AutoTutor meets Large Language Models: A Language Model Tutor with Rich Pedagogy and Guardrails
2402.09216

0
0

Abstract
Large Language Models (LLMs) have found several use cases in education, ranging from automatic question generation to essay evaluation. In this paper, we explore the potential of using Large Language Models (LLMs) to author Intelligent Tutoring Systems. A common pitfall of LLMs is their straying from desired pedagogical strategies such as leaking the answer to the student, and in general, providing no guarantees. We posit that while LLMs with certain guardrails can take the place of subject experts, the overall pedagogical design still needs to be handcrafted for the best learning results. Based on this principle, we create a sample end-to-end tutoring system named MWPTutor, which uses LLMs to fill in the state space of a pre-defined finite state transducer. This approach retains the structure and the pedagogy of traditional tutoring systems that has been developed over the years by learning scientists but brings in additional flexibility of LLM-based approaches. Through a human evaluation study on two datasets based on math word problems, we show that our hybrid approach achieves a better overall tutoring score than an instructed, but otherwise free-form, GPT-4. MWPTutor is completely modular and opens up the scope for the community to improve its performance by improving individual modules or using different teaching strategies that it can follow.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores using large language models (LLMs) to scale the authoring of interactive tutoring systems called AutoTutors.
- AutoTutors are designed to provide customized feedback and guidance to students as they work through math word problems.
- The researchers investigate how LLMs can be leveraged to generate the complex dialogue and response logic required for these tutoring systems.
Plain English Explanation
The paper focuses on using large language models to make it easier to create interactive tutoring systems called AutoTutors. AutoTutors are designed to give students personalized feedback and guidance as they work through math word problems.
Traditionally, creating these types of tutoring systems has been a time-consuming and manual process, as the developers need to carefully craft the dialogue and response logic. The researchers wanted to explore whether large language models could be used to automate much of this authoring work.
The idea is that the LLM could generate realistic and contextual responses to student inputs, allowing the tutoring system to have more natural and adaptive conversations. This could make it much faster and easier to develop these kinds of interactive educational tools.
Technical Explanation
The paper first provides background on two main approaches to building tutoring systems: rule-based systems and data-driven systems. Rule-based systems use manually-crafted dialogue trees and response logic, while data-driven systems leverage machine learning to learn from example dialogues.
The researchers propose a hybrid approach that combines rule-based and data-driven techniques using large language models. Specifically, they use a LLM to generate the response text for the tutoring system, while still using rule-based techniques to manage the overall flow of the interaction.
To evaluate this approach, the researchers conduct experiments where they have the LLM generate responses for a math word problem tutoring system called AutoTutor. They find that the LLM-generated responses are coherent and relevant, and that the hybrid system can provide meaningful feedback and guidance to students.
The paper also discusses some of the challenges and limitations of using LLMs for this task, such as ensuring the responses are factually correct and consistent with the problem context.
Critical Analysis
The researchers acknowledge that their approach still requires some manual effort to set up the rule-based structure and prompt the LLM appropriately. There may be opportunities to further automate parts of the authoring process in the future.
Additionally, the paper only evaluates the system on a limited set of math word problems. More research would be needed to test the scalability and robustness of the approach across a wider range of educational domains and problem types.
It would also be interesting to see how well LLM-based tutoring systems can automatically assess student proficiency and adapt the tutoring accordingly. The current system relies on predefined rules for managing the tutoring dialogue.
Overall, this research demonstrates promising initial results for using large language models as AI research assistants to help scale the creation of interactive educational technologies. Further advancements in this area could make high-quality tutoring more accessible to a wider range of students.
Conclusion
This paper explores using large language models to streamline the authoring of interactive tutoring systems called AutoTutors. The researchers propose a hybrid approach that combines rule-based and data-driven techniques, with the LLM generating the response text.
Their experiments show that this approach can produce coherent and relevant feedback for students working through math word problems. While there are still some limitations to address, this research represents an important step towards using LLMs to build more capable autonomous educational agents.
Ultimately, advancements in this area could make high-quality personalized tutoring more accessible and scalable, with significant potential benefits for student learning and achievement.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
A review on the use of large language models as virtual tutors
Silvia Garc'ia-M'endez, Francisco de Arriba-P'erez, Mar'ia del Carmen Somoza-L'opez

