Decentralized Peer Review in Open Science: A Mechanism Proposal

0
🛠️
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Peer review is a critical part of academic publishing, but it currently lacks incentives and transparency, harming its credibility.
- Researchers are not rewarded for high-quality reviews or penalized for poor ones, and confidential reports lead to a loss of insights and vulnerability to misconduct.
- The proposed system aims to address these issues by remunerating reviewers, publishing anonymized reports, tracking reviewer reputation, and providing digital certificates.
- Automated by blockchain technology, the system seeks to increase the quality and speed of peer review while reducing the chance and impact of erroneous judgments.
Plain English Explanation
Peer review is a crucial process in academic publishing, where researchers evaluate each other's work before it is published. However, this process has some significant problems. Researchers who do high-quality reviews are not rewarded for their efforts, and those who do poor reviews are not penalized. Additionally, the review reports are kept confidential, which means the community can't see the insights and feedback provided by the reviewers. This lack of transparency also makes the review process vulnerable to scientific misconduct, where researchers might try to influence the process unfairly.
The proposed system aims to fix these issues by paying reviewers for their work, publishing the review reports (with the reviewers' identities hidden), tracking the reputation of the reviewers, and providing digital certificates to acknowledge their contributions. This system is powered by blockchain technology, which ensures that the process is transparent and secure. The goal is to improve the quality and speed of peer review, while also reducing the chances of errors or unfair practices.
Technical Explanation
The key elements of the proposed system are:
-
Remuneration for Reviewers: The system uses a blockchain-based reputation system to track and reward reviewers for their contributions. Reviewers are paid for their work, which incentivizes them to provide high-quality reviews.
-
Transparent, Anonymized Report Publication: The review reports are published anonymously, allowing the community to scrutinize the feedback and insights provided by the reviewers. This transparency helps to maintain the credibility of the review process.
-
Reviewer Reputation Tracking: The system tracks the reputation of reviewers based on the quality of their reviews, as perceived by the community. This helps to identify and reward the best reviewers.
-
Digital Certificates: Reviewers are awarded digital certificates to acknowledge their contributions, which can be used to enhance their academic profiles and careers.
The system is automated using transparent smart-contract blockchain technology, which ensures the integrity and security of the review process. This approach aims to increase the quality and speed of peer review, while also reducing the chance and impact of erroneous judgments.
Critical Analysis
The proposed system addresses several important issues in the current peer review process, such as the lack of incentives for reviewers and the lack of transparency. By remunering reviewers and publicly sharing the review reports, the system aims to improve the quality and credibility of the review process.
However, one potential limitation of the system is the reliance on the community's perception of review quality to track reviewer reputation. This could be subject to biases and may not always accurately reflect the true quality of the reviews. Additionally, the system's effectiveness in reducing scientific misconduct and erroneous judgments will depend on the specific implementation details and the adoption by the research community.
Further research could explore ways to more objectively assess review quality, perhaps by using language models to analyze the consistency and thoroughness of reviews. Additionally, the system could be integrated with other AI-powered tools to further automate and streamline the peer review process.
Conclusion
The proposed system aims to address the key issues in the current peer review process by providing incentives for reviewers, increasing transparency, and tracking reviewer reputation. By leveraging blockchain technology, the system seeks to improve the quality and speed of peer review while reducing the chance and impact of erroneous judgments.
While the system has promising features, further research and experimentation will be needed to fully assess its effectiveness and address any potential limitations. Overall, this proposal represents a significant step towards enhancing the credibility and efficiency of the peer review process, which is essential for the advancement of scientific knowledge.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🛠️

0
Decentralized Peer Review in Open Science: A Mechanism Proposal
Andreas Finke, Thomas Hensel
Peer review is a laborious, yet essential, part of academic publishing with crucial impact on the scientific endeavor. The current lack of incentives and transparency harms the credibility of this process. Researchers are neither rewarded for superior nor penalized for bad reviews. Additionally, confidential reports cause a loss of insights and make the review process vulnerable to scientific misconduct. We propose a community-owned and -governed system that 1) remunerates reviewers for their efforts, 2) publishes the (anonymized) reports for scrutiny by the community, 3) tracks reputation of reviewers and 4) provides digital certificates. Automated by transparent smart-contract blockchain technology, the system aims to increase quality and speed of peer review while lowering the chance and impact of erroneous judgements.
Read more4/30/2024


