Benchmarking Counterfactual Image Generation
2403.20287

0
0
🖼️
Abstract
Generative AI has revolutionised visual content editing, empowering users to effortlessly modify images and videos. However, not all edits are equal. To perform realistic edits in domains such as natural image or medical imaging, modifications must respect causal relationships inherent to the data generation process. Such image editing falls into the counterfactual image generation regime. Evaluating counterfactual image generation is substantially complex: not only it lacks observable ground truths, but also requires adherence to causal constraints. Although several counterfactual image generation methods and evaluation metrics exist, a comprehensive comparison within a unified setting is lacking. We present a comparison framework to thoroughly benchmark counterfactual image generation methods. We integrate all models that have been used for the task at hand and expand them to novel datasets and causal graphs, demonstrating the superiority of Hierarchical VAEs across most datasets and metrics. Our framework is implemented in a user-friendly Python package that can be extended to incorporate additional SCMs, causal methods, generative models, and datasets for the community to build on.
Create account to get full access
Introduction
Related work
Methodology
Results
Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Appendix
Appendix 0.A Experimental details
Appendix 0.B Qualitative results
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
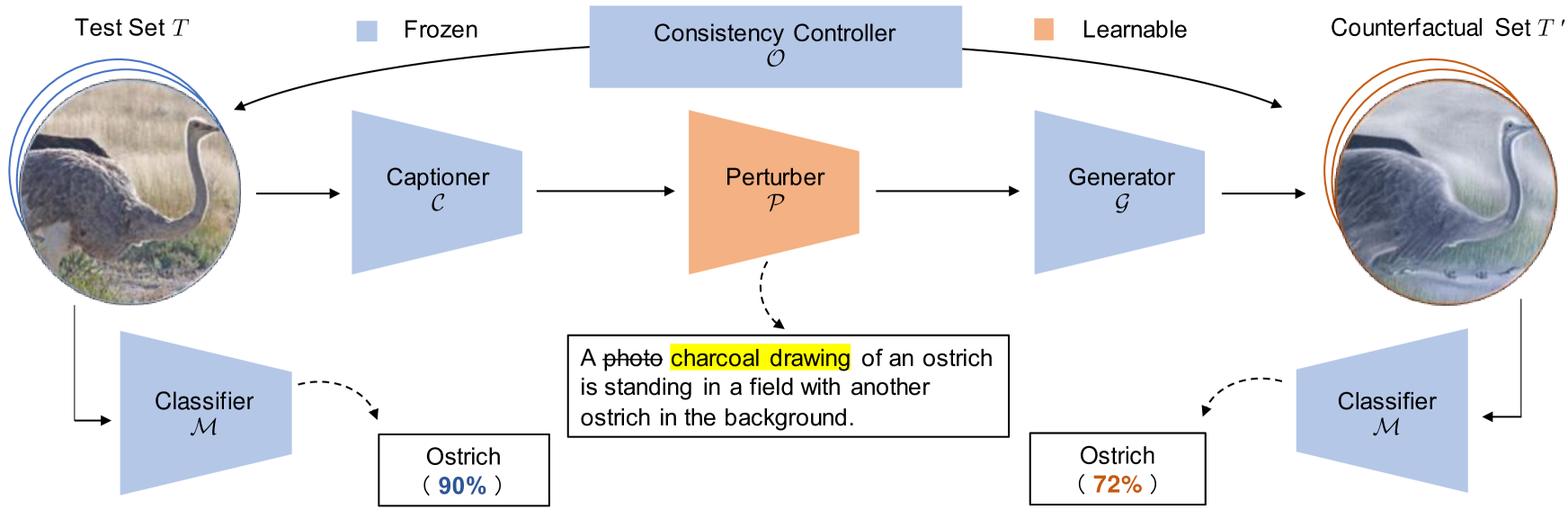
Reinforcing Pre-trained Models Using Counterfactual Images
Xiang Li, Ren Togo, Keisuke Maeda, Takahiro Ogawa, Miki Haseyama

