Comparative Analysis of Advanced Feature Matching Algorithms in Challenging High Spatial Resolution Optical Satellite Stereo Scenarios
2405.06246

0
0
✨
Abstract
Feature matching determines the orientation accuracy for the High Spatial Resolution (HSR) optical satellite stereos, subsequently impacting several significant applications such as 3D reconstruction and change detection. However, the matching of off-track HSR optical satellite stereos often encounters challenging conditions including wide-baseline observation, significant radiometric differences, multi-temporal changes, varying spatial resolutions, inconsistent spectral resolution, and diverse sensors. In this study, we evaluate various advanced feature matching algorithms for HSR optical satellite stereos. Utilizing a specially constructed dataset from five satellites across six challenging scenarios, HSROSS Dataset, we conduct a comparative analysis of four algorithms: the traditional SIFT, and deep-learning based methods including SuperPoint + SuperGlue, SuperPoint + LightGlue, and LoFTR. Our findings highlight overall superior performance of SuperPoint + LightGlue in balancing robustness, accuracy, distribution, and efficiency, showcasing its potential in complex HSR optical satellite scenarios.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Evaluates various feature matching algorithms for high spatial resolution (HSR) optical satellite stereo images
- Focuses on challenging conditions like wide-baseline, radiometric differences, multi-temporal changes, varying resolutions, and diverse sensors
- Compares traditional SIFT and deep learning-based methods like SuperPoint + SuperGlue, SuperPoint + LightGlue, and LoFTR
- Identifies SuperPoint + LightGlue as the overall top performer, balancing robustness, accuracy, distribution, and efficiency
Plain English Explanation
Matching features, or identifying the same points in multiple images, is crucial for several important applications using high-resolution satellite imagery, such as 3D reconstruction and change detection. However, this task can be very challenging when dealing with satellite stereo images captured under diverse conditions, like wide camera angles, differences in lighting, changes over time, and varying camera resolutions and sensors.
This study evaluates several advanced feature matching algorithms to determine which ones work best for these complex satellite image scenarios. The researchers created a specialized dataset, called the HSROSS Dataset, which includes images from five different satellites across six challenging conditions. They then compared the performance of traditional SIFT and newer deep learning-based methods like SuperPoint + SuperGlue, SuperPoint + LightGlue, and LoFTR.
The results show that the SuperPoint + LightGlue approach outperforms the others, providing a good balance of robustness, accuracy, distribution, and efficiency. This makes it a promising option for tackling complex feature matching tasks in high-resolution satellite imagery, which are vital for applications like 3D reconstruction and change detection.
Technical Explanation
The researchers constructed the HSROSS Dataset, which includes stereo image pairs from five different high spatial resolution (HSR) optical satellites across six challenging scenarios: wide-baseline, significant radiometric differences, multi-temporal changes, varying spatial resolutions, inconsistent spectral resolution, and diverse sensors.
They then evaluated the performance of four feature matching algorithms on this dataset:
- SIFT: A traditional feature detection and description method
- SuperPoint + SuperGlue: A deep learning-based approach that uses SuperPoint for feature detection and SuperGlue for feature matching
- SuperPoint + LightGlue: Similar to the above, but uses a lighter-weight version of SuperGlue for matching
- LoFTR: Another deep learning-based method that uses a Transformer-based architecture for feature matching
The key metrics assessed were robustness, accuracy, distribution, and efficiency. The results showed that SuperPoint + LightGlue achieved the best overall performance, demonstrating strong capabilities in handling the diverse and challenging conditions present in the HSROSS Dataset.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive evaluation of feature matching algorithms for HSR optical satellite stereo images, which is an important and practical problem. The creation of the HSROSS Dataset is a valuable contribution, as it offers a standardized benchmark for assessing algorithm performance under realistic and complex satellite imaging scenarios.
However, the paper does not discuss potential limitations or caveats of the study. For example, it would be helpful to know the specific geographic regions and land cover types represented in the dataset, as this could impact the generalizability of the results. Additionally, the paper does not address potential biases in the dataset or how representative it is of real-world satellite imaging conditions.
Furthermore, the paper could have delved deeper into the inner workings of the algorithms and why SuperPoint + LightGlue outperformed the other methods. Providing more insights into the strengths and weaknesses of each approach would help readers better understand the trade-offs and make more informed decisions when selecting a feature matching algorithm for their own satellite imaging applications.
Conclusion
This study offers a robust evaluation of feature matching algorithms for high-resolution satellite stereo imagery, highlighting the superior performance of the SuperPoint + LightGlue approach. The findings have important implications for a wide range of satellite-based applications, such as 3D reconstruction, change detection, and urban planning. As satellite imaging continues to advance, developing robust and efficient feature matching methods will be crucial for unlocking the full potential of these powerful tools.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🖼️
SAR image matching algorithm based on multi-class features
Mazhi Qiang, Fengming Zhou

