Deception Analysis with Artificial Intelligence: An Interdisciplinary Perspective

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper explores the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in analyzing and detecting deception, taking an interdisciplinary approach.
- It examines the challenges and opportunities in leveraging AI for deception detection, drawing insights from various fields such as psychology, cognitive science, and computer science.
- The research aims to advance the understanding of deception and develop more effective AI-based tools for detecting and mitigating deceptive behaviors.
Plain English Explanation
The paper investigates how AI can be used to analyze and identify deception, which is the act of intentionally misleading or deceiving others. The researchers take a multidisciplinary approach, combining insights from fields like psychology, cognitive science, and computer science.
Deception is a complex human behavior that can have significant consequences, both in personal and professional contexts. The researchers believe that by using AI-powered tools, we can better understand the mechanisms behind deception and develop more effective ways to detect it.
For example, AI algorithms could be trained to analyze verbal and non-verbal cues, such as tone of voice, facial expressions, and body language, to identify potential deception. The researchers also explore how AI-driven analysis of written communication, such as emails or social media posts, could help uncover patterns and signs of deception.
By taking an interdisciplinary approach, the researchers aim to gain a deeper understanding of deception and how it manifests in different contexts. This knowledge could then be used to develop more reliable and accurate AI-based deception detection systems, which could have important applications in fields like law enforcement, national security, and business decision-making.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents an interdisciplinary perspective on the use of artificial intelligence (AI) for deception analysis. It draws insights from fields such as psychology, cognitive science, and computer science to explore the challenges and opportunities in leveraging AI for deception detection.
The researchers propose a comprehensive roadmap for developing AI-based deception analysis tools. This includes exploring various modalities, such as verbal, non-verbal, and written communication, to capture the multifaceted nature of deceptive behavior.
The paper also delves into the complex interplay between human and AI agents in the context of deception detection. It examines how AI systems can be designed to effectively collaborate with human experts, leveraging their respective strengths to enhance the accuracy and reliability of deception analysis.
Critical Analysis
The paper acknowledges the inherent complexities and challenges in developing effective AI-based deception detection systems. The researchers note that deception is a highly context-dependent and multifaceted phenomenon, which can make it difficult to generalize detection models across different domains and situations.
Additionally, the paper highlights the potential for bias and ethical concerns in the development and deployment of such AI systems. It emphasizes the need for careful consideration of the social, legal, and privacy implications of using AI for deception analysis, particularly in sensitive areas like law enforcement and national security.
The researchers also identify the need for further interdisciplinary collaboration and empirical studies to better understand the cognitive and behavioral mechanisms underlying deception. They call for more research to explore the long-term effects of AI-driven deception detection on human-AI interaction and trust.
Conclusion
The paper presents a comprehensive and interdisciplinary approach to the use of artificial intelligence in deception analysis. It recognizes the significant potential of AI-based tools to enhance our understanding of deceptive behavior and improve the effectiveness of deception detection.
However, the researchers also emphasize the need for a cautious and responsible approach, addressing the complex ethical and societal implications of such technologies. By fostering continued collaboration across disciplines, the paper aims to advance the field of deception analysis and contribute to the development of more reliable and trustworthy AI-driven deception detection systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Deception Analysis with Artificial Intelligence: An Interdisciplinary Perspective
Stefan Sarkadi
Humans and machines interact more frequently than ever and our societies are becoming increasingly hybrid. A consequence of this hybridisation is the degradation of societal trust due to the prevalence of AI-enabled deception. Yet, despite our understanding of the role of trust in AI in the recent years, we still do not have a computational theory to be able to fully understand and explain the role deception plays in this context. This is a problem because while our ability to explain deception in hybrid societies is delayed, the design of AI agents may keep advancing towards fully autonomous deceptive machines, which would pose new challenges to dealing with deception. In this paper we build a timely and meaningful interdisciplinary perspective on deceptive AI and reinforce a 20 year old socio-cognitive perspective on trust and deception, by proposing the development of DAMAS -- a holistic Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) framework for the socio-cognitive modelling and analysis of deception. In a nutshell this paper covers the topic of modelling and explaining deception using AI approaches from the perspectives of Computer Science, Philosophy, Psychology, Ethics, and Intelligence Analysis.
Read more6/12/2024

