Fairness-aware Age-of-Information Minimization in WPT-Assisted Short-Packet THz Communications for mURLLC
2404.02159

0
0

Abstract
The technological landscape is swiftly advancing towards large-scale systems, creating significant opportunities, particularly in the domain of Terahertz (THz) communications. Networks designed for massive connectivity, comprising numerous Internet of Things (IoT) devices, are at the forefront of this advancement. In this paper, we consider Wireless Power Transfer (WPT)-enabled networks that support these IoT devices with massive Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communication (mURLLC) services.The focus of such networks is information freshness, with the Age-of-Information (AoI) serving as the pivotal performance metric. In particular, we aim to minimize the maximum AoI among IoT devices by optimizing the scheduling policy. Our analytical findings establish the convexity property of the problem, which can be solved efficiently. Furthermore, we introduce the concept of AoI-oriented cluster capacity, examining the relationship between the number of supported devices and the AoI performance in the network. Numerical simulations validate the advantage of our proposed approach in enhancing AoI performance, indicating its potential to guide the design of future THz communication systems for IoT applications requiring mURLLC services.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a fairness-aware optimization framework to minimize the age-of-information (AoI) in wireless power transfer (WPT)-assisted short-packet terahertz (THz) communications for mission-critical ultra-reliable low-latency communications (mURLLC).
- The authors investigate the tradeoff between minimizing the average AoI and ensuring fairness among users, and propose a fairness-aware optimization problem to address this.
- The research aims to enable efficient and reliable data delivery in emerging mURLLC applications, such as industrial automation and autonomous vehicles, by optimizing the AoI performance.
Plain English Explanation
In this paper, the researchers are looking at a specific type of wireless communication called terahertz (THz) communication, which is used for mission-critical applications that require very fast and reliable data delivery, like industrial automation or self-driving cars.
They are trying to solve a problem called "age-of-information" (AoI), which is all about making sure the information being transmitted is as up-to-date as possible. The older the information, the higher the AoI. The researchers want to find a way to minimize the AoI while also making sure the system is fair to all the users.
To do this, they use a technique called wireless power transfer (WPT), which allows devices to charge their batteries wirelessly. The researchers incorporate WPT into the THz communication system and then try to optimize the system to minimize the AoI and ensure fairness.
This research is important because it can help make mission-critical applications like industrial automation and autonomous vehicles more efficient and reliable by keeping the information they use as up-to-date as possible.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a fairness-aware optimization framework to minimize the age-of-information (AoI) in wireless power transfer-assisted short-packet terahertz (THz) communications for mission-critical ultra-reliable low-latency communications (mURLLC) applications.
The authors formulate an optimization problem that aims to balance the tradeoff between minimizing the average AoI and ensuring fairness among users. The problem is solved using a Lagrangian dual decomposition method, which allows for efficient distributed implementation.
The proposed approach is evaluated through numerical simulations, which demonstrate its effectiveness in reducing the average AoI while maintaining fairness across users. The results show that the fairness-aware optimization outperforms a baseline scheme that only minimizes the average AoI without considering fairness.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a well-designed optimization framework to address the important problem of minimizing AoI in WPT-assisted THz communications for mURLLC applications. The authors' consideration of fairness is a key strength, as it ensures that the optimization scheme does not unfairly prioritize certain users over others.
However, the paper does not explore the impact of various system parameters, such as the number of users or the wireless channel conditions, on the performance of the proposed approach. Additionally, the authors do not discuss the computational complexity of the Lagrangian dual decomposition method, which could be an important factor in practical deployments.
Further research could investigate the resilience of the fairness-aware optimization to different system conditions, as well as explore alternative optimization techniques that may offer improved performance or lower complexity. Cooperative sensing and communication in integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) networks could also be an interesting area to consider in the context of mURLLC applications.
Conclusion
This paper presents a fairness-aware optimization framework to minimize the age-of-information (AoI) in WPT-assisted short-packet THz communications for mission-critical ultra-reliable low-latency communications (mURLLC). The proposed approach aims to balance the tradeoff between minimizing the average AoI and ensuring fairness among users, which is crucial for enabling efficient and reliable data delivery in emerging mURLLC applications, such as industrial automation and autonomous vehicles.
The research demonstrates the potential of incorporating fairness considerations into AoI optimization, and highlights the importance of addressing both performance and equity in the design of communication systems for mission-critical applications.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Age-Threshold Slotted ALOHA for Optimizing Information Freshness in Mobile Networks
Fangming Zhao, Nikolaos Pappas, Chuan Ma, Xinghua Sun, Tony Q. S. Quek, Howard H. Yang

