Cyber Attacks on Maritime Assets and their Impacts on Health and Safety Aboard: A Holistic View

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
• This research paper examines the impacts of cyber attacks on maritime assets, focusing on their effects on the health and safety of personnel aboard. • The paper takes a holistic view, considering the interconnected nature of maritime energy infrastructure and the potential ripple effects of cyber incidents. • Key topics covered include the vulnerabilities of maritime systems, the cascading impacts on critical operations, and the implications for crew well-being.
Plain English Explanation
Ships, ports, and other maritime infrastructure rely heavily on digital systems and technologies to operate. This makes them vulnerable to cyber attacks, where hackers can infiltrate and disrupt these systems. When a cyber attack occurs, it can have far-reaching consequences beyond just the targeted asset.
For example, if a hacker takes control of a ship's navigation systems, they could steer the vessel off course or even cause a collision. This could lead to spills, explosions, or other environmental disasters. The crew members aboard the ship would then be at risk of injury or even death.
Similarly, a cyber attack on a port's cargo handling systems could delay the loading and unloading of goods, causing supply chain disruptions and economic losses. The stress and uncertainty created by these incidents can also take a toll on the mental and physical health of the workers involved.
The researchers in this paper aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of these kinds of interconnected vulnerabilities and impacts. By considering the maritime sector as a complex, interconnected system, they hope to better prepare for and mitigate the effects of cyber attacks on the health and safety of personnel.
Technical Explanation
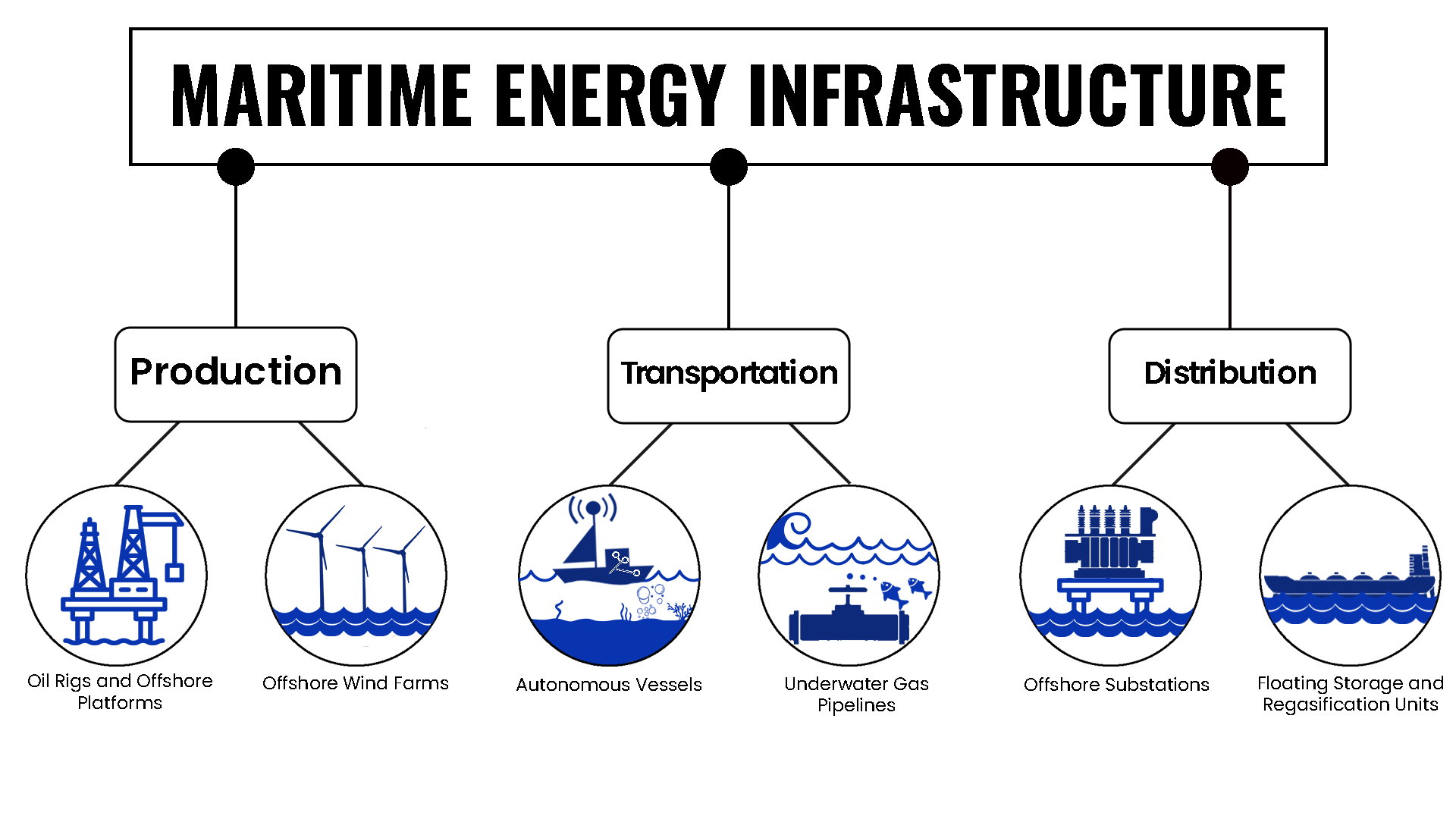
The paper begins by exploring the key components of maritime energy infrastructure, including ships, ports, and offshore platforms. It highlights the reliance of these assets on digital systems for navigation, cargo handling, and other critical operations.