0
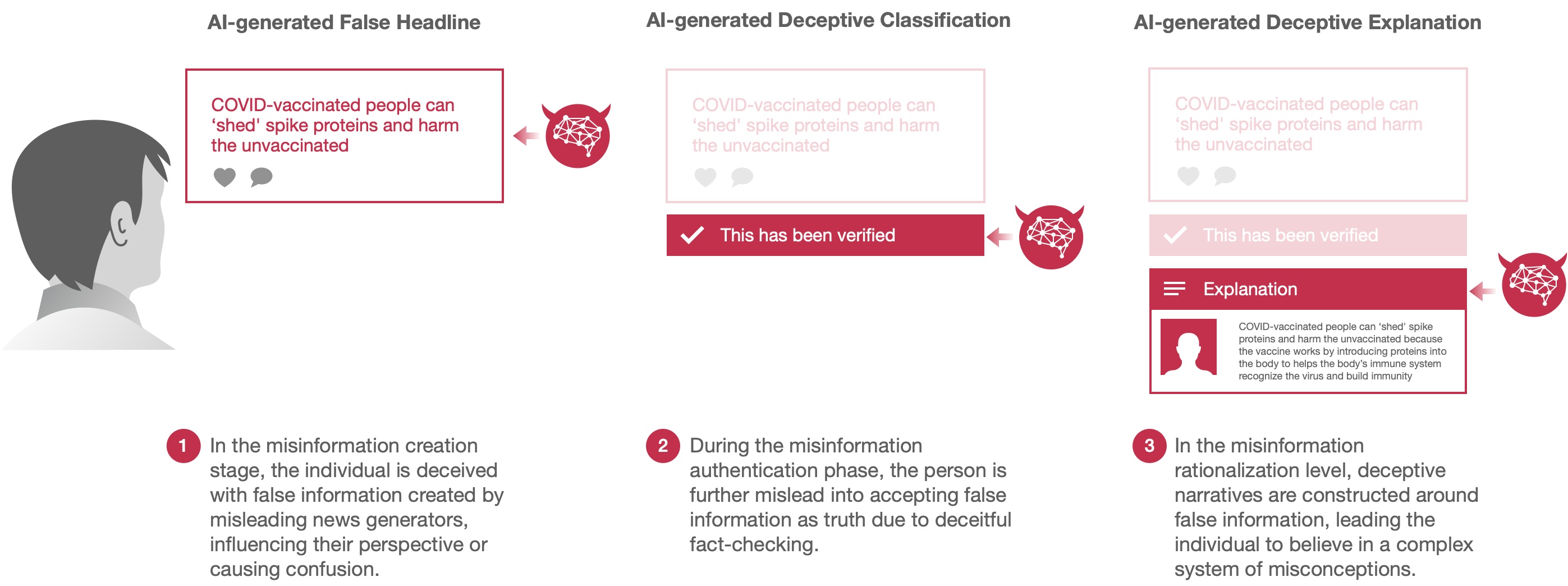
Deceptive AI systems that give explanations are more convincing than honest AI systems and can amplify belief in misinformation
Valdemar Danry, Pat Pataranutaporn, Matthew Groh, Ziv Epstein, Pattie Maes
Advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems, specifically large language models (LLMs), have the capability to generate not just misinformation, but also deceptive explanations that can justify and propagate false information and erode trust in the truth. We examined the impact of deceptive AI generated explanations on individuals' beliefs in a pre-registered online experiment with 23,840 observations from 1,192 participants. We found that in addition to being more persuasive than accurate and honest explanations, AI-generated deceptive explanations can significantly amplify belief in false news headlines and undermine true ones as compared to AI systems that simply classify the headline incorrectly as being true/false. Moreover, our results show that personal factors such as cognitive reflection and trust in AI do not necessarily protect individuals from these effects caused by deceptive AI generated explanations. Instead, our results show that the logical validity of AI generated deceptive explanations, that is whether the explanation has a causal effect on the truthfulness of the AI's classification, plays a critical role in countering their persuasiveness - with logically invalid explanations being deemed less credible. This underscores the importance of teaching logical reasoning and critical thinking skills to identify logically invalid arguments, fostering greater resilience against advanced AI-driven misinformation.
Read more8/2/2024
🏅

0
Bias Mitigation via Compensation: A Reinforcement Learning Perspective
Nandhini Swaminathan, David Danks
As AI increasingly integrates with human decision-making, we must carefully consider interactions between the two. In particular, current approaches focus on optimizing individual agent actions but often overlook the nuances of collective intelligence. Group dynamics might require that one agent (e.g., the AI system) compensate for biases and errors in another agent (e.g., the human), but this compensation should be carefully developed. We provide a theoretical framework for algorithmic compensation that synthesizes game theory and reinforcement learning principles to demonstrate the natural emergence of deceptive outcomes from the continuous learning dynamics of agents. We provide simulation results involving Markov Decision Processes (MDP) learning to interact. This work then underpins our ethical analysis of the conditions in which AI agents should adapt to biases and behaviors of other agents in dynamic and complex decision-making environments. Overall, our approach addresses the nuanced role of strategic deception of humans, challenging previous assumptions about its detrimental effects. We assert that compensation for others' biases can enhance coordination and ethical alignment: strategic deception, when ethically managed, can positively shape human-AI interactions.
Read more5/1/2024
🎲

0
Trust in AI: Progress, Challenges, and Future Directions
Saleh Afroogh, Ali Akbari, Evan Malone, Mohammadali Kargar, Hananeh Alambeigi
The increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) systems in our daily life through various applications, services, and products explains the significance of trust/distrust in AI from a user perspective. AI-driven systems (as opposed to other technologies) have ubiquitously diffused in our life not only as some beneficial tools to be used by human agents but also are going to be substitutive agents on our behalf, or manipulative minds that would influence human thought, decision, and agency. Trust/distrust in AI plays the role of a regulator and could significantly control the level of this diffusion, as trust can increase, and distrust may reduce the rate of adoption of AI. Recently, varieties of studies have paid attention to the variant dimension of trust/distrust in AI, and its relevant considerations. In this systematic literature review, after conceptualization of trust in the current AI literature review, we will investigate trust in different types of human-Machine interaction, and its impact on technology acceptance in different domains. In addition to that, we propose a taxonomy of technical (i.e., safety, accuracy, robustness) and non-technical axiological (i.e., ethical, legal, and mixed) trustworthiness metrics, and some trustworthy measurements. Moreover, we examine some major trust-breakers in AI (e.g., autonomy and dignity threat), and trust makers; and propose some future directions and probable solutions for the transition to a trustworthy AI.
Read more4/5/2024