CloudSim 7G: An Integrated Toolkit for Modeling and Simulation of Future Generation Cloud Computing Environments

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- CloudSim 7G is an integrated toolkit for modeling and simulating future generation cloud computing environments.
- It provides a comprehensive platform for researchers and developers to design and evaluate their cloud computing infrastructure, applications, and services.
- The toolkit includes features for simulating various cloud computing components, such as data centers, virtual machines, and network topologies.
Plain English Explanation
CloudSim 7G is a software tool that allows researchers and developers to create detailed models and simulations of cloud computing systems. It helps them understand how these complex systems will work and perform without having to build the actual infrastructure.
The tool can simulate different components of a cloud computing environment, such as the data centers that store and process data, the virtual machines that run applications, and the network connections that transfer data between them. This allows researchers to experiment with different cloud configurations and workloads to see how they might behave in the real world.
Technical Explanation
CloudSim 7G is designed to model and simulate the components of future generation cloud computing environments. It includes features for representing data centers, virtual machines, and network topologies. Researchers can use the toolkit to design and evaluate their cloud infrastructure, applications, and services without having to build the actual system.
The toolkit provides a range of customization options, allowing users to specify the hardware and software configurations of the cloud components. It also supports the simulation of various resource management and scheduling policies, enabling the exploration of different strategies for allocating resources and running workloads.
Critical Analysis
The paper does not provide a comprehensive evaluation of the CloudSim 7G toolkit's performance or limitations. While it highlights the tool's features and capabilities, there is limited discussion of the accuracy of the simulations or the computational overhead required to run them.
Additionally, the paper does not address potential issues with the scalability of the toolkit as the simulated cloud environments become more complex. It would be important to understand how CloudSim 7G handles large-scale, heterogeneous cloud systems and the challenges that may arise in such scenarios.
Further research could explore the integration of CloudSim 7G with other cloud simulation or emulation tools, as well as its applicability to emerging cloud computing paradigms, such as edge computing and serverless architectures.
Conclusion
CloudSim 7G is a comprehensive toolkit that enables researchers and developers to model and simulate future generation cloud computing environments. By providing a flexible platform for experimenting with cloud infrastructure, applications, and services, the tool can help inform the design and deployment of real-world cloud systems.
While the paper highlights the toolkit's capabilities, further research and evaluation are needed to assess its practical limitations and potential areas for improvement. Nonetheless, CloudSim 7G represents an important step forward in the field of cloud computing simulation and can contribute to the development of more efficient and reliable cloud-based solutions.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
CloudSim 7G: An Integrated Toolkit for Modeling and Simulation of Future Generation Cloud Computing Environments
Remo Andreoli, Jie Zhao, Tommaso Cucinotta, Rajkumar Buyya
Cloud Computing has established itself as an efficient and cost-effective paradigm for the execution of web-based applications, and scientific workloads, that need elasticity and on-demand scalability capabilities. However, the evaluation of novel resource provisioning and management techniques is a major challenge due to the complexity of large-scale data centers. Therefore, Cloud simulators are an essential tool for academic and industrial researchers, to investigate on the effectiveness of novel algorithms and mechanisms in large-scale scenarios. This article unveils CloudSim7G, the seventh generation of CloudSim, one of the first simulators specialized in evaluating resource management techniques for Cloud infrastructures. In particular, CloudSim7G features a re-engineered and generalized internal architecture to facilitate the integration of multiple CloudSim extensions, which were previously available independently and often had compatibility issues, within the same simulated environment. Such architectural change is coupled with an extensive refactoring and refinement of the codebase, leading to the removal of over 13,000 lines of code without loss of functionality. As a result, CloudSim7G delivers significantly better performance in both run-time and total memory allocated (up to ~20% less heap memory allocated), along with increased flexibility, ease-of-use, and extensibility of the framework. These improvements benefit not only CloudSim developers but also researchers and practitioners using the framework for modeling and simulating next-generation cloud computing environments.
