A Comprehensive Survey of Scientific Large Language Models and Their Applications in Scientific Discovery
2406.10833

0
0

Abstract
In many scientific fields, large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized the way with which text and other modalities of data (e.g., molecules and proteins) are dealt, achieving superior performance in various applications and augmenting the scientific discovery process. Nevertheless, previous surveys on scientific LLMs often concentrate on one to two fields or a single modality. In this paper, we aim to provide a more holistic view of the research landscape by unveiling cross-field and cross-modal connections between scientific LLMs regarding their architectures and pre-training techniques. To this end, we comprehensively survey over 250 scientific LLMs, discuss their commonalities and differences, as well as summarize pre-training datasets and evaluation tasks for each field and modality. Moreover, we investigate how LLMs have been deployed to benefit scientific discovery. Resources related to this survey are available at https://github.com/yuzhimanhua/Awesome-Scientific-Language-Models.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Comprehensive survey of scientific large language models (LLMs) and their applications in scientific discovery
- Covers a wide range of topics, including LLMs in general science, medicine, efficient LLM design, and LLM multilingualism
- Provides insights into the current state of LLM research and development, as well as potential future directions
Plain English Explanation
This paper is a detailed review of large language models (LLMs) and how they are being used in scientific research and discovery. LLMs are a type of artificial intelligence that can process and generate human-like text. The researchers looked at how LLMs are being applied across different scientific domains, such as general science, medicine, and efficient LLM design. They also examined the latest advancements in using LLMs for multilingual tasks.
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of LLM research and development, highlighting both the promising applications of these models in scientific discovery as well as some of the challenges and limitations that researchers are working to address. By summarizing the key findings and insights from a wide range of studies, the authors aim to help readers better understand the potential of LLMs to revolutionize scientific research and exploration.
Technical Explanation
The researchers conducted a thorough review of the existing literature on scientific LLMs, examining their architecture, training methods, and applications across various scientific domains. For general science, they looked at how LLMs can be used for tasks like text generation, question answering, and knowledge extraction. In the medical field, they explored the use of LLMs for drug discovery, clinical decision support, and medical text analysis.
The paper also delves into techniques for designing more efficient LLMs, such as parameter sharing and knowledge distillation, which can help reduce the computational and memory requirements of these models without sacrificing performance. Additionally, the researchers examined the latest advancements in using LLMs for multilingual tasks, which is crucial for expanding the reach and accessibility of scientific knowledge.
Throughout the paper, the authors highlight the key insights and findings from the reviewed studies, providing a comprehensive understanding of the current state of scientific LLM research and the potential future directions for this field.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough and well-researched overview of the current state of scientific LLM research, covering a wide range of applications and advancements. However, the authors also acknowledge some of the limitations and challenges associated with these models, such as the need for larger and more diverse training datasets, the potential for bias and fairness issues, and the computational and energy demands of training and deploying LLMs.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the ethical considerations and potential societal implications of the widespread adoption of LLMs in scientific research and discovery. As these models become more prevalent, it will be crucial for researchers to carefully examine the potential risks and develop appropriate safeguards and governance frameworks to ensure that the use of LLMs in science is aligned with ethical principles and societal values.
Overall, this paper serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners working in the field of scientific LLMs, but it also highlights the need for continued critical analysis and further research to address the lingering challenges and potential pitfalls associated with these powerful AI models.
Conclusion
This comprehensive survey of scientific large language models (LLMs) and their applications in scientific discovery provides a detailed and insightful overview of the current state of this rapidly evolving field. The researchers have done an excellent job of synthesizing the existing literature, highlighting the key advancements and insights across a range of scientific domains, from general science to medicine to efficient LLM design and multilingualism.
The paper's findings suggest that LLMs hold tremendous potential to revolutionize scientific research and discovery, enabling more efficient and effective approaches to tasks like text generation, question answering, and knowledge extraction. However, the authors also acknowledge the ongoing challenges and limitations of these models, such as the need for larger and more diverse training data, the potential for bias and fairness issues, and the computational demands of training and deploying LLMs.
As the field of scientific LLMs continues to evolve, it will be crucial for researchers, policymakers, and the broader scientific community to engage in ongoing critical analysis and discussion to ensure that the development and deployment of these models is aligned with ethical principles and societal values. By doing so, we can harness the power of LLMs to drive scientific progress while mitigating the potential risks and unintended consequences.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬
A Comprehensive Survey of Large Language Models and Multimodal Large Language Models in Medicine
Hanguang Xiao, Feizhong Zhou, Xingyue Liu, Tianqi Liu, Zhipeng Li, Xin Liu, Xiaoxuan Huang