0
0
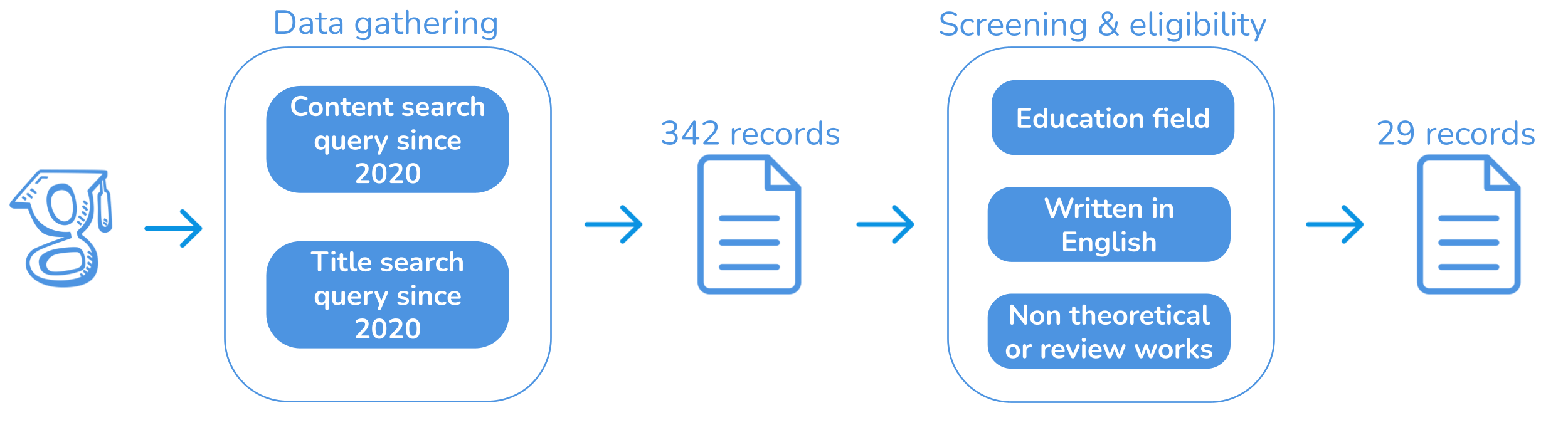
Transformer architectures contribute to managing long-term dependencies for Natural Language Processing, representing one of the most recent changes in the field. These architectures are the basis of the innovative, cutting-edge Large Language Models (LLMs) that have produced a huge buzz in several fields and industrial sectors, among the ones education stands out. Accordingly, these generative Artificial Intelligence-based solutions have directed the change in techniques and the evolution in educational methods and contents, along with network infrastructure, towards high-quality learning. Given the popularity of LLMs, this review seeks to provide a comprehensive overview of those solutions designed specifically to generate and evaluate educational materials and which involve students and teachers in their design or experimental plan. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first review of educational applications (e.g., student assessment) of LLMs. As expected, the most common role of these systems is as virtual tutors for automatic question generation. Moreover, the most popular models are GTP-3 and BERT. However, due to the continuous launch of new generative models, new works are expected to be published shortly.
5/21/2024
Large Language Models for Education: A Survey and Outlook
Shen Wang, Tianlong Xu, Hang Li, Chaoli Zhang, Joleen Liang, Jiliang Tang, Philip S. Yu, Qingsong Wen