Read more8/27/2024

0
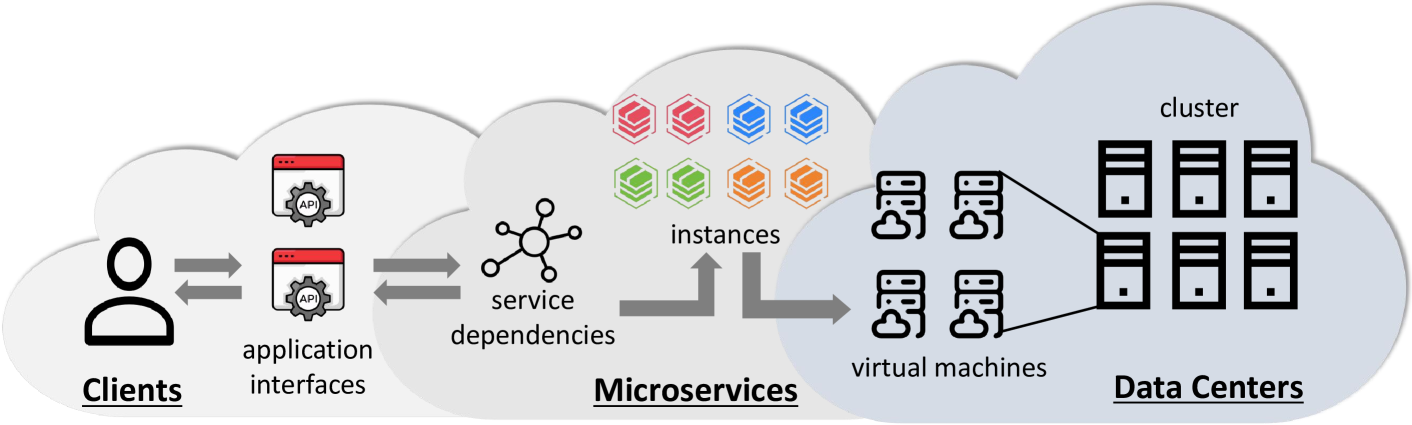
CloudNativeSim: a toolkit for modeling and simulation of cloud-native applications
Jingfeng Wu, Minxian Xu, Yiyuan He, Kejiang Ye, Chengzhong Xu
Cloud-native applications are increasingly becoming popular in modern software design. Employing a microservice-based architecture into these applications is a prevalent strategy that enhances system availability and flexibility. However, cloud-native applications also introduce new challenges, such as frequent inter-service communication and the complexity of managing heterogeneous codebases and hardware, resulting in unpredictable complexity and dynamism. Furthermore, as applications scale, only limited research teams or enterprises possess the resources for large-scale deployment and testing, which impedes progress in the cloud-native domain. To address these challenges, we propose CloudNativeSim, a simulator for cloud-native applications with a microservice-based architecture. CloudNativeSim offers several key benefits: (i) comprehensive and dynamic modeling for cloud-native applications, (ii) an extended simulation framework with new policy interfaces for scheduling cloud-native applications, and (iii) support for customized application scenarios and user feedback based on Quality of Service (QoS) metrics. CloudNativeSim can be easily deployed on standard computers to manage a high volume of requests and services. Its performance was validated through a case study, demonstrating higher than 94.5% accuracy in terms of response time. The study further highlights the feasibility of CloudNativeSim by illustrating the effects of various scaling policies.
Read more9/10/2024

0
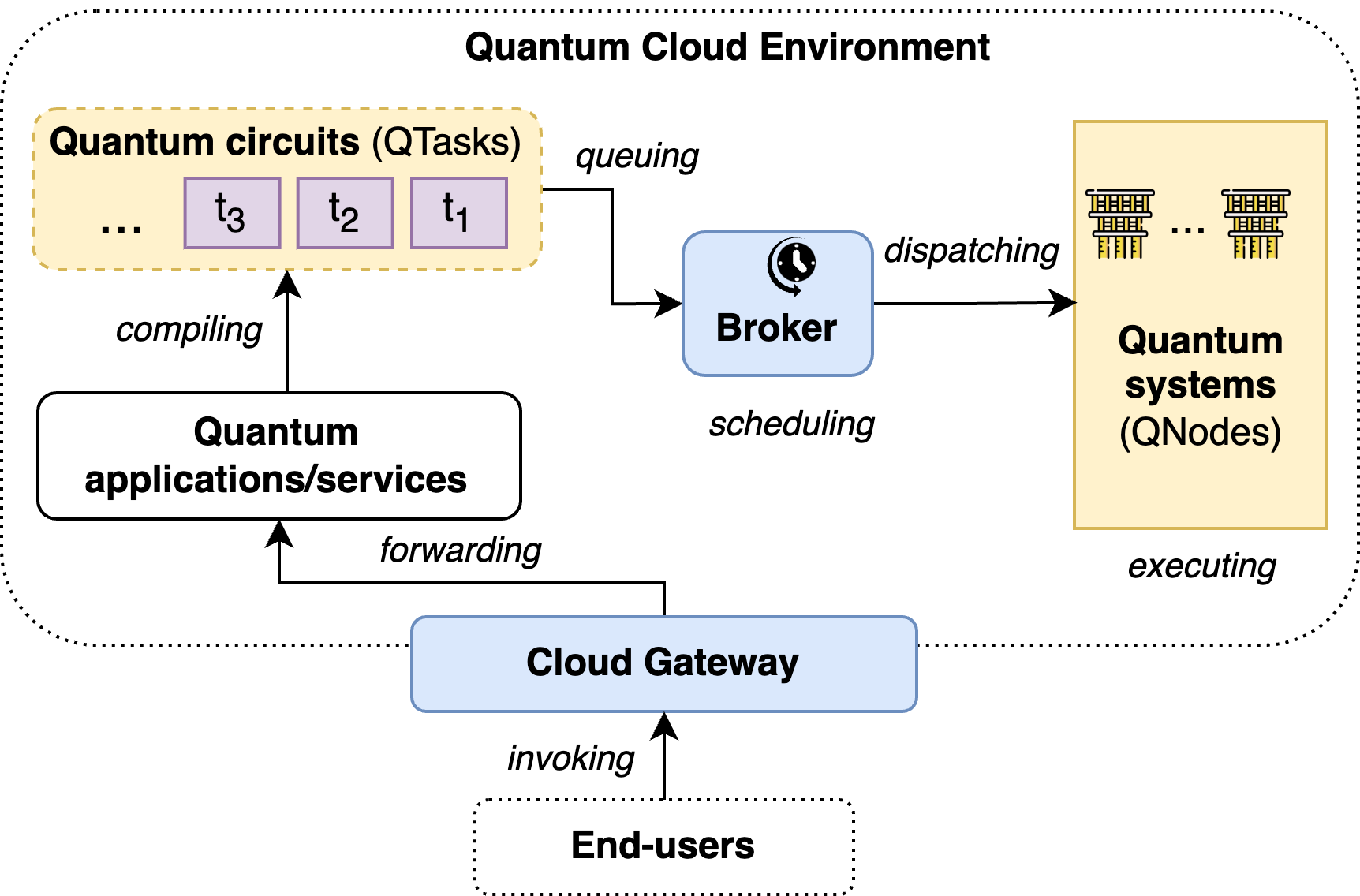
QSimPy: A Learning-centric Simulation Framework for Quantum Cloud Resource Management
Hoa T. Nguyen, Muhammad Usman, Rajkumar Buyya
Quantum cloud computing is an emerging computing paradigm that allows seamless access to quantum hardware as cloud-based services. However, effective use of quantum resources is challenging and necessitates robust simulation frameworks for effective resource management design and evaluation. To address this need, we proposed QSimPy, a novel discrete-event simulation framework designed with the