0
0
Since the release of ChatGPT and GPT-4, large language models (LLMs) and multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have garnered significant attention due to their powerful and general capabilities in understanding, reasoning, and generation, thereby offering new paradigms for the integration of artificial intelligence with medicine. This survey comprehensively overviews the development background and principles of LLMs and MLLMs, as well as explores their application scenarios, challenges, and future directions in medicine. Specifically, this survey begins by focusing on the paradigm shift, tracing the evolution from traditional models to LLMs and MLLMs, summarizing the model structures to provide detailed foundational knowledge. Subsequently, the survey details the entire process from constructing and evaluating to using LLMs and MLLMs with a clear logic. Following this, to emphasize the significant value of LLMs and MLLMs in healthcare, we survey and summarize 6 promising applications in healthcare. Finally, the survey discusses the challenges faced by medical LLMs and MLLMs and proposes a feasible approach and direction for the subsequent integration of artificial intelligence with medicine. Thus, this survey aims to provide researchers with a valuable and comprehensive reference guide from the perspectives of the background, principles, and clinical applications of LLMs and MLLMs.
5/15/2024
💬
Large Language Models for Medicine: A Survey
Yanxin Zheng, Wensheng Gan, Zefeng Chen, Zhenlian Qi, Qian Liang, Philip S. Yu

0
0
To address challenges in the digital economy's landscape of digital intelligence, large language models (LLMs) have been developed. Improvements in computational power and available resources have significantly advanced LLMs, allowing their integration into diverse domains for human life. Medical LLMs are essential application tools with potential across various medical scenarios. In this paper, we review LLM developments, focusing on the requirements and applications of medical LLMs. We provide a concise overview of existing models, aiming to explore advanced research directions and benefit researchers for future medical applications. We emphasize the advantages of medical LLMs in applications, as well as the challenges encountered during their development. Finally, we suggest directions for technical integration to mitigate challenges and potential research directions for the future of medical LLMs, aiming to meet the demands of the medical field better.
5/24/2024
💬
Efficient Large Language Models: A Survey
Zhongwei Wan, Xin Wang, Che Liu, Samiul Alam, Yu Zheng, Jiachen Liu, Zhongnan Qu, Shen Yan, Yi Zhu, Quanlu Zhang, Mosharaf Chowdhury, Mi Zhang