0
0
We optimize the Age of Information (AoI) in mobile networks using the age-threshold slotted ALOHA (TSA) protocol. The network comprises multiple source-destination pairs, where each source sends a sequence of status update packets to its destination over a shared spectrum. The TSA protocol stipulates that a source node must remain silent until its AoI reaches a predefined threshold, after which the node accesses the radio channel with a certain probability. Using stochastic geometry tools, we derive analytical expressions for the transmission success probability, mean peak AoI, and time-average AoI. Subsequently, we obtain closed-form expressions for the optimal update rate and age threshold that minimize the mean peak and time-average AoI, respectively. In addition, we establish a scaling law for the mean peak AoI and time-average AoI in mobile networks, revealing that the optimal mean peak AoI and time-average AoI increase linearly with the deployment density. Notably, the growth rate of time-average AoI under TSA is half of that under conventional slotted ALOHA. When considering the optimal mean peak AoI, the TSA protocol exhibits comparable performance to the traditional slotted ALOHA protocol. These findings conclusively affirm the advantage of TSA in reducing higher-order AoI, particularly in densely deployed networks.
6/6/2024
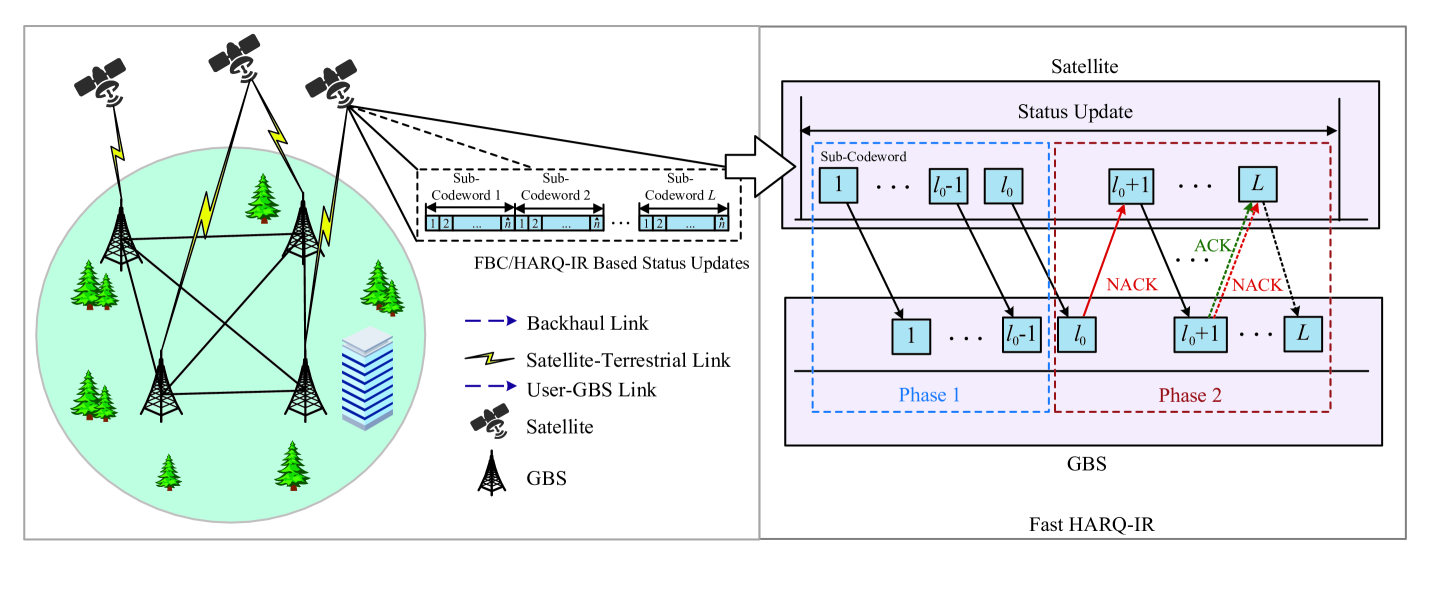
Statistical QoS Provisioning Architecture for 6G Satellite-Terrestrial Integrated Networks
Jingqing Wang, Wenchi Cheng, Wei Zhang, Hui Liang