0
BeerReview: A Blockchain-enabled Peer Review Platform
Guodong Jin, Zihan Zhou, Wenzheng Tang, Kanglei Yu, Hao Xu, Erwu Liu
In an era of increasing concerns over intellectual property rights, traditional peer review systems face challenges including plagiarism, malicious attacks, and unauthorized data access. BeerReview, a blockchain-enabled peer review platform, offers a robust solution, enabling experts and scholars to participate actively in the review process without concerns about plagiarism or security threats. Following the completion of its alpha testing, BeerReview demonstrates the potential for expanded deployment. This platform offers improved convenience and more robust intellectual property protection within the peer review process with open source initiative.
Read more5/31/2024


0
AgentReview: Exploring Peer Review Dynamics with LLM Agents
Yiqiao Jin, Qinlin Zhao, Yiyang Wang, Hao Chen, Kaijie Zhu, Yijia Xiao, Jindong Wang
Peer review is fundamental to the integrity and advancement of scientific publication. Traditional methods of peer review analyses often rely on exploration and statistics of existing peer review data, which do not adequately address the multivariate nature of the process, account for the latent variables, and are further constrained by privacy concerns due to the sensitive nature of the data. We introduce AgentReview, the first large language model (LLM) based peer review simulation framework, which effectively disentangles the impacts of multiple latent factors and addresses the privacy issue. Our study reveals significant insights, including a notable 37.1% variation in paper decisions due to reviewers' biases, supported by sociological theories such as the social influence theory, altruism fatigue, and authority bias. We believe that this study could offer valuable insights to improve the design of peer review mechanisms.
Read more6/19/2024

0
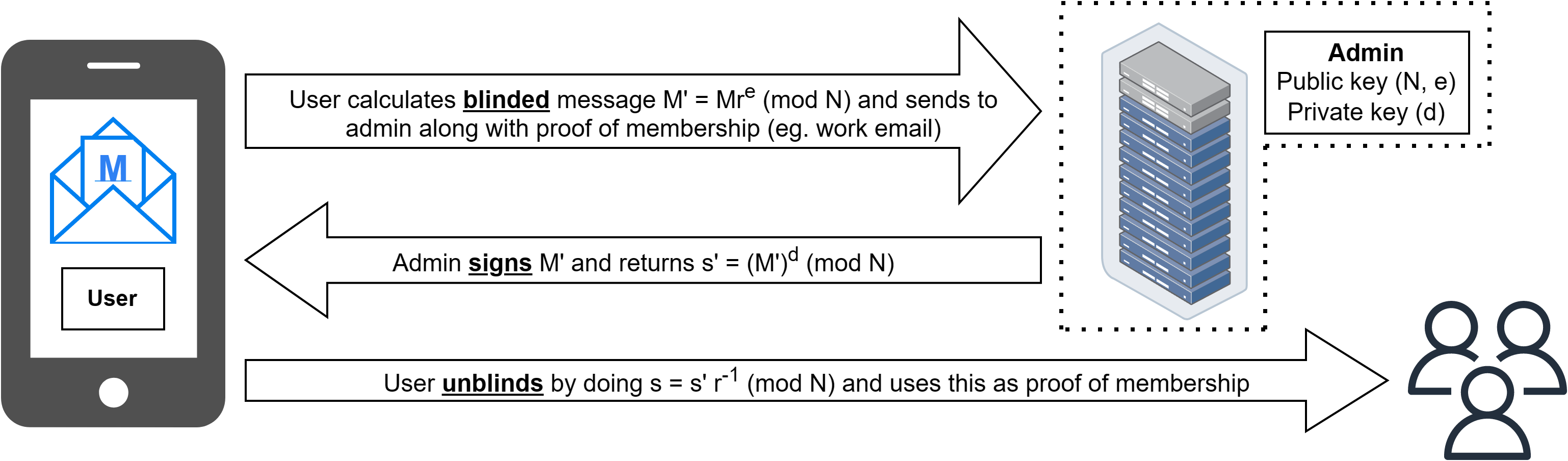
TrustRate: A Decentralized Platform for Hijack-Resistant Anonymous Reviews
Rohit Dwivedula, Sriram Sridhar, Sambhav Satija, Muthian Sivathanu, Nishanth Chandran, Divya Gupta, Satya Lokam
Reviews and ratings by users form a central component in several widely used products today (e.g., product reviews, ratings of online content, etc.), but today's platforms for managing such reviews are ad-hoc and vulnerable to various forms of tampering and hijack by fake reviews either by bots or motivated paid workers. We define a new metric called 'hijack-resistance' for such review platforms, and then present TrustRate, an end-to-end decentralized, hijack-resistant platform for authentic, anonymous, tamper-proof reviews. With a prototype implementation and evaluation at the scale of thousands of nodes, we demonstrate the efficacy and performance of our platform, towards a new paradigm for building products based on trusted reviews by end users without having to trust a single organization that manages the reviews.
Read more7/23/2024