A review on the use of large language models as virtual tutors
2405.11983

0
0
Abstract
Transformer architectures contribute to managing long-term dependencies for Natural Language Processing, representing one of the most recent changes in the field. These architectures are the basis of the innovative, cutting-edge Large Language Models (LLMs) that have produced a huge buzz in several fields and industrial sectors, among the ones education stands out. Accordingly, these generative Artificial Intelligence-based solutions have directed the change in techniques and the evolution in educational methods and contents, along with network infrastructure, towards high-quality learning. Given the popularity of LLMs, this review seeks to provide a comprehensive overview of those solutions designed specifically to generate and evaluate educational materials and which involve students and teachers in their design or experimental plan. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first review of educational applications (e.g., student assessment) of LLMs. As expected, the most common role of these systems is as virtual tutors for automatic question generation. Moreover, the most popular models are GTP-3 and BERT. However, due to the continuous launch of new generative models, new works are expected to be published shortly.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper reviews the use of large language models (LLMs) as virtual tutors in education and learning.
- It explores the potential benefits, challenges, and future outlook of LLMs in this context.
- The paper covers various applications of LLMs, including autotutor meets large language models, LLMs for mathematicians, and multilingual generation with LLMs.
- It also discusses the integration of LLMs with multimodal vision models for enhanced educational experiences.
Plain English Explanation
Large language models (LLMs) are powerful AI systems that can understand and generate human-like text. This paper explores the idea of using these LLMs as virtual tutors in education and learning. The researchers believe that LLMs could offer several benefits, such as personalized learning experiences, 24/7 availability, and the ability to handle a wide range of subjects and tasks.
For example, an LLM-based virtual tutor could help students learn math by providing step-by-step explanations, answering questions, and even generating custom practice problems. Similarly, an LLM could assist students with language learning by engaging them in conversations, providing feedback on their writing, and explaining grammar rules.
The paper also discusses the potential challenges of using LLMs as virtual tutors, such as ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information they provide, addressing ethical concerns around privacy and bias, and integrating them seamlessly into existing educational systems.
Overall, the researchers believe that the use of LLMs in education holds a lot of promise, but more research and careful implementation are needed to realize their full potential.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by providing an overview of the current state of large language models (LLMs) and their potential applications in education and learning. The authors highlight the impressive capabilities of LLMs, such as their ability to understand and generate human-like text, as well as their potential to offer personalized learning experiences, 24/7 availability, and the ability to handle a wide range of subjects and tasks.
The paper then delves into several specific applications of LLMs as virtual tutors. For instance, the authors discuss the AutoTutor system, which integrates LLMs to engage students in natural language dialogues and provide personalized feedback and guidance. Similarly, the paper explores the use of LLMs to assist mathematicians in their work, such as generating proofs, solving problems, and explaining concepts.
The paper also covers the potential of LLMs in multilingual learning, where they could facilitate language translation, content generation, and cross-cultural communication. Additionally, the authors discuss the integration of LLMs with multimodal vision models to create more immersive and engaging educational experiences.
Throughout the paper, the authors address the key challenges and limitations of using LLMs as virtual tutors, such as ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information they provide, addressing ethical concerns around privacy and bias, and integrating them seamlessly into existing educational systems.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive and well-researched overview of the potential use of large language models (LLMs) as virtual tutors in education and learning. The authors have done an excellent job of highlighting the various applications and benefits of this approach, as well as the potential challenges and limitations.
One of the key strengths of the paper is its in-depth exploration of specific use cases, such as the integration of LLMs with AutoTutor, their use in assisting mathematicians, and their potential in multilingual learning. These detailed examples help readers better understand the practical implications and the technical considerations involved.
However, the paper could have delved deeper into some of the ethical and privacy concerns around the use of LLMs in education. While the authors do acknowledge these issues, more thorough discussion and potential mitigation strategies could have strengthened the critical analysis.
Additionally, the paper could have explored the potential impact of LLMs on the role of human teachers and the overall educational ecosystem. It would be valuable to understand how these virtual tutors could complement or potentially disrupt traditional teaching methods and the implications for the future of education.
Overall, this paper provides a solid foundation for understanding the current state of LLMs in education and their future potential. The authors have done a commendable job of synthesizing the relevant research and presenting it in a clear and accessible manner.
Conclusion
This paper offers a comprehensive review of the use of large language models (LLMs) as virtual tutors in education and learning. The researchers have identified the potential benefits of LLMs, such as personalized learning experiences, 24/7 availability, and the ability to handle a wide range of subjects and tasks.
The paper explores various applications of LLMs in education, including integrating them with systems like AutoTutor, assisting mathematicians, enabling multilingual learning, and combining them with multimodal vision models. These examples demonstrate the versatility and potential of LLMs in enhancing educational experiences.
While the paper acknowledges the challenges and limitations of using LLMs as virtual tutors, such as ensuring accuracy, addressing ethical concerns, and integrating them into existing systems, the overall outlook is positive. The researchers believe that with further research and careful implementation, the use of LLMs in education could lead to significant advancements in personalized and accessible learning.
As the field of artificial intelligence continues to evolve, the integration of LLMs into education may become an increasingly important area of study, with the potential to revolutionize the way we teach and learn.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
A Survey on Large Language Models from Concept to Implementation
Chen Wang, Jin Zhao, Jiaqi Gong

