Defining Quantum Games

0
👀
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper surveys existing quantum physics-related games and proposes a definition for the concept of "quantum games."
- The authors define quantum games as rule-based games that use the principles or reference the theory of quantum physics or quantum phenomena through three proposed dimensions: the perceivable dimension of quantum physics, the dimension of quantum technologies, and the dimension of scientific purposes like citizen science or education.
- The paper also discusses the concept of "quantum computer games" and "games on quantum computers," as well as the definition of "science games."
- The authors note that there are various games exploring quantum physics and quantum computing through digital, analog, and hybrid means, driven by diverse incentives.
- As interest in games as educational tools for supporting quantum literacy grows, understanding the diverse landscape of quantum games becomes increasingly important.
- The authors propose that the three dimensions of quantum games identified in this article be used for designing, analyzing, and defining the phenomenon of quantum games.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers in this paper looked at different games that are related to quantum physics. They wanted to come up with a clear definition for the concept of "quantum games." [https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/natural-language-ai-quantum-computing-2024-research]
The researchers defined quantum games as any type of rule-based game that uses the principles or ideas from quantum physics, or that talks about quantum phenomena. These games can do this in three main ways:
- The perceivable dimension of quantum physics: The game somehow lets players experience or see aspects of quantum physics.
- The dimension of quantum technologies: The game is about quantum technologies, like quantum computers.
- The dimension of scientific purposes: The game is designed for educational purposes or to help with scientific research, like citizen science projects.
The paper also discusses "quantum computer games" - games that are played on actual quantum computers. [https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/challenges-reinforcement-learning-quantum-circuit-design] It also talks about the definition of "science games" in general.
The researchers note that there are many different games that explore quantum physics and quantum computing, using digital, analog, and hybrid approaches. These games are being developed for a variety of reasons. [https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/agent-based-modelling-quantum-prisoners-dilemma]
As more people become interested in using games to teach about quantum physics, it's important to understand the wide range of quantum games that are out there. The researchers suggest that the three dimensions they identified should be used to design, analyze, and define quantum games going forward.
Technical Explanation
The paper surveys the existing landscape of quantum physics-related games and proposes a framework for defining the concept of "quantum games." The authors define quantum games as any type of rule-based game that uses the principles or references the theory of quantum physics or quantum phenomena through three proposed dimensions:
- The perceivable dimension of quantum physics: Games that allow players to perceive or experience aspects of quantum physics, such as quantum superposition, entanglement, or tunneling. [https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/quantum-tunneling-from-theory-to-error-mitigated]
- The dimension of quantum technologies: Games that are focused on quantum technologies, such as quantum computing or quantum sensing.
- The dimension of scientific purposes: Games designed for educational purposes or to support scientific research, such as citizen science projects.
The paper also discusses the concept of "quantum computer games" - games that are designed to run on actual quantum computers. Additionally, the authors provide an overview of the definition of "science games" in general.
The researchers note that there is a diverse landscape of games exploring quantum physics and quantum computing through digital, analog, and hybrid approaches, driven by a variety of incentives and goals. As interest in using games as educational tools to support quantum literacy grows, understanding this diverse landscape becomes increasingly important.
The authors propose that the three dimensions of quantum games identified in this paper should be used as a framework for designing, analyzing, and defining the phenomenon of quantum games going forward.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive survey of the existing landscape of quantum physics-related games and proposes a useful framework for defining the concept of "quantum games." The three dimensions identified - the perceivable dimension of quantum physics, the dimension of quantum technologies, and the dimension of scientific purposes - offer a clear and intuitive way to categorize and analyze the diverse range of games in this space.
One potential limitation of the research is that the paper does not delve deeply into the specific mechanics, design, or player experiences of the various quantum games mentioned. A more detailed analysis of the gameplay and learning outcomes of these games could provide additional insights into the efficacy of using games as educational tools for quantum literacy.
Additionally, the paper does not address potential challenges or barriers to the widespread adoption of quantum games, such as the technical complexity of the subject matter, the availability of suitable hardware (e.g., quantum computers), or the need for specialized game development expertise. Exploring these types of practical considerations could help inform the future development and deployment of quantum games. [https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/scalable-quantum-detector-tomography-by-high-performance]
Overall, the paper presents a solid foundation for understanding the emerging field of quantum games and offers a useful framework for further research and development in this area. By continuing to explore the diverse landscape of quantum games and their potential educational and scientific applications, researchers and game designers can make valuable contributions to the growing field of quantum literacy.
Conclusion
This paper provides a comprehensive survey of existing quantum physics-related games and proposes a definition for the concept of "quantum games." The authors identify three key dimensions - the perceivable dimension of quantum physics, the dimension of quantum technologies, and the dimension of scientific purposes - that can be used to design, analyze, and define the phenomenon of quantum games.
As interest in using games as educational tools to support quantum literacy grows, the insights and framework presented in this paper can help researchers, game designers, and educators better understand the diverse landscape of quantum games and their potential applications. By continuing to explore and develop innovative quantum games, the field can make important contributions to the advancement of quantum education and scientific research.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
👀