0
0
Synthetic aperture radar has the ability to work 24/7 and 24/7, and has high application value. Propose a new SAR image matching algorithm based on multi class features, mainly using two different types of features: straight lines and regions to enhance the robustness of the matching algorithm; On the basis of using prior knowledge of images, combined with LSD (Line Segment Detector) line detection and template matching algorithm, by analyzing the attribute correlation between line and surface features in SAR images, selecting line and region features in SAR images to match the images, the matching accuracy between SAR images and visible light images is improved, and the probability of matching errors is reduced. The experimental results have verified that this algorithm can obtain high-precision matching results, achieve precise target positioning, and has good robustness to changes in perspective and lighting. The results are accurate and false positives are controllable.
5/7/2024
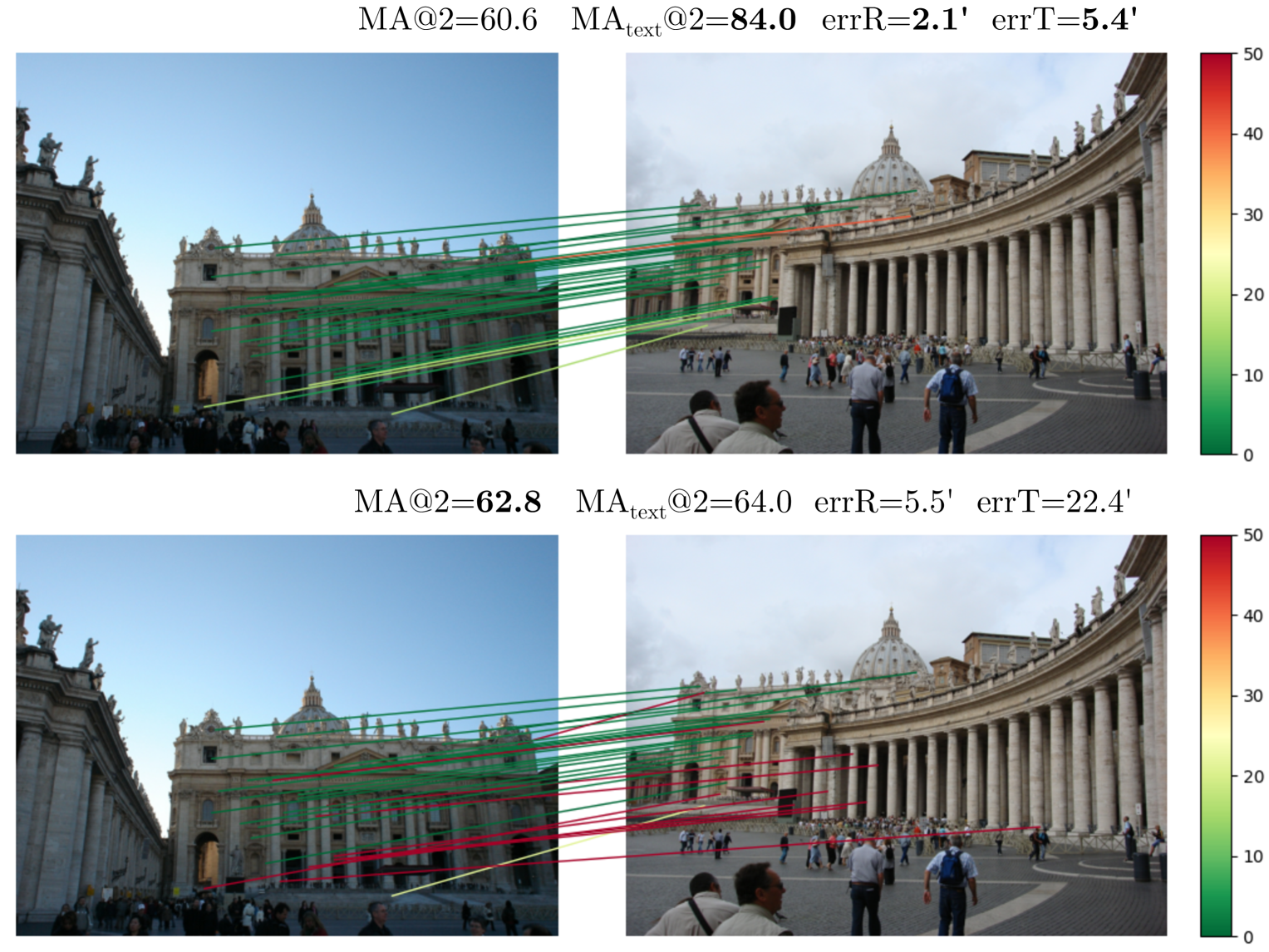
Are Semi-Dense Detector-Free Methods Good at Matching Local Features?
Matthieu Vilain, R'emi Giraud, Hugo Germain, Guillaume Bourmaud

