DIDChain: Advancing Supply Chain Data Management with Decentralized Identifiers and Blockchain

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Blockchain technology and decentralized identifiers (DIDs) are used to improve supply chain data management
- The proposed DIDChain system aims to enhance traceability, data integrity, and digital identity in supply chains
- Key features include decentralized identity management, verifiable credentials, and integration with the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS)
Plain English Explanation
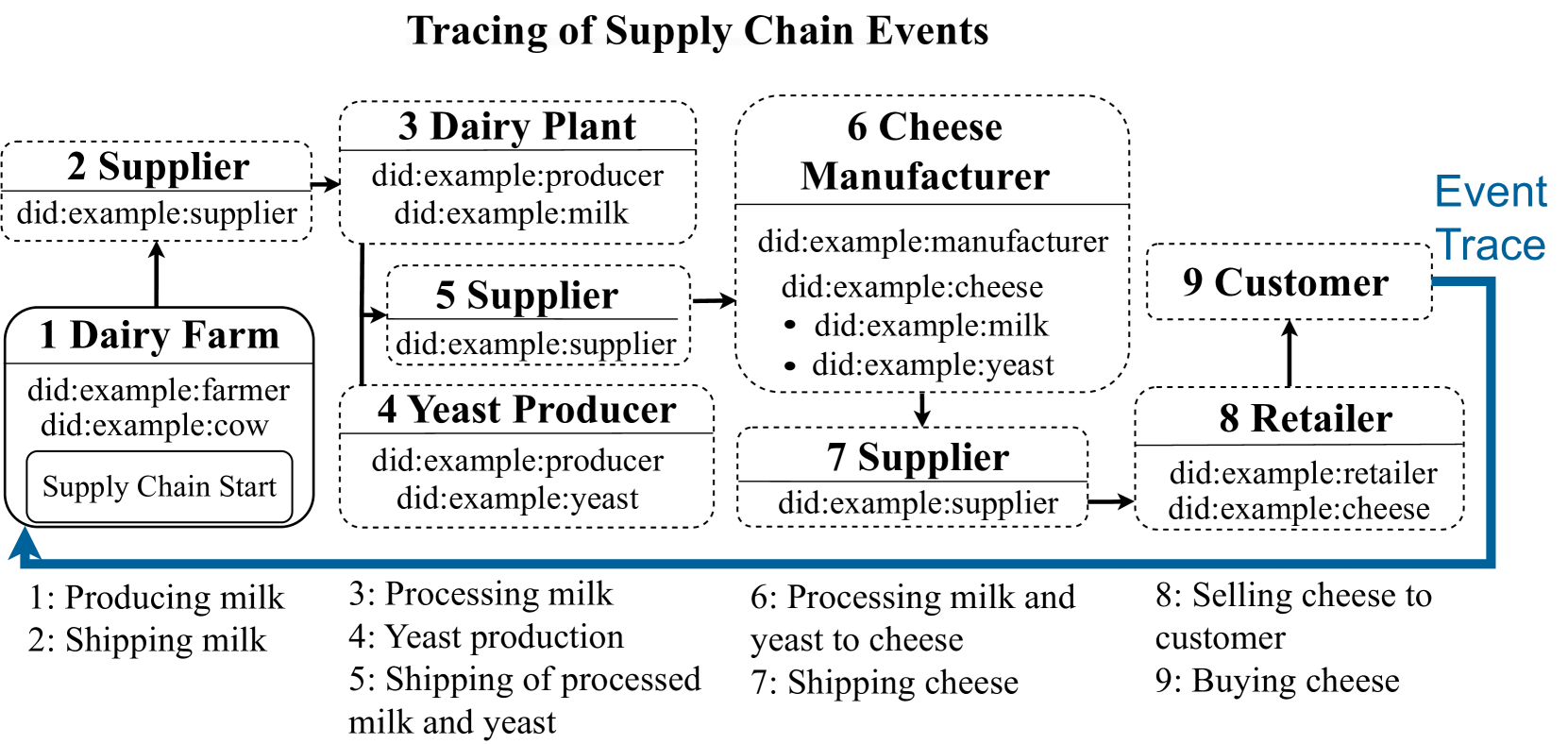
DIDChain is a system that uses blockchain technology and decentralized identifiers (DIDs) to help manage data in supply chains more effectively. Supply chains often involve many different organizations and players, making it challenging to keep track of information and ensure its integrity.
