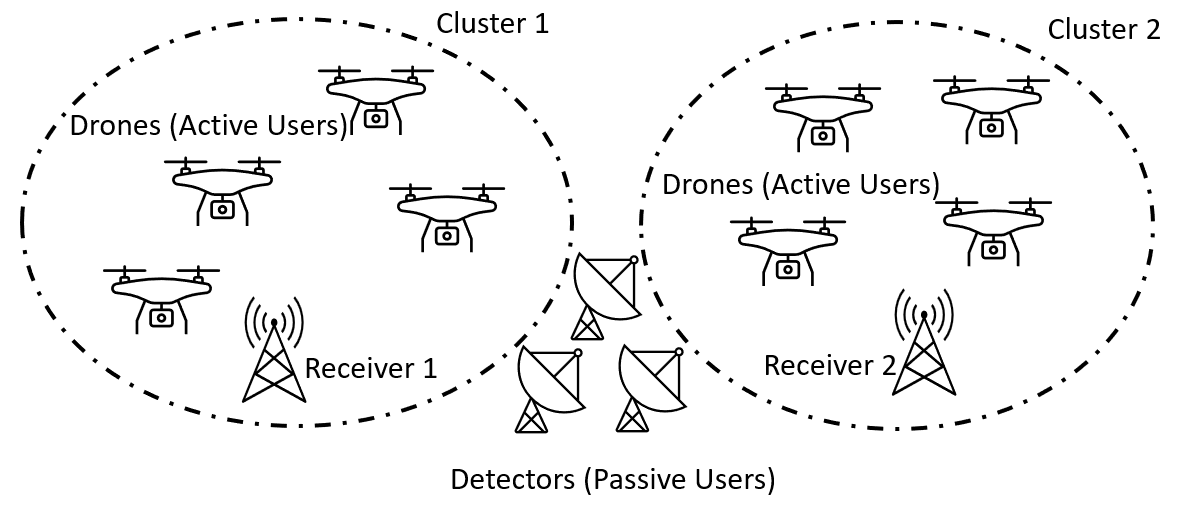
Optimizing Age of Information in Random Access Networks: A Second-Order Approach for Active/Passive Users
Siqi Fan, Yuxin Zhong, I-Hong Hou, Clement K Kam

0
0
In this paper, we study the moments of the Age of Information (AoI) for both active and passive users in a random access network. In this network, active users broadcast sensing data, while passive users detect in-band radio activities from out-of-network devices, such as jammers. Collisions occur when multiple active users transmit simultaneously. Passive users can detect radio activities only when no active user transmits. Each active user's transmission behavior follows a Markov process. We aim to minimize the weighted sum of any moments of AoI for both user types. To achieve this, we employ a second-order analysis of system behavior. Specifically, we characterize an active user's transmission Markov process using its mean and temporal variance. We show that any moment of the AoI can be approximated by a function of these two parameters. This insight enables us to analyze and optimize the transmission Markov process for active users. We apply this strategy to two different random access models. Simulation results show that policies derived from this strategy outperform other baseline policies.
6/4/2024
🔄
Exact Analysis of the Age of Information in the Multi-Source M/GI/1 Queueing System
Yoshiaki Inoue, Tetsuya Takine

0
0
We consider a situation that multiple monitoring applications (each with a different sensor-monitor pair) compete for a common service resource such as a communication link. Each sensor reports the latest state of its own time-varying information source to its corresponding monitor, incurring queueing and processing delays at the shared resource. The primary performance metric of interest is the age of information (AoI) of each sensor-monitor pair, which is defined as the elapsed time from the generation of the information currently displayed on the monitor. Although the multi-source first-come first-served (FCFS) M/GI/1 queue is one of the most fundamental model to describe such competing sensors, its exact analysis has been an open problem for years. In this paper, we show that the Laplace-Stieltjes transform (LST) of the stationary distribution of the AoI in this model, as well as the mean AoI, is given by a simple explicit formula, utilizing the double Laplace transform of the transient workload in the M/GI/1 queue.
4/9/2024

Fairness-aware Age-of-Information Minimization in WPT-Assisted Short-Packet THz Communications for mURLLC
Yao Zhu, Xiaopeng Yuan, Yulin Hu, Bo Ai, Ruikang Wang, Bin Han, Anke Schmeink

0
0
The technological landscape is swiftly advancing towards large-scale systems, creating significant opportunities, particularly in the domain of Terahertz (THz) communications. Networks designed for massive connectivity, comprising numerous Internet of Things (IoT) devices, are at the forefront of this advancement. In this paper, we consider Wireless Power Transfer (WPT)-enabled networks that support these IoT devices with massive Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communication (mURLLC) services.The focus of such networks is information freshness, with the Age-of-Information (AoI) serving as the pivotal performance metric. In particular, we aim to minimize the maximum AoI among IoT devices by optimizing the scheduling policy. Our analytical findings establish the convexity property of the problem, which can be solved efficiently. Furthermore, we introduce the concept of AoI-oriented cluster capacity, examining the relationship between the number of supported devices and the AoI performance in the network. Numerical simulations validate the advantage of our proposed approach in enhancing AoI performance, indicating its potential to guide the design of future THz communication systems for IoT applications requiring mURLLC services.
4/4/2024

Age of Information Versions: a Semantic View of Markov Source Monitoring
Mehrdad Salimnejad, Marios Kountouris, Anthony Ephremides, Nikolaos Pappas

0
0
We consider the problem of real-time remote monitoring of a two-state Markov process, where a sensor observes the state of the source and makes a decision on whether to transmit the status updates over an unreliable channel or not. We introduce a modified randomized stationary sampling and transmission policy where the decision to perform sampling occurs probabilistically depending on the current state of the source and whether the system was in a sync state during the previous time slot or not. We then propose two new performance metrics, coined the Version Innovation Age (VIA) and the Age of Incorrect Version (AoIV) and analyze their performance under the modified randomized stationary and other state-of-the-art sampling and transmission policies. Specifically, we derive closed-form expressions for the distribution and the average of VIA, AoIV, and Age of Incorrect Information (AoII) under these policies. Furthermore, we formulate and solve three constrained optimization problems. The first optimization problem aims to minimize the average VIA subject to constraints on the time-averaged sampling cost and time-averaged reconstruction error. In the second and third problems, the objective is to minimize the average AoIV and AoII, respectively, while considering a constraint on the time-averaged sampling cost. Finally, we compare the performance of various sampling and transmission policies and identify the conditions under which each policy outperforms the others in optimizing the proposed metrics.
6/24/2024