0
0
The emergence of massive ultra-reliable and low latency communications (mURLLC) as a category of time/reliability-sensitive service over 6G networks has received considerable research attention, which has presented unprecedented challenges. As one of the key enablers for 6G, satellite-terrestrial integrated networks (STIN) have been developed to offer more expansive connectivity and comprehensive 3D coverage in space-aerial-terrestrial domains for supporting 6G mission-critical mURLLC applications while fulfilling diverse and rigorous quality of service (QoS) requirements. In the context of these mURLLC-driven satellite services, data freshness assumes paramount importance, as outdated data may engender unpredictable or catastrophic outcomes. To effectively measure data freshness in satellite-terrestrial integrated communications, age of information (AoI) has recently surfaced as a new dimension of QoS metric to support time-sensitive applications. It is crucial to design new analytical models that ensure stringent and diverse QoS metrics bounded by different key parameters, including AoI, delay, and reliability, over 6G satellite-terrestrial integrated networks. However, due to the complicated and dynamic nature of satellite-terrestrial integrated network environments, the research on efficiently defining new statistical QoS schemes while taking into account varying degrees of freedom has still been in their infancy. To remedy these deficiencies, in this paper we develop statistical QoS provisioning schemes over 6G satellite-terrestrial integrated networks in the finite blocklength regime. Particularly, we firstly introduce and review key technologies for supporting mURLLC. Secondly, we formulate a number of novel fundamental statistical-QoS metrics in the finite blocklength regime. Finally, we conduct a set of simulations to evaluate our developed statistical QoS schemes.
6/10/2024
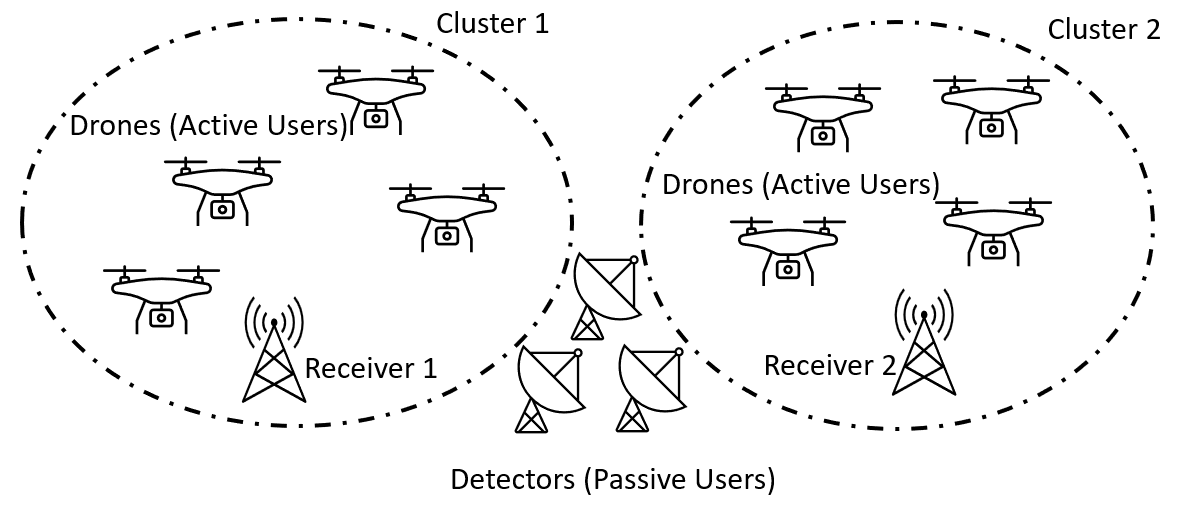
Optimizing Age of Information in Random Access Networks: A Second-Order Approach for Active/Passive Users
Siqi Fan, Yuxin Zhong, I-Hong Hou, Clement K Kam

0
0
In this paper, we study the moments of the Age of Information (AoI) for both active and passive users in a random access network. In this network, active users broadcast sensing data, while passive users detect in-band radio activities from out-of-network devices, such as jammers. Collisions occur when multiple active users transmit simultaneously. Passive users can detect radio activities only when no active user transmits. Each active user's transmission behavior follows a Markov process. We aim to minimize the weighted sum of any moments of AoI for both user types. To achieve this, we employ a second-order analysis of system behavior. Specifically, we characterize an active user's transmission Markov process using its mean and temporal variance. We show that any moment of the AoI can be approximated by a function of these two parameters. This insight enables us to analyze and optimize the transmission Markov process for active users. We apply this strategy to two different random access models. Simulation results show that policies derived from this strategy outperform other baseline policies.
6/4/2024
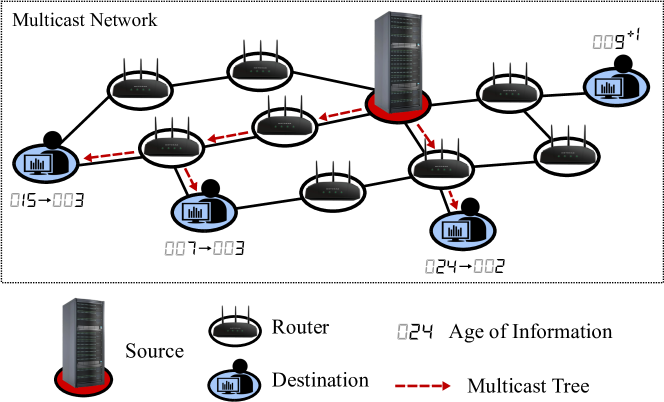
Age-minimal Multicast by Graph Attention Reinforcement Learning
Yanning Zhang, Guocheng Liao, Shengbin Cao, Ning Yang, Meng Zhang

0
0
Age of Information (AoI) is an emerging metric used to assess the timeliness of information, gaining research interest in real-time multicast applications such as video streaming and metaverse platforms. In this paper, we consider a dynamic multicast network with energy constraints, where our objective is to minimize the expected time-average AoI through energy-constrained multicast routing and scheduling. The inherent complexity of the problem, given the NP-hardness and intertwined scheduling and routing decisions, makes existing approaches inapplicable. To address these challenges, we decompose the original problem into two subtasks, each amenable to reinforcement learning (RL) methods. Subsequently, we propose an innovative framework based on graph attention networks (GATs) to effectively capture graph information with superior generalization capabilities. To validate our framework, we conduct experiments on three datasets including a real-world dataset called AS-733, and show that our proposed scheme reduces the average weighted AoI by 62.9% and reduces the energy consumption by at most 72.5% compared to baselines.
6/3/2024