main focus of facilitating learning-centric approaches for quantum resource management problems in cloud environments. Underpinned by extensibility, compatibility, and reusability principles, QSimPy provides a lightweight simulation environment based on SimPy, a well-known Python-based simulation engine for modeling dynamics of quantum cloud resources and task operations. We integrate the Gymnasium environment into our framework to support the creation of simulated environments for developing and evaluating reinforcement learning-based techniques for optimizing quantum cloud resource management. The QSimPy framework encapsulates the operational intricacies of quantum cloud environments, supporting research in dynamic task allocation and optimization through DRL approaches. We also demonstrate the use of QSimPy in developing reinforcement learning policies for quantum task placement problems, demonstrating its potential as a useful framework for future quantum cloud research.
Read more5/3/2024


0
AirCompSim: A Discrete Event Simulator for Air Computing
Baris Yamansavascilar, Atay Ozgovde, Cem Ersoy
Air components, including UAVs, planes, balloons, and satellites have been widely utilized since the fixed capacity of ground infrastructure cannot meet the dynamic load of the users. However, since those air components should be coordinated in order to achieve the desired quality of service, several next-generation paradigms have been defined including air computing. Nevertheless, even though many studies and open research issues exist for air computing, there are limited test environments that cannot satisfy the performance evaluation requirements of the dynamic environment. Therefore, in this study, we introduce our discrete event simulator, AirCompSim, which fulfills an air computing environment considering dynamically changing requirements, loads, and capacities through its modular structure. To show its capabilities, a dynamic capacity enhancement scenario is used for investigating the effect of the number of users, UAVs, and requirements of different application types on the average task success rate, service time, and server utilization. The results demonstrate that AirCompSim can be used for experiments in air computing.
Read more9/4/2024