AI-enhanced Collective Intelligence

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Explores the state of the art and future prospects of AI-enhanced collective intelligence
- Examines the intersection of artificial intelligence, multi-agent systems, and human-machine collaboration
- Discusses the potential of combining human and machine intelligence to tackle complex challenges
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores the emerging field of AI-enhanced collective intelligence. This refers to the idea of combining artificial intelligence (AI) with human intelligence and collaboration to tackle complex problems more effectively.
The authors explain that collective intelligence arises when groups of people or machines work together, sharing information and ideas. By integrating AI into these collective systems, the researchers believe we can unlock new levels of problem-solving and decision-making capabilities.
The paper discusses various approaches to evolving AI collectives that can enhance and complement human intelligence. This includes techniques like collective attention in human-AI teams and understanding when combinations of humans and AI are most useful.
Overall, the researchers are optimistic about the potential of AI-enhanced collective intelligence to help solve complex global challenges and improve decision-making in a wide range of domains.
Technical Explanation
The paper provides an overview of the state of the art and future prospects of AI-enhanced collective intelligence. It examines the intersection of AI, multi-agent systems, and human-machine collaboration, exploring how these can be combined to tackle complex problems more effectively.
The authors discuss the concept of collective intelligence, which emerges when groups of people or machines work together, sharing information and ideas. They argue that by integrating AI into these collective systems, we can unlock new levels of problem-solving and decision-making capabilities.
The paper explores various approaches to evolving AI collectives that can enhance and complement human intelligence. This includes techniques like collective attention in human-AI teams, which examines how AI systems can help direct the collective focus of human-machine teams, and understanding when combinations of humans and AI are most useful.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of AI-enhanced collective intelligence, highlighting both the potential benefits and the challenges involved. While the researchers are generally optimistic about the future of this field, they do acknowledge some caveats and areas for further research.
One potential limitation mentioned is the complexity of designing effective human-AI collaboration frameworks that can truly leverage the complementary strengths of both. The paper suggests that more work is needed to understand the dynamic interplay between human and machine agents within these collective systems.
Additionally, the researchers note that the ethical implications of AI-enhanced collective intelligence, such as issues of transparency, accountability, and bias, will need to be carefully considered as the field continues to evolve. Encouraging critical thinking and a nuanced understanding of both the opportunities and risks will be crucial as this technology progresses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the paper presents a compelling vision for the future of AI-enhanced collective intelligence. By combining the unique capabilities of humans and machines, the researchers believe we can develop more effective problem-solving and decision-making systems that can tackle complex global challenges.
While the field is still in its early stages, the authors are optimistic about the potential impact of these technologies, particularly in areas like scientific discovery, policy-making, and social innovation. As the research continues to evolve, it will be important to maintain a balanced perspective, acknowledging both the benefits and the potential risks, in order to ensure that these technologies are developed and deployed responsibly.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
AI-enhanced Collective Intelligence
Hao Cui, Taha Yasseri
The current societal challenges exceed the capacity of human individual or collective effort alone. As AI evolves, its role within human collectives is poised to vary from an assistive tool to a participatory member. Humans and AI possess complementary capabilities that, when synergized, can achieve a level of collective intelligence that surpasses the collective capabilities of either humans or AI in isolation. However, the interactions in human-AI systems are inherently complex, involving intricate processes and interdependencies. This narrative review incorporates perspectives from complex network science to conceptualize a multilayer representation of human-AI collective intelligence, comprising cognition, physical, and information layers. Within this multilayer network, humans and AI agents exhibit varying characteristics; humans differ in diversity from surface-level to deep-level attributes, while AI agents range in degrees of functionality and anthropomorphism. The interplay among these agents shapes the overall structure and dynamics of the system. We explore how agents' diversity and interactions influence the system's collective intelligence. Furthermore, we present an analysis of real-world instances of AI-enhanced collective intelligence. We conclude by addressing the potential challenges in AI-enhanced collective intelligence and offer perspectives on future developments in this field.
Read more8/14/2024
🔎

0
A social path to human-like artificial intelligence
Edgar A. Du'e~nez-Guzm'an, Suzanne Sadedin, Jane X. Wang, Kevin R. McKee, Joel Z. Leibo
Traditionally, cognitive and computer scientists have viewed intelligence solipsistically, as a property of unitary agents devoid of social context. Given the success of contemporary learning algorithms, we argue that the bottleneck in artificial intelligence (AI) progress is shifting from data assimilation to novel data generation. We bring together evidence showing that natural intelligence emerges at multiple scales in networks of interacting agents via collective living, social relationships and major evolutionary transitions, which contribute to novel data generation through mechanisms such as population pressures, arms races, Machiavellian selection, social learning and cumulative culture. Many breakthroughs in AI exploit some of these processes, from multi-agent structures enabling algorithms to master complex games like Capture-The-Flag and StarCraft II, to strategic communication in Diplomacy and the shaping of AI data streams by other AIs. Moving beyond a solipsistic view of agency to integrate these mechanisms suggests a path to human-like compounding innovation through ongoing novel data generation.
Read more5/28/2024