The DIDChain system addresses this by providing a decentralized way to manage digital identities and verifiable credentials. This allows supply chain participants to have their own unique digital IDs that can be used to verify the origin and authenticity of the data they contribute.
DIDChain also integrates with the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), a decentralized file storage network. This helps ensure the traceability and integrity of the data captured throughout the supply chain, as it is stored in a distributed manner rather than in a single, central location.
By leveraging these decentralized technologies, DIDChain aims to improve transparency, trust, and efficiency in supply chain data management. This could be particularly valuable in industries where product quality, provenance, and compliance are critical concerns.
Technical Explanation
DIDChain is a system that uses blockchain technology and decentralized identifiers (DIDs) to enhance supply chain data management. The key features of the DIDChain system include:
-
Decentralized Identity Management: DIDChain allows supply chain participants to create and manage their own unique digital identities using DIDs. These identities can be used to verify the source and authenticity of the data they contribute.
-
Verifiable Credentials: DIDChain supports the use of verifiable credentials, which are tamper-evident digital credentials that can be cryptographically verified. This helps ensure the integrity of the data captured throughout the supply chain.
-
IPFS Integration: DIDChain integrates with the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), a decentralized file storage network. This allows supply chain data to be stored in a distributed manner, improving traceability and preventing data tampering.
The architecture of DIDChain involves a blockchain-based infrastructure that manages the DIDs and verifiable credentials, as well as an IPFS-based data storage system for the supply chain data. This combination of decentralized identity management and distributed data storage aims to enhance the overall traceability, data integrity, and transparency of supply chain operations.
Critical Analysis
The DIDChain paper presents a promising approach to improving supply chain data management using decentralized technologies. However, the paper does not address several important considerations:
-
Scalability: The paper does not discuss the scalability of the DIDChain system, particularly as the number of supply chain participants and the volume of data grow. Ensuring the system can handle large-scale deployments is crucial for real-world adoption.
-
Interoperability: The paper does not mention how DIDChain would integrate with existing supply chain systems and processes. Ensuring seamless interoperability is essential for the successful integration of the DIDChain system.
-
Governance: The paper does not provide details on the governance model for the DIDChain system, such as how decisions are made, who has authority, and how disputes are resolved. A well-defined governance structure is necessary for the long-term sustainability and trust in the system.
-
Regulatory Compliance: The paper does not address how the DIDChain system would comply with relevant data privacy and security regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or industry-specific requirements. Addressing regulatory concerns is crucial for widespread adoption.
Overall, the DIDChain paper presents an interesting concept, but further research and development are needed to address these critical implementation and operational challenges.
Conclusion
The DIDChain system proposes the use of blockchain technology and decentralized identifiers (DIDs) to enhance supply chain data management. By providing a decentralized approach to identity management, verifiable credentials, and data storage, DIDChain aims to improve the traceability, data integrity, and transparency of supply chain operations.
If successfully implemented, the DIDChain system could have significant implications for industries where product quality, provenance, and compliance are critical concerns, such as food supply chains, pharmaceutical supply chains, or IoT-enabled supply chains.
However, the paper does not address several important considerations, such as scalability, interoperability, governance, and regulatory compliance. Further research and development are needed to address these challenges and pave the way for the widespread adoption of the DIDChain system.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
DIDChain: Advancing Supply Chain Data Management with Decentralized Identifiers and Blockchain
Patrick Herbke, Sid Lamichhane, Kaustabh Barman, Sanjeet Raj Pandey, Axel Kupper, Andreas Abraham, Markus Sabadello
Supply chain data management faces challenges in traceability, transparency, and trust. These issues stem from data silos and communication barriers. This research introduces DIDChain, a framework leveraging blockchain technology, Decentralized Identifiers, and the InterPlanetary File System. DIDChain improves supply chain data management. To address privacy concerns, DIDChain employs a hybrid blockchain architecture that combines public blockchain transparency with the control of private systems. Our hybrid approach preserves the authenticity and reliability of supply chain events. It also respects the data privacy requirements of the participants in the supply chain. Central to DIDChain is the cheqd infrastructure. The cheqd infrastructure enables digital tracing of asset events, such as an asset moving from the milk-producing dairy farm to the cheese manufacturer. In this research, assets are raw materials and products. The cheqd infrastructure ensures the traceability and reliability of assets in the management of supply chain data. Our contribution to blockchain-enabled supply chain systems demonstrates the robustness of DIDChain. Integrating blockchain technology through DIDChain offers a solution to data silos and communication barriers. With DIDChain, we propose a framework to transform the supply chain infrastructure across industries.