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in important tasks such as natural language understanding and language generation, and thus have the potential to make a substantial impact on our society. Such capabilities, however, come with the considerable resources they demand, highlighting the strong need to develop effective techniques for addressing their efficiency challenges. In this survey, we provide a systematic and comprehensive review of efficient LLMs research. We organize the literature in a taxonomy consisting of three main categories, covering distinct yet interconnected efficient LLMs topics from model-centric, data-centric, and framework-centric perspective, respectively. We have also created a GitHub repository where we organize the papers featured in this survey at https://github.com/AIoT-MLSys-Lab/Efficient-LLMs-Survey. We will actively maintain the repository and incorporate new research as it emerges. We hope our survey can serve as a valuable resource to help researchers and practitioners gain a systematic understanding of efficient LLMs research and inspire them to contribute to this important and exciting field.
5/24/2024
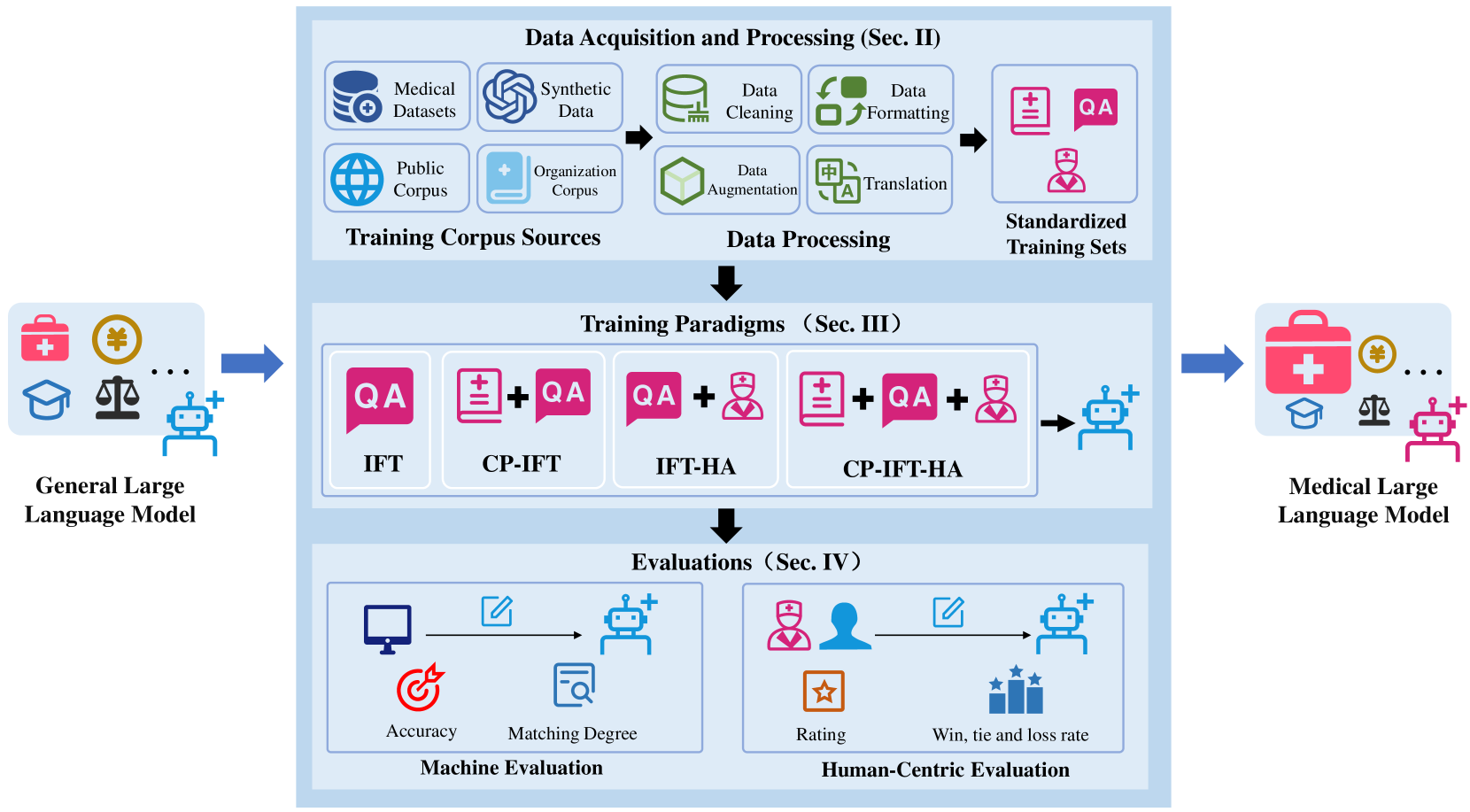
A Survey on Large Language Models from General Purpose to Medical Applications: Datasets, Methodologies, and Evaluations
Jinqiang Wang, Huansheng Ning, Yi Peng, Qikai Wei, Daniel Tesfai, Wenwei Mao, Tao Zhu, Runhe Huang

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated surprising performance across various natural language processing tasks. Recently, medical LLMs enhanced with domain-specific knowledge have exhibited excellent capabilities in medical consultation and diagnosis. These models can smoothly simulate doctor-patient dialogues and provide professional medical advice. Most medical LLMs are developed through continued training of open-source general LLMs, which require significantly fewer computational resources than training LLMs from scratch. Additionally, this approach offers better protection of patient privacy compared to API-based solutions. This survey systematically explores how to train medical LLMs based on general LLMs. It covers: (a) how to acquire training corpus and construct customized medical training sets, (b) how to choose a appropriate training paradigm, (c) how to choose a suitable evaluation benchmark, and (d) existing challenges and promising future research directions are discussed. This survey can provide guidance for the development of LLMs focused on various medical applications, such as medical education, diagnostic planning, and clinical assistants.
6/18/2024