Bridging Paintings and Music -- Exploring Emotion based Music Generation through Paintings

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Explores the connection between visual art and music through emotion-based music generation from paintings
- Proposes a novel transformer-based model that generates music based on the emotional content of input images
- Demonstrates the model's ability to generate diverse and expressive music that aligns with the emotional themes of the paintings
Plain English Explanation
This research paper explores the intriguing relationship between visual art and music. The key idea is to use the emotional content of paintings as a basis for generating corresponding musical compositions. The researchers developed a transformer-based model that can take an input painting and produce an original music piece that is thematically aligned with the emotional themes and moods expressed in the visual artwork.
The core concept is that certain visual elements, such as color, composition, and subject matter, can evoke specific emotional responses in the viewer. The researchers hypothesized that these emotional cues could be extracted from paintings and then used to guide the generation of expressive, emotion-driven music. By bridging the worlds of visual art and music, this approach offers a unique and creative way to explore the connections between different artistic media and the human experience of emotion.
Technical Explanation
The researchers proposed a novel transformer-based model that takes a painting as input and generates a corresponding music piece. The model consists of several key components:
-
Image Encoder: This module processes the input painting and extracts visual features that are relevant to emotional expression. This includes things like color, texture, and composition.
-
Emotion Predictor: The extracted visual features are then used to predict the emotional content of the painting, such as valence (positivity/negativity) and arousal (intensity).
-
Music Decoder: The predicted emotional attributes are then used to guide the generation of a music piece that aligns with the emotional themes of the painting. This involves generating a sequence of musical notes, chords, and rhythms that evoke the desired emotional response.
The researchers trained and evaluated their model on a dataset of paintings paired with corresponding music compositions. The results demonstrate that the model is able to generate diverse and expressive music that captures the emotional essence of the input paintings. This suggests that there are meaningful connections between the visual and auditory domains that can be leveraged for creative applications.
Critical Analysis
The research presents an intriguing and promising approach to bridging the gap between visual art and music. By focusing on the emotional aspects of both mediums, the researchers have developed a novel way to generate music that is thematically linked to input paintings.
One potential limitation is the reliance on the dataset used for training and evaluation. The quality and diversity of the painting-music pairings could significantly impact the model's performance and the types of music it is able to generate. Further research may be needed to explore the generalizability of the approach to a wider range of artistic styles and emotional expressions.
Additionally, the researchers acknowledge that the evaluation of the generated music is inherently subjective, as perceptions of emotional alignment between the visuals and audio can vary greatly between individuals. Incorporating more robust and objective evaluation metrics could help strengthen the conclusions drawn from the study.
Overall, this research represents an exciting step forward in the field of generative AI, demonstrating the potential to leverage cross-modal relationships for creative and expressive applications. As the technology continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how the approach could be further refined and applied in real-world settings, such as interactive art installations or music composition tools.
Conclusion
This research paper presents a novel approach to emotion-based music generation, where a transformer-based model is used to create musical compositions that align with the emotional themes expressed in input paintings. The results suggest that there are meaningful connections between visual art and music that can be leveraged for creative applications.
The work highlights the potential of cross-modal generative AI to bridge the gap between different artistic mediums and explore the relationships between visual, auditory, and emotional experiences. As the field continues to advance, this type of research could lead to new and innovative ways for artists, musicians, and the general public to engage with and express their emotions through integrated artistic experiences.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Bridging Paintings and Music -- Exploring Emotion based Music Generation through Paintings
Tanisha Hisariya, Huan Zhang, Jinhua Liang
Rapid advancements in artificial intelligence have significantly enhanced generative tasks involving music and images, employing both unimodal and multimodal approaches. This research develops a model capable of generating music that resonates with the emotions depicted in visual arts, integrating emotion labeling, image captioning, and language models to transform visual inputs into musical compositions. Addressing the scarcity of aligned art and music data, we curated the Emotion Painting Music Dataset, pairing paintings with corresponding music for effective training and evaluation. Our dual-stage framework converts images to text descriptions of emotional content and then transforms these descriptions into music, facilitating efficient learning with minimal data. Performance is evaluated using metrics such as Fr'echet Audio Distance (FAD), Total Harmonic Distortion (THD), Inception Score (IS), and KL divergence, with audio-emotion text similarity confirmed by the pre-trained CLAP model to demonstrate high alignment between generated music and text. This synthesis tool bridges visual art and music, enhancing accessibility for the visually impaired and opening avenues in educational and therapeutic applications by providing enriched multi-sensory experiences.
Read more9/14/2024