0
Defining Quantum Games
Laura Piispanen, Marcel Pfaffhauser, James Wootton, Julian Togelius, Annakaisa Kultima
In this article, we survey the existing quantum physics related games and based on them propose a definition for the concept of quantum games. We define quantum games as any type of rule-based games that use the principles or reference the theory of quantum physics or quantum phenomena through any of three proposed dimensions: the perceivable dimension of quantum physics, the dimension of quantum technologies, and the dimension of scientific purposes like citizen science or education. We also discuss the concept of quantum computer games, games on quantum computers and discuss the definitions for the concept of science games. At the same time, there are various games exploring quantum physics and quantum computing through digital, analogue, and hybrid means with diverse incentives driving their development. As interest in games as educational tools for supporting quantum literacy grows, understanding the diverse landscape of quantum games becomes increasingly important. We propose that three dimensions of quantum games identified in this article are used for designing, analysing and defining the phenomenon of quantum games.
Read more4/12/2024

0
Quantum Computing Education for Computer Science Students: Bridging the Gap with Layered Learning and Intuitive Analogies
Anila Mjeda, Hazel Murray
Quantum computing presents a transformative potential for the world of computing. However, integrating this technology into the curriculum for computer science students who lack prior exposure to quantum mechanics and advanced mathematics remains a challenging task. This paper proposes a scaffolded learning approach aimed at equipping computer science students with essential quantum principles. By introducing foundational quantum concepts through relatable analogies and a layered learning approach based on classical computation, this approach seeks to bridge the gap between classical and quantum computing. This differs from previous approaches which build quantum computing fundamentals from the prerequisite of linear algebra and mathematics. The paper offers a considered set of intuitive analogies for foundation quantum concepts including entanglement, superposition, quantum data structures and quantum algorithms. These analogies coupled with a computing-based layered learning approach, lay the groundwork for a comprehensive teaching methodology tailored for undergraduate third level computer science students.
Read more5/16/2024


0
Cyber Physical Games
Warisa Sritriratanarak, Paulo Garcia
We describe a formulation of multi-agents operating within a Cyber-Physical System, resulting in collaborative or adversarial games. We show that the non-determinism inherent in the communication medium between agents and the underlying physical environment gives rise to environment evolution that is a probabilistic function of agents' strategies. We name these emergent properties Cyber Physical Games and study its properties. We present an algorithmic model that determines the most likely system evolution, approximating Cyber Physical Games through Probabilistic Finite State Automata, and evaluate it on collaborative and adversarial versions of the Iterated Boolean Game, comparing theoretical results with simulated ones. Results support the validity of the proposed model, and suggest several required research directions to continue evolving our understanding of Cyber Physical System, as well as how to best design agents that must operate within such environments.
Read more7/9/2024

