Distributed Pilot Assignment for Distributed Massive-MIMO Networks

0
🌀
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Distributed massive MIMO networks suffer from a critical issue called pilot contamination, where the reuse of pilot sequences leads to performance degradation.
- This paper proposes a novel distributed pilot assignment scheme to effectively mitigate the impact of pilot contamination.
- The proposed scheme reduces signaling overhead and enhances fault-tolerance.
- Numerical simulations show the proposed scheme outperforms existing centralized and distributed schemes in mitigating pilot contamination and enhancing network throughput.
Plain English Explanation
Massive MIMO (multiple-input, multiple-output) systems are a type of wireless network that use a large number of antennas to improve communication performance. In these networks, each device needs to estimate the wireless channel between itself and the network's antennas. This is done by transmitting and receiving "pilot" signals.
However, because there are a limited number of unique pilot signals available, the same pilots often need to be reused across different devices. This can lead to a problem called "pilot contamination," where the channel estimates become corrupted, and the network's performance suffers.
The paper proposes a new way to assign pilot signals to devices in a distributed manner, without relying on a central coordinator. This distributed pilot assignment scheme not only helps reduce the overall signaling overhead in the network, but it also makes the system more resilient to faults or failures.
Through extensive simulations, the researchers show that their proposed scheme outperforms existing centralized and distributed approaches in terms of mitigating pilot contamination and boosting the overall network throughput. This means devices can communicate more effectively, leading to better performance for applications that rely on massive MIMO networks, such as IoT (Internet of Things) systems.
Technical Explanation
The paper addresses the problem of pilot contamination in massive MIMO systems, which occurs when the limited availability of orthogonal pilot sequences leads to their reuse across different devices, causing degradation in channel estimation and overall network performance.
The proposed scheme utilizes a distributed approach to assign pilot sequences to devices, without the need for a centralized controller. This not only reduces the signaling overhead required for pilot assignment but also enhances the system's fault-tolerance, as there is no single point of failure.
The researchers conduct extensive numerical simulations to evaluate the performance of the proposed scheme, comparing it to existing centralized and distributed approaches. The results show that the proposed scheme significantly outperforms the alternatives in terms of mitigating pilot contamination and enhancing overall network throughput.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive solution to the pilot contamination problem in massive MIMO networks, which is a critical issue for the scalability and practical deployment of these systems. The distributed nature of the proposed scheme is a particular strength, as it addresses the limitations of centralized approaches and enhances the system's resilience.
However, the paper does not explore the impact of the proposed scheme on other aspects of the network, such as user-AP (access point) association and power control optimization. It would be valuable to understand how the distributed pilot assignment interacts with these other important network management functions.
Additionally, the paper does not provide a detailed analysis of the computational complexity and signaling overhead associated with the proposed scheme. While the authors claim that it reduces signaling overhead, a more quantitative assessment would help readers understand the practical implementation implications.
Further research could also explore the performance of the proposed scheme in more realistic scenarios, such as considering the impact of user mobility and channel estimation errors. This would help validate the scheme's robustness and applicability in real-world deployments.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel distributed pilot assignment scheme that effectively mitigates the impact of pilot contamination in massive MIMO networks. By leveraging a decentralized approach, the proposed scheme reduces signaling overhead and enhances the system's fault-tolerance, leading to significant improvements in network throughput compared to existing centralized and distributed solutions.
The results of this research have important implications for the scalability and practical deployment of massive MIMO technologies, particularly in the context of IoT systems that require reliable and high-performance wireless connectivity. As the demand for ubiquitous and efficient wireless communication continues to grow, innovations like the one presented in this paper will play a crucial role in realizing the full potential of massive MIMO networks.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🌀

0
Distributed Pilot Assignment for Distributed Massive-MIMO Networks
Mohd Saif Ali Khan, Samar Agnihotri, Karthik R. M