0
0
This paper proposes a novel framework to reinforce classification models using language-guided generated counterfactual images. Deep learning classification models are often trained using datasets that mirror real-world scenarios. In this training process, because learning is based solely on correlations with labels, there is a risk that models may learn spurious relationships, such as an overreliance on features not central to the subject, like background elements in images. However, due to the black-box nature of the decision-making process in deep learning models, identifying and addressing these vulnerabilities has been particularly challenging. We introduce a novel framework for reinforcing the classification models, which consists of a two-stage process. First, we identify model weaknesses by testing the model using the counterfactual image dataset, which is generated by perturbed image captions. Subsequently, we employ the counterfactual images as an augmented dataset to fine-tune and reinforce the classification model. Through extensive experiments on several classification models across various datasets, we revealed that fine-tuning with a small set of counterfactual images effectively strengthens the model.
6/21/2024

CEval: A Benchmark for Evaluating Counterfactual Text Generation
Van Bach Nguyen, Jorg Schlotterer, Christin Seifert

0
0
Counterfactual text generation aims to minimally change a text, such that it is classified differently. Judging advancements in method development for counterfactual text generation is hindered by a non-uniform usage of data sets and metrics in related work. We propose CEval, a benchmark for comparing counterfactual text generation methods. CEval unifies counterfactual and text quality metrics, includes common counterfactual datasets with human annotations, standard baselines (MICE, GDBA, CREST) and the open-source language model LLAMA-2. Our experiments found no perfect method for generating counterfactual text. Methods that excel at counterfactual metrics often produce lower-quality text while LLMs with simple prompts generate high-quality text but struggle with counterfactual criteria. By making CEval available as an open-source Python library, we encourage the community to contribute more methods and maintain consistent evaluation in future work.
4/29/2024
🗣️
Counterfactual Generative Models for Time-Varying Treatments
Shenghao Wu, Wenbin Zhou, Minshuo Chen, Shixiang Zhu

0
0
Estimating the counterfactual outcome of treatment is essential for decision-making in public health and clinical science, among others. Often, treatments are administered in a sequential, time-varying manner, leading to an exponentially increased number of possible counterfactual outcomes. Furthermore, in modern applications, the outcomes are high-dimensional and conventional average treatment effect estimation fails to capture disparities in individuals. To tackle these challenges, we propose a novel conditional generative framework capable of producing counterfactual samples under time-varying treatment, without the need for explicit density estimation. Our method carefully addresses the distribution mismatch between the observed and counterfactual distributions via a loss function based on inverse probability re-weighting, and supports integration with state-of-the-art conditional generative models such as the guided diffusion and conditional variational autoencoder. We present a thorough evaluation of our method using both synthetic and real-world data. Our results demonstrate that our method is capable of generating high-quality counterfactual samples and outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines.
6/18/2024

Towards Characterizing Domain Counterfactuals For Invertible Latent Causal Models
Zeyu Zhou, Ruqi Bai, Sean Kulinski, Murat Kocaoglu, David I. Inouye

0
0
Answering counterfactual queries has important applications such as explainability, robustness, and fairness but is challenging when the causal variables are unobserved and the observations are non-linear mixtures of these latent variables, such as pixels in images. One approach is to recover the latent Structural Causal Model (SCM), which may be infeasible in practice due to requiring strong assumptions, e.g., linearity of the causal mechanisms or perfect atomic interventions. Meanwhile, more practical ML-based approaches using naive domain translation models to generate counterfactual samples lack theoretical grounding and may construct invalid counterfactuals. In this work, we strive to strike a balance between practicality and theoretical guarantees by analyzing a specific type of causal query called domain counterfactuals, which hypothesizes what a sample would have looked like if it had been generated in a different domain (or environment). We show that recovering the latent SCM is unnecessary for estimating domain counterfactuals, thereby sidestepping some of the theoretic challenges. By assuming invertibility and sparsity of intervention, we prove domain counterfactual estimation error can be bounded by a data fit term and intervention sparsity term. Building upon our theoretical results, we develop a theoretically grounded practical algorithm that simplifies the modeling process to generative model estimation under autoregressive and shared parameter constraints that enforce intervention sparsity. Finally, we show an improvement in counterfactual estimation over baseline methods through extensive simulated and image-based experiments.
4/16/2024