0
Quantum Computing: Vision and Challenges
Sukhpal Singh Gill, Oktay Cetinkaya, Stefano Marrone, Daniel Claudino, David Haunschild, Leon Schlote, Huaming Wu, Carlo Ottaviani, Xiaoyuan Liu, Sree Pragna Machupalli, Kamalpreet Kaur, Priyansh Arora, Ji Liu, Ahmed Farouk, Houbing Herbert Song, Steve Uhlig, Kotagiri Ramamohanarao
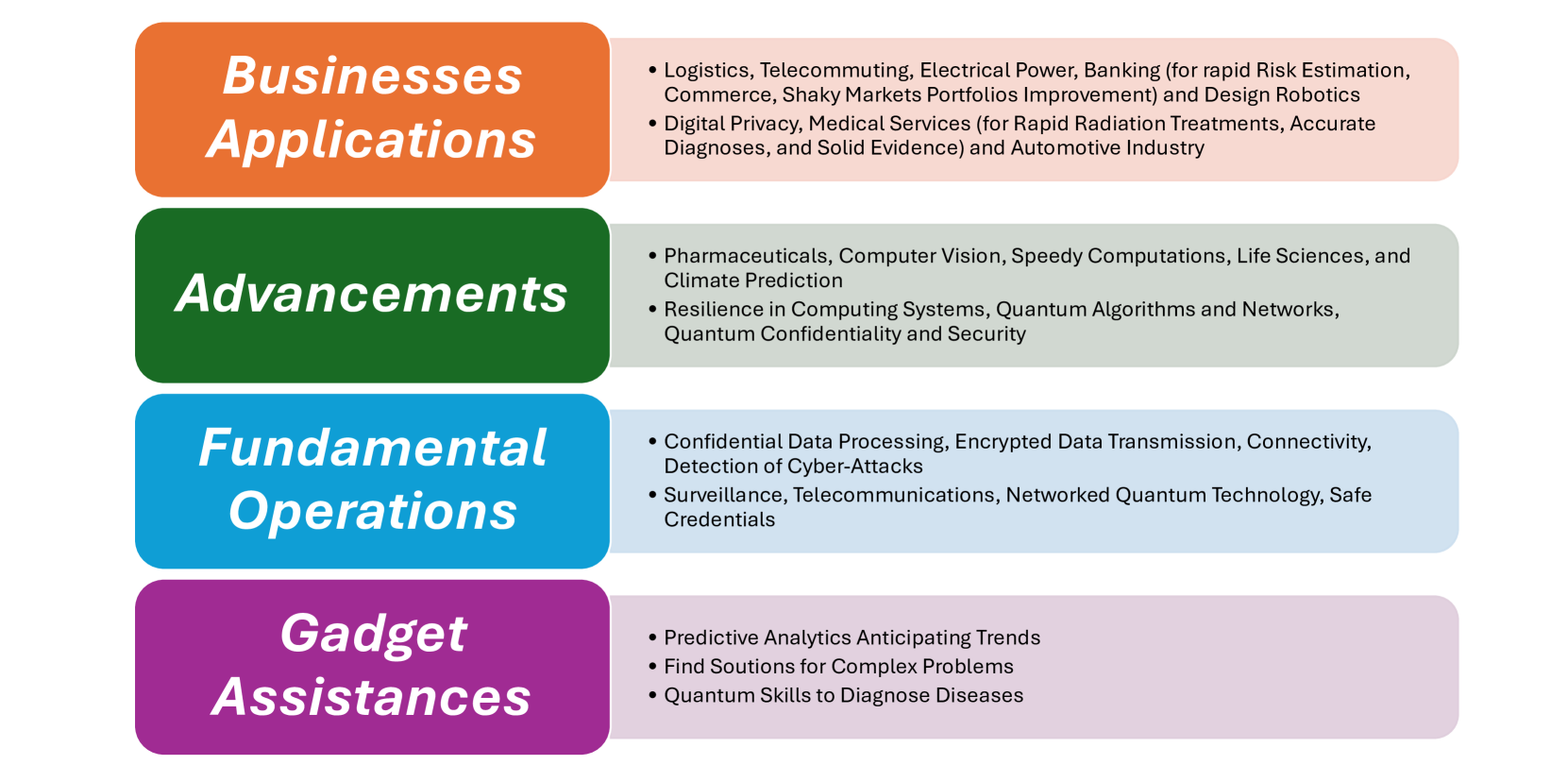
The recent development of quantum computing, which uses entanglement, superposition, and other quantum fundamental concepts, can provide substantial processing advantages over traditional computing. These quantum features help solve many complex problems that cannot be solved otherwise with conventional computing methods. These problems include modeling quantum mechanics, logistics, chemical-based advances, drug design, statistical science, sustainable energy, banking, reliable communication, and quantum chemical engineering. The last few years have witnessed remarkable progress in quantum software and algorithm creation and quantum hardware research, which has significantly advanced the prospect of realizing quantum computers. It would be helpful to have comprehensive literature research on this area to grasp the current status and find outstanding problems that require considerable attention from the research community working in the quantum computing industry. To better understand quantum computing, this paper examines the foundations and vision based on current research in this area. We discuss cutting-edge developments in quantum computer hardware advancement and subsequent advances in quantum cryptography, quantum software, and high-scalability quantum computers. Many potential challenges and exciting new trends for quantum technology research and development are highlighted in this paper for a broader debate.
Read more9/9/2024