The authors then analyze the various cyber threats and attack vectors that can compromise these systems, such as malware, network intrusions, and supply chain vulnerabilities. They discuss how successful cyber attacks can disrupt normal maritime activities, leading to accidents, environmental damage, and operational disruptions.
The paper also explores the cascading effects of these cyber incidents on the health and safety of personnel aboard ships and in port facilities. This includes the potential for injuries, exposure to hazardous materials, and mental health impacts due to stress and uncertainty.
To address these challenges, the researchers propose a [holistic, cyber-sensorium approach that integrates cybersecurity, occupational health, and maritime operations. This framework aims to enhance the resilience of the maritime sector by improving the security of cloud-based services and promoting better coordination between various stakeholders.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive and well-researched overview of the complex interplay between cyber threats, maritime operations, and the health and safety of personnel. The authors have effectively highlighted the interconnected nature of these issues and the need for a holistic approach to address them.
One potential limitation of the study is the lack of in-depth case studies or empirical data on the specific impacts of cyber attacks on maritime health and safety. While the authors discuss theoretical scenarios, more real-world examples could have strengthened the analysis and provided deeper insights.
Additionally, the paper could have explored the legal and regulatory frameworks governing cybersecurity and occupational safety in the maritime sector, as well as the challenges in implementing effective policies and standards across this global industry.
Conclusion
This research paper makes a valuable contribution to the understanding of the complex and multifaceted impacts of cyber attacks on the maritime industry. By taking a holistic view, the authors have shed light on the far-reaching consequences of such incidents, particularly on the health and safety of the personnel involved.
The proposed cyber-sensorium approach offers a promising framework for enhancing the resilience of the maritime sector, but its practical implementation and effectiveness will require further study and collaboration among industry stakeholders, policymakers, and security experts.