0
0
Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), particularly those built on Transformer architectures, have significantly broadened the scope of natural language processing (NLP) applications, transcending their initial use in chatbot technology. This paper investigates the multifaceted applications of these models, with an emphasis on the GPT series. This exploration focuses on the transformative impact of artificial intelligence (AI) driven tools in revolutionizing traditional tasks like coding and problem-solving, while also paving new paths in research and development across diverse industries. From code interpretation and image captioning to facilitating the construction of interactive systems and advancing computational domains, Transformer models exemplify a synergy of deep learning, data analysis, and neural network design. This survey provides an in-depth look at the latest research in Transformer models, highlighting their versatility and the potential they hold for transforming diverse application sectors, thereby offering readers a comprehensive understanding of the current and future landscape of Transformer-based LLMs in practical applications.
5/29/2024
Large Language Models for Education: A Survey and Outlook
Shen Wang, Tianlong Xu, Hang Li, Chaoli Zhang, Joleen Liang, Jiliang Tang, Philip S. Yu, Qingsong Wen

0
0
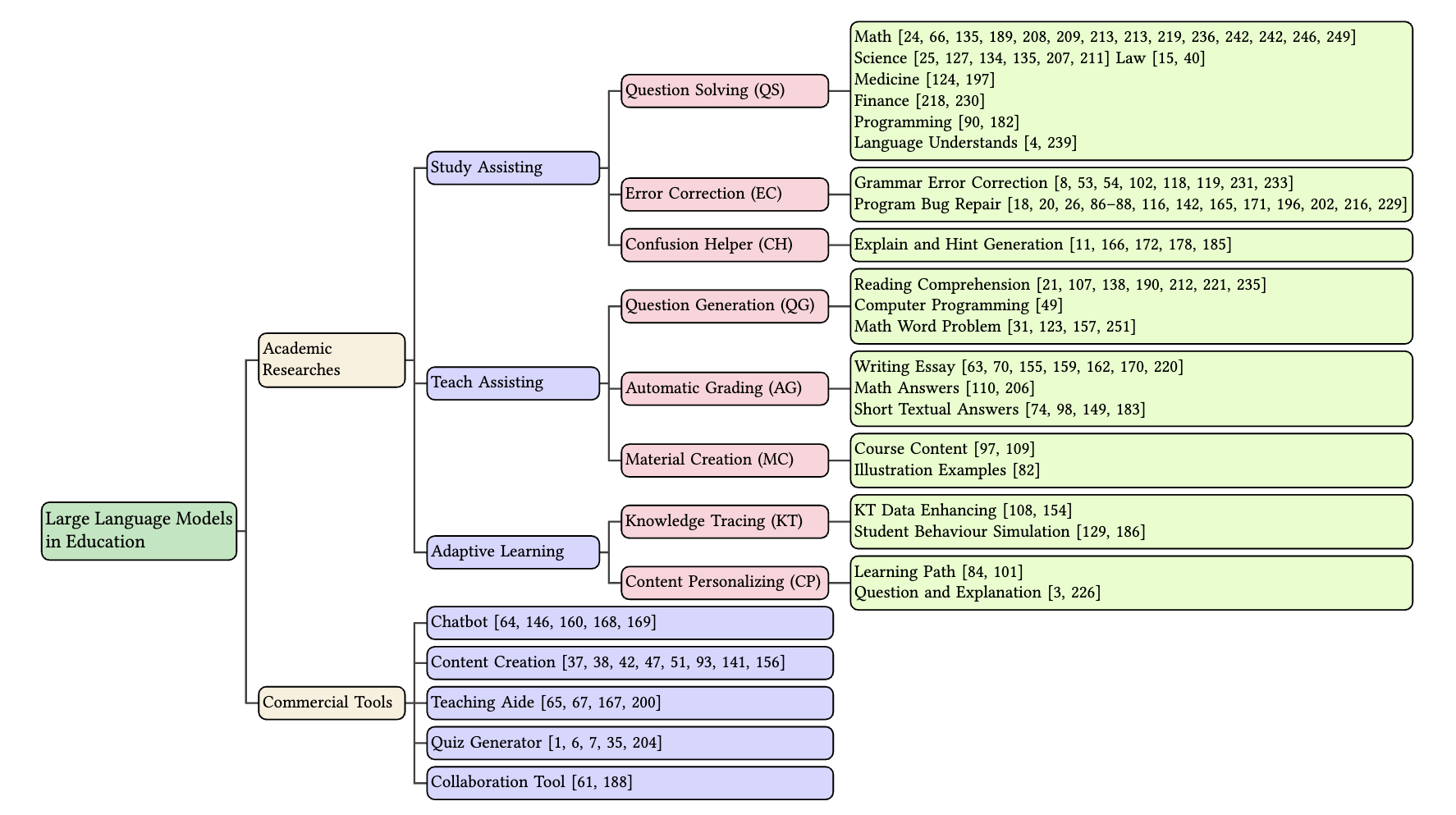
The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has brought in a new era of possibilities in the realm of education. This survey paper summarizes the various technologies of LLMs in educational settings from multifaceted perspectives, encompassing student and teacher assistance, adaptive learning, and commercial tools. We systematically review the technological advancements in each perspective, organize related datasets and benchmarks, and identify the risks and challenges associated with deploying LLMs in education. Furthermore, we outline future research opportunities, highlighting the potential promising directions. Our survey aims to provide a comprehensive technological picture for educators, researchers, and policymakers to harness the power of LLMs to revolutionize educational practices and foster a more effective personalized learning environment.
4/3/2024
💬
Large Language Models for Education: A Survey
Hanyi Xu, Wensheng Gan, Zhenlian Qi, Jiayang Wu, Philip S. Yu