0
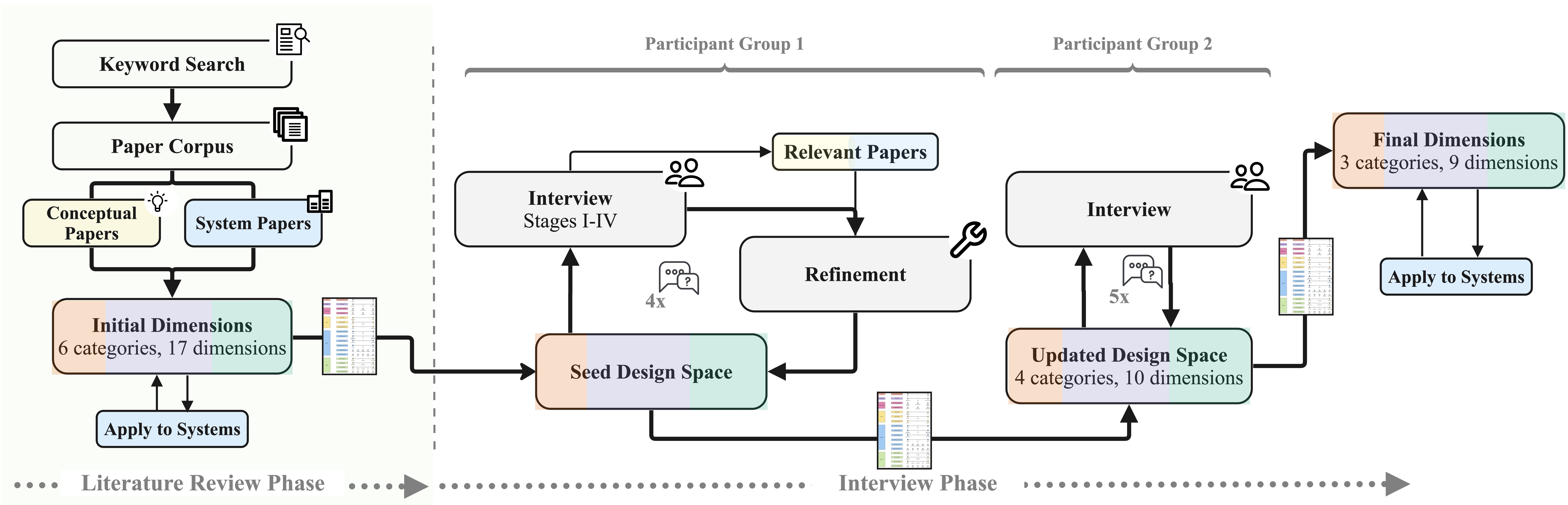
Deconstructing Human-AI Collaboration: Agency, Interaction, and Adaptation
Steffen Holter, Mennatallah El-Assady
As full AI-based automation remains out of reach in most real-world applications, the focus has instead shifted to leveraging the strengths of both human and AI agents, creating effective collaborative systems. The rapid advances in this area have yielded increasingly more complex systems and frameworks, while the nuance of their characterization has gotten more vague. Similarly, the existing conceptual models no longer capture the elaborate processes of these systems nor describe the entire scope of their collaboration paradigms. In this paper, we propose a new unified set of dimensions through which to analyze and describe human-AI systems. Our conceptual model is centered around three high-level aspects - agency, interaction, and adaptation - and is developed through a multi-step process. Firstly, an initial design space is proposed by surveying the literature and consolidating existing definitions and conceptual frameworks. Secondly, this model is iteratively refined and validated by conducting semi-structured interviews with nine researchers in this field. Lastly, to illustrate the applicability of our design space, we utilize it to provide a structured description of selected human-AI systems.
Read more4/19/2024


0
Evolving AI Collectives to Enhance Human Diversity and Enable Self-Regulation
Shiyang Lai, Yujin Potter, Junsol Kim, Richard Zhuang, Dawn Song, James Evans
Large language model behavior is shaped by the language of those with whom they interact. This capacity and their increasing prevalence online portend that they will intentionally or unintentionally program one another and form emergent AI subjectivities, relationships, and collectives. Here, we call upon the research community to investigate these societies of interacting artificial intelligences to increase their rewards and reduce their risks for human society and the health of online environments. We use a small community of models and their evolving outputs to illustrate how such emergent, decentralized AI collectives can spontaneously expand the bounds of human diversity and reduce the risk of toxic, anti-social behavior online. Finally, we discuss opportunities for AI cross-moderation and address ethical issues and design challenges associated with creating and maintaining free-formed AI collectives.
Read more6/21/2024