Overall, this paper serves as an important reminder of the need to prioritize cybersecurity and occupational safety as integral components of maritime operations, in order to protect both the physical assets and the human lives at stake.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Cyber Attacks on Maritime Assets and their Impacts on Health and Safety Aboard: A Holistic View
Mohammad Ammar, Irfan Ahmad Khan
There has been an unprecedented digitization drive in the industrial sector, especially in the maritime industry. The profusion of intelligent electronic devices and IOT-enabled cyber-physical systems (CPS) has helped in the efficient use of resources and increased convenience. CPS has enabled real-time remote command and control of industrial assets. Unlike the relatively isolated legacy systems, the intertwined nature of Information Technology(IT) and Operations Technology(OT) brought by Industry 4.0 has increased the complexity of the systems, thereby increasing the attack surface. This work explores the possible consequences of these attacks from a more holistic view, focusing on high-risk assets such as offshore oil rigs, offshore wind farms, and autonomous vessels. The attacks have become more aggressive with the proliferation of such technologies, disrupting the physical process, causing fire and explosion hazards, and endangering human life and environmental health. The possible attack scenarios, the attack vectors, and their physical consequences have been discussed from the perspective of personnel safety and health, along with known security breaches of such nature. To the best of the authors' knowledge, seldom has any work been done that accentuates the possible human and environmental impacts of such attacks.
Read more7/12/2024
🏷️

0
Analyzing the Attack Surface and Threats of Industrial Internet of Things Devices
Simon Liebl, Leah Lathrop, Ulrich Raithel, Andreas A{ss}muth, Ian Ferguson, Matthias Sollner
The growing connectivity of industrial devices as a result of the Internet of Things is increasing the risks to Industrial Control Systems. Since attacks on such devices can also cause damage to people and machines, they must be properly secured. Therefore, a threat analysis is required in order to identify weaknesses and thus mitigate the risk. In this paper, we present a systematic and holistic procedure for analyzing the attack surface and threats of Industrial Internet of Things devices. Our approach is to consider all components including hardware, software and data, assets, threats and attacks throughout the entire product life cycle.
Read more5/28/2024
📊

0
Cyberattack Data Analysis in IoT Environments using Big Data
Neelam Patidar, Sally Zreiqat, Sirisha Mahesh, Jongwook Woo
In the landscape of the Internet of Things (IoT), transforming various industries, our research addresses the growing connectivity and security challenges, including interoperability and standardized protocols. Despite the anticipated exponential growth in IoT connections, network security remains a major concern due to inadequate datasets that fail to fully encompass potential cyberattacks in realistic IoT environments. Using Apache Hadoop and Hive, our in-depth analysis of security vulnerabilities identified intricate patterns and threats, such as attack behavior, network traffic anomalies, TCP flag usage, and targeted attacks, underscoring the critical need for robust data platforms to enhance IoT security.
Read more6/18/2024
🤿

0
Resilience of the Electric Grid through Trustable IoT-Coordinated Assets
Vineet J. Nair, Venkatesh Venkataramanan, Priyank Srivastava, Partha S. Sarker, Anurag Srivastava, Laurentiu D. Marinovici, Jun Zha, Christopher Irwin, Prateek Mittal, John Williams, H. Vincent Poor, Anuradha M. Annaswamy
The electricity grid has evolved from a physical system to a cyber-physical system with digital devices that perform measurement, control, communication, computation, and actuation. The increased penetration of distributed energy resources (DERs) that include renewable generation, flexible loads, and storage provides extraordinary opportunities for improvements in efficiency and sustainability. However, they can introduce new vulnerabilities in the form of cyberattacks, which can cause significant challenges in ensuring grid resilience. %, i.e. the ability to rapidly restore grid services in the face of severe disruptions. We propose a framework in this paper for achieving grid resilience through suitably coordinated assets including a network of Internet of Things (IoT) devices. A local electricity market is proposed to identify trustable assets and carry out this coordination. Situational Awareness (SA) of locally available DERs with the ability to inject power or reduce consumption is enabled by the market, together with a monitoring procedure for their trustability and commitment. With this SA, we show that a variety of cyberattacks can be mitigated using local trustable resources without stressing the bulk grid. The demonstrations are carried out using a variety of platforms with a high-fidelity co-simulation platform, real-time hardware-in-the-loop validation, and a utility-friendly simulator.
Read more6/24/2024