0
0
Artificial intelligence (AI) has a profound impact on traditional education. In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have been increasingly used in various applications such as natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, and autonomous driving. LLMs have also been applied in many fields, including recommendation, finance, government, education, legal affairs, and finance. As powerful auxiliary tools, LLMs incorporate various technologies such as deep learning, pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning. The use of LLMs for smart education (LLMEdu) has been a significant strategic direction for countries worldwide. While LLMs have shown great promise in improving teaching quality, changing education models, and modifying teacher roles, the technologies are still facing several challenges. In this paper, we conduct a systematic review of LLMEdu, focusing on current technologies, challenges, and future developments. We first summarize the current state of LLMEdu and then introduce the characteristics of LLMs and education, as well as the benefits of integrating LLMs into education. We also review the process of integrating LLMs into the education industry, as well as the introduction of related technologies. Finally, we discuss the challenges and problems faced by LLMEdu, as well as prospects for future optimization of LLMEdu.
5/24/2024

AutoTutor meets Large Language Models: A Language Model Tutor with Rich Pedagogy and Guardrails
Sankalan Pal Chowdhury, Vil'em Zouhar, Mrinmaya Sachan

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have found several use cases in education, ranging from automatic question generation to essay evaluation. In this paper, we explore the potential of using Large Language Models (LLMs) to author Intelligent Tutoring Systems. A common pitfall of LLMs is their straying from desired pedagogical strategies such as leaking the answer to the student, and in general, providing no guarantees. We posit that while LLMs with certain guardrails can take the place of subject experts, the overall pedagogical design still needs to be handcrafted for the best learning results. Based on this principle, we create a sample end-to-end tutoring system named MWPTutor, which uses LLMs to fill in the state space of a pre-defined finite state transducer. This approach retains the structure and the pedagogy of traditional tutoring systems that has been developed over the years by learning scientists but brings in additional flexibility of LLM-based approaches. Through a human evaluation study on two datasets based on math word problems, we show that our hybrid approach achieves a better overall tutoring score than an instructed, but otherwise free-form, GPT-4. MWPTutor is completely modular and opens up the scope for the community to improve its performance by improving individual modules or using different teaching strategies that it can follow.
4/26/2024