0
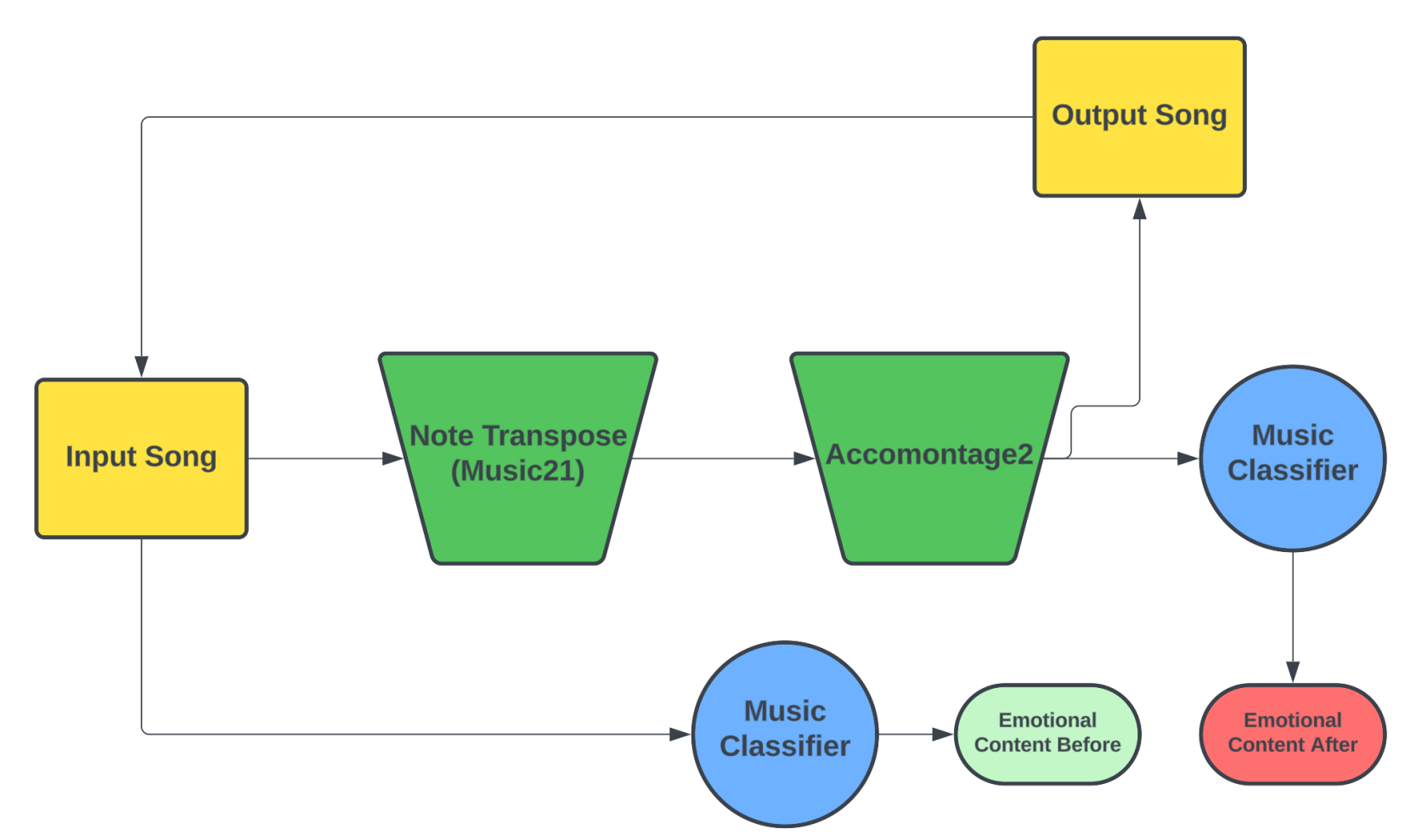
Emotion Manipulation Through Music -- A Deep Learning Interactive Visual Approach
Adel N. Abdalla, Jared Osborne, Razvan Andonie
Music evokes emotion in many people. We introduce a novel way to manipulate the emotional content of a song using AI tools. Our goal is to achieve the desired emotion while leaving the original melody as intact as possible. For this, we create an interactive pipeline capable of shifting an input song into a diametrically opposed emotion and visualize this result through Russel's Circumplex model. Our approach is a proof-of-concept for Semantic Manipulation of Music, a novel field aimed at modifying the emotional content of existing music. We design a deep learning model able to assess the accuracy of our modifications to key, SoundFont instrumentation, and other musical features. The accuracy of our model is in-line with the current state of the art techniques on the 4Q Emotion dataset. With further refinement, this research may contribute to on-demand custom music generation, the automated remixing of existing work, and music playlists tuned for emotional progression.
Read more6/14/2024


0
Emotion-driven Piano Music Generation via Two-stage Disentanglement and Functional Representation
Jingyue Huang, Ke Chen, Yi-Hsuan Yang
Managing the emotional aspect remains a challenge in automatic music generation. Prior works aim to learn various emotions at once, leading to inadequate modeling. This paper explores the disentanglement of emotions in piano performance generation through a two-stage framework. The first stage focuses on valence modeling of lead sheet, and the second stage addresses arousal modeling by introducing performance-level attributes. To further capture features that shape valence, an aspect less explored by previous approaches, we introduce a novel functional representation of symbolic music. This representation aims to capture the emotional impact of major-minor tonality, as well as the interactions among notes, chords, and key signatures. Objective and subjective experiments validate the effectiveness of our framework in both emotional valence and arousal modeling. We further leverage our framework in a novel application of emotional controls, showing a broad potential in emotion-driven music generation.
Read more7/31/2024
🤖

0
Robot Synesthesia: A Sound and Emotion Guided AI Painter
Vihaan Misra, Peter Schaldenbrand, Jean Oh
If a picture paints a thousand words, sound may voice a million. While recent robotic painting and image synthesis methods have achieved progress in generating visuals from text inputs, the translation of sound into images is vastly unexplored. Generally, sound-based interfaces and sonic interactions have the potential to expand accessibility and control for the user and provide a means to convey complex emotions and the dynamic aspects of the real world. In this paper, we propose an approach for using sound and speech to guide a robotic painting process, known here as robot synesthesia. For general sound, we encode the simulated paintings and input sounds into the same latent space. For speech, we decouple speech into its transcribed text and the tone of the speech. Whereas we use the text to control the content, we estimate the emotions from the tone to guide the mood of the painting. Our approach has been fully integrated with FRIDA, a robotic painting framework, adding sound and speech to FRIDA's existing input modalities, such as text and style. In two surveys, participants were able to correctly guess the emotion or natural sound used to generate a given painting more than twice as likely as random chance. On our sound-guided image manipulation and music-guided paintings, we discuss the results qualitatively.
Read more5/27/2024