0
0
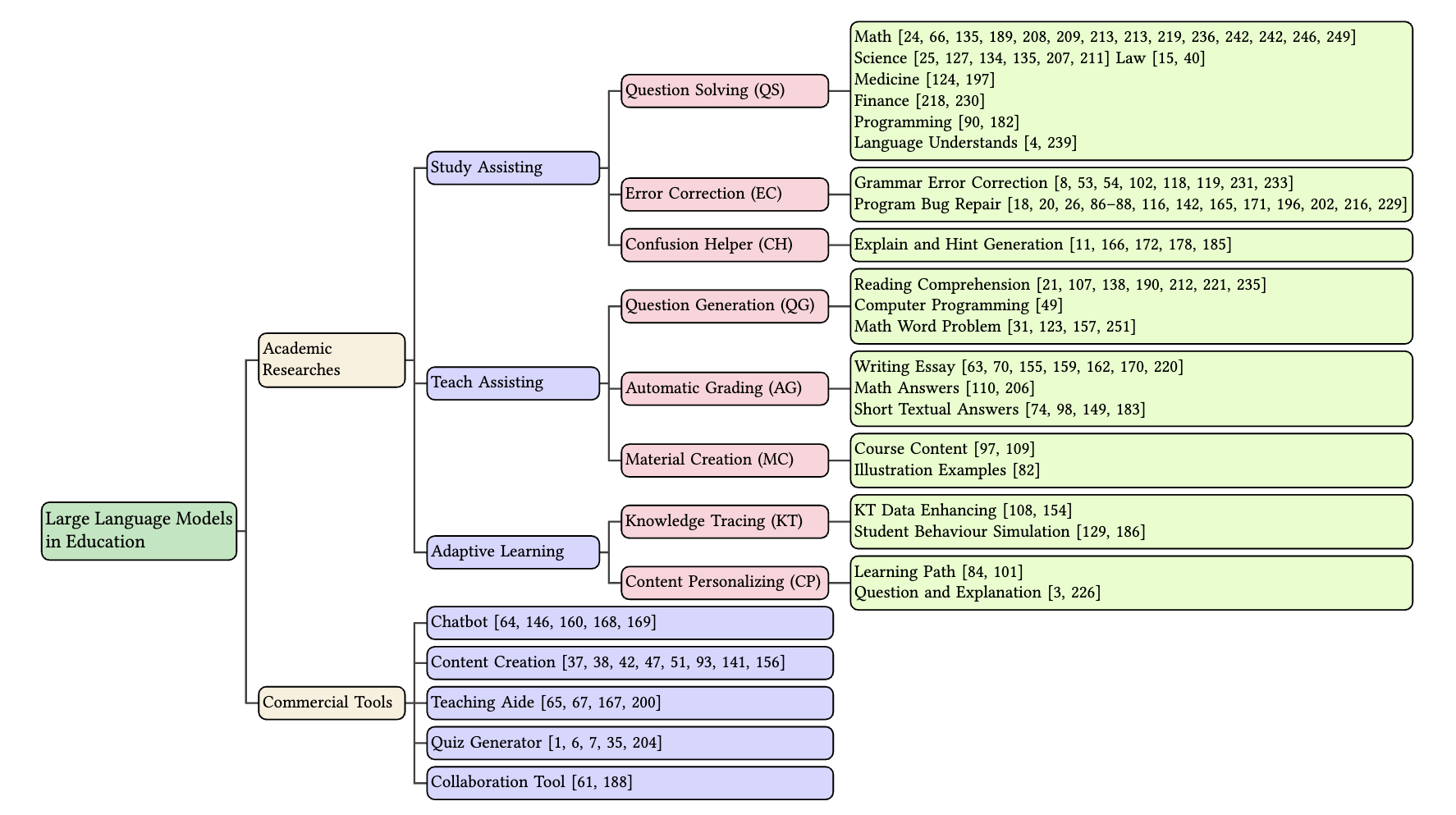
The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has brought in a new era of possibilities in the realm of education. This survey paper summarizes the various technologies of LLMs in educational settings from multifaceted perspectives, encompassing student and teacher assistance, adaptive learning, and commercial tools. We systematically review the technological advancements in each perspective, organize related datasets and benchmarks, and identify the risks and challenges associated with deploying LLMs in education. Furthermore, we outline future research opportunities, highlighting the potential promising directions. Our survey aims to provide a comprehensive technological picture for educators, researchers, and policymakers to harness the power of LLMs to revolutionize educational practices and foster a more effective personalized learning environment.
4/3/2024
💬
Exploring the Capabilities of Prompted Large Language Models in Educational and Assessment Applications
Subhankar Maity, Aniket Deroy, Sudeshna Sarkar

0
0
In the era of generative artificial intelligence (AI), the fusion of large language models (LLMs) offers unprecedented opportunities for innovation in the field of modern education. We embark on an exploration of prompted LLMs within the context of educational and assessment applications to uncover their potential. Through a series of carefully crafted research questions, we investigate the effectiveness of prompt-based techniques in generating open-ended questions from school-level textbooks, assess their efficiency in generating open-ended questions from undergraduate-level technical textbooks, and explore the feasibility of employing a chain-of-thought inspired multi-stage prompting approach for language-agnostic multiple-choice question (MCQ) generation. Additionally, we evaluate the ability of prompted LLMs for language learning, exemplified through a case study in the low-resource Indian language Bengali, to explain Bengali grammatical errors. We also evaluate the potential of prompted LLMs to assess human resource (HR) spoken interview transcripts. By juxtaposing the capabilities of LLMs with those of human experts across various educational tasks and domains, our aim is to shed light on the potential and limitations of LLMs in reshaping educational practices.
5/21/2024
💬
Large Language Models for Education: A Survey
Hanyi Xu, Wensheng Gan, Zhenlian Qi, Jiayang Wu, Philip S. Yu

0
0
Artificial intelligence (AI) has a profound impact on traditional education. In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have been increasingly used in various applications such as natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, and autonomous driving. LLMs have also been applied in many fields, including recommendation, finance, government, education, legal affairs, and finance. As powerful auxiliary tools, LLMs incorporate various technologies such as deep learning, pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning. The use of LLMs for smart education (LLMEdu) has been a significant strategic direction for countries worldwide. While LLMs have shown great promise in improving teaching quality, changing education models, and modifying teacher roles, the technologies are still facing several challenges. In this paper, we conduct a systematic review of LLMEdu, focusing on current technologies, challenges, and future developments. We first summarize the current state of LLMEdu and then introduce the characteristics of LLMs and education, as well as the benefits of integrating LLMs into education. We also review the process of integrating LLMs into the education industry, as well as the introduction of related technologies. Finally, we discuss the challenges and problems faced by LLMEdu, as well as prospects for future optimization of LLMEdu.
5/24/2024