0
0
Semi-dense detector-free approaches (SDF), such as LoFTR, are currently among the most popular image matching methods. While SDF methods are trained to establish correspondences between two images, their performances are almost exclusively evaluated using relative pose estimation metrics. Thus, the link between their ability to establish correspondences and the quality of the resulting estimated pose has thus far received little attention. This paper is a first attempt to study this link. We start with proposing a novel structured attention-based image matching architecture (SAM). It allows us to show a counter-intuitive result on two datasets (MegaDepth and HPatches): on the one hand SAM either outperforms or is on par with SDF methods in terms of pose/homography estimation metrics, but on the other hand SDF approaches are significantly better than SAM in terms of matching accuracy. We then propose to limit the computation of the matching accuracy to textured regions, and show that in this case SAM often surpasses SDF methods. Our findings highlight a strong correlation between the ability to establish accurate correspondences in textured regions and the accuracy of the resulting estimated pose/homography. Our code will be made available.
6/4/2024

A Semantic Segmentation-guided Approach for Ground-to-Aerial Image Matching
Francesco Pro, Nikolaos Dionelis, Luca Maiano, Bertrand Le Saux, Irene Amerini

0
0
Nowadays the accurate geo-localization of ground-view images has an important role across domains as diverse as journalism, forensics analysis, transports, and Earth Observation. This work addresses the problem of matching a query ground-view image with the corresponding satellite image without GPS data. This is done by comparing the features from a ground-view image and a satellite one, innovatively leveraging the corresponding latter's segmentation mask through a three-stream Siamese-like network. The proposed method, Semantic Align Net (SAN), focuses on limited Field-of-View (FoV) and ground panorama images (images with a FoV of 360{deg}). The novelty lies in the fusion of satellite images in combination with their semantic segmentation masks, aimed at ensuring that the model can extract useful features and focus on the significant parts of the images. This work shows how SAN through semantic analysis of images improves the performance on the unlabelled CVUSA dataset for all the tested FoVs.
5/24/2024
🌿
Advancing Applications of Satellite Photogrammetry: Novel Approaches for Built-up Area Modeling and Natural Environment Monitoring using Stereo/Multi-view Satellite Image-derived 3D Data
Shengxi Gui

0
0
With the development of remote sensing technology in recent decades, spaceborne sensors with sub-meter and meter spatial resolution (Worldview and PlanetScope) have achieved a considerable image quality to generate 3D geospatial data via a stereo matching pipeline. These achievements have significantly increased the data accessibility in 3D, necessitating adapting these 3D geospatial data to analyze human and natural environments. This dissertation explores several novel approaches based on stereo and multi-view satellite image-derived 3D geospatial data, to deal with remote sensing application issues for built-up area modeling and natural environment monitoring, including building model 3D reconstruction, glacier dynamics tracking, and lake algae monitoring. Specifically, the dissertation introduces four parts of novel approaches that deal with the spatial and temporal challenges with satellite-derived 3D data. The first study advances LoD-2 building modeling from satellite-derived Orthophoto and DSMs with a novel approach employing a model-driven workflow that generates building rectangular 3D geometry models. Secondly, we further enhanced our building reconstruction framework for dense urban areas and non-rectangular purposes, we implemented deep learning for unit-level segmentation and introduced a gradient-based circle reconstruction for circular buildings to develop a polygon composition technique for advanced building LoD2 reconstruction. Our third study utilizes high-spatiotemporal resolution PlanetScope satellite imagery for glacier tracking at 3D level in mid-latitude regions. Finally, we proposed a term as Algal Behavior Function to refine the quantification of chlorophyll-a concentrations from satellite imagery in water quality monitoring, addressing algae fluctuations and timing discrepancies between satellite observations and field measurements, thus enhancing the precision of underwater algae volume estimates. Overall, this dissertation demonstrates the extensive potential of satellite photogrammetry applications in addressing urban and environmental challenges. It further showcases innovative analytical methodologies that enhance the applicability of adapting stereo and multi-view very high-resolution satellite-derived 3D data. (See full abstract in the document)
4/22/2024