Read more9/4/2024
✨

0
Bridging Trust into the Blockchain: A Systematic Review on On-Chain Identity
Awid Vaziry, Kaustabh Barman, Patrick Herbke
The ongoing regulation of blockchain-based services and applications requires the identification of users who are issuing transactions on the blockchain. This systematic review explores the current status, identifies research gaps, and outlines future research directions for establishing trusted and privacy-compliant identities on the blockchain (on-chain identity). A systematic search term was applied across various scientific databases, collecting 2232 potentially relevant research papers. These papers were narrowed down in two methodologically executed steps to 98 and finally to 13 relevant sources. The relevant articles were then systematically analyzed based on a set of screening questions. The results of the selected studies have provided insightful findings on the mechanisms of on-chain identities. On-chain identities are established using zero-knowledge proofs, public key infrastructure/certificates, and web of trust approaches. The technologies and architectures used by the authors are also highlighted. Trust has emerged as a key research gap, manifesting in two ways: firstly, a gap in how to trust the digital identity representation of a physical human; secondly, a gap in how to trust identity providers that issue identity confirmations on-chain. Potential future research avenues are suggested to help fill the current gaps in establishing trust and on-chain identities.
Read more7/26/2024


0
Self-Sovereign Identity for Consented and Content-Based Access to Medical Records using Blockchain
Marie Tcholakian, Karolina Gorna, Maryline Laurent, Hella Kaffel Ben Ayed, Montassar Naghmouchi
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and Medical Data are classified as personal data in every privacy law, meaning that any related service that includes processing such data must come with full security, confidentiality, privacy and accountability. Solutions for health data management, as in storing it, sharing and processing it, are emerging quickly and were significantly boosted by the Covid-19 pandemic that created a need to move things online. EHRs makes a crucial part of digital identity data, and the same digital identity trends -- as in self sovereign identity powered by decentralized ledger technologies like Blockchain, are being researched or implemented in contexts managing digital interactions between health facilities, patients and health professionals. In this paper, we propose a blockchain-based solution enabling secure exchange of EHRs between different parties powered by a self-sovereign identity (SSI) wallet and decentralized identifiers. We also make use of a consortium IPFS network for off-chain storage and attribute-based encryption (ABE) to ensure data confidentiality and integrity. Through our solution, we grant users full control over their medical data, and enable them to securely share it in total confidentiality over secure communication channels between user wallets using encryption. We also use DIDs for better user privacy and limit any possible correlations or identification by using pairwise DIDs. Overall, combining this set of technologies guarantees secure exchange of EHRs, secure storage and management along with by-design features inherited from the technological stack.
Read more8/1/2024
📈

0
Haina Storage: A Decentralized Secure Storage Framework Based on Improved Blockchain Structure
Zijian Zhou, Caimei Wang, Xiaoheng Deng, Jianhao Lu, Qilue Wen, Chen Zhang, Hong Li
Although the decentralized storage technology based on the blockchain can effectively realize secure data storage on cloud services. However, there are still some problems in the existing schemes, such as low storage capacity and low efficiency. To address related issues, we propose a novel decentralized storage framework, which mainly includes four aspects: (1) we proposed a Bi-direction Circular Linked Chain Structure (BCLCS), which improves data's storage capacity and applicability in decentralized storage. (2) A Proof of Resources (PoR) decision model is proposed. By introducing the network environment as an essential evaluation parameter of storage right decision, the energy and time consumption of decision-making are reduced, and the fairness of decision-making is improved. (3) A chain structure dynamic locking mechanism (CSDLM) is designed to realize anti-traverse and access control. (4) A Bi-directional data Access Mechanism (BDAM) is proposed, which improves the efficiency of data access and acquisition in decentralized storage mode. The experimental results show that the framework has significantly improved the shortcomings of the current decentralized storage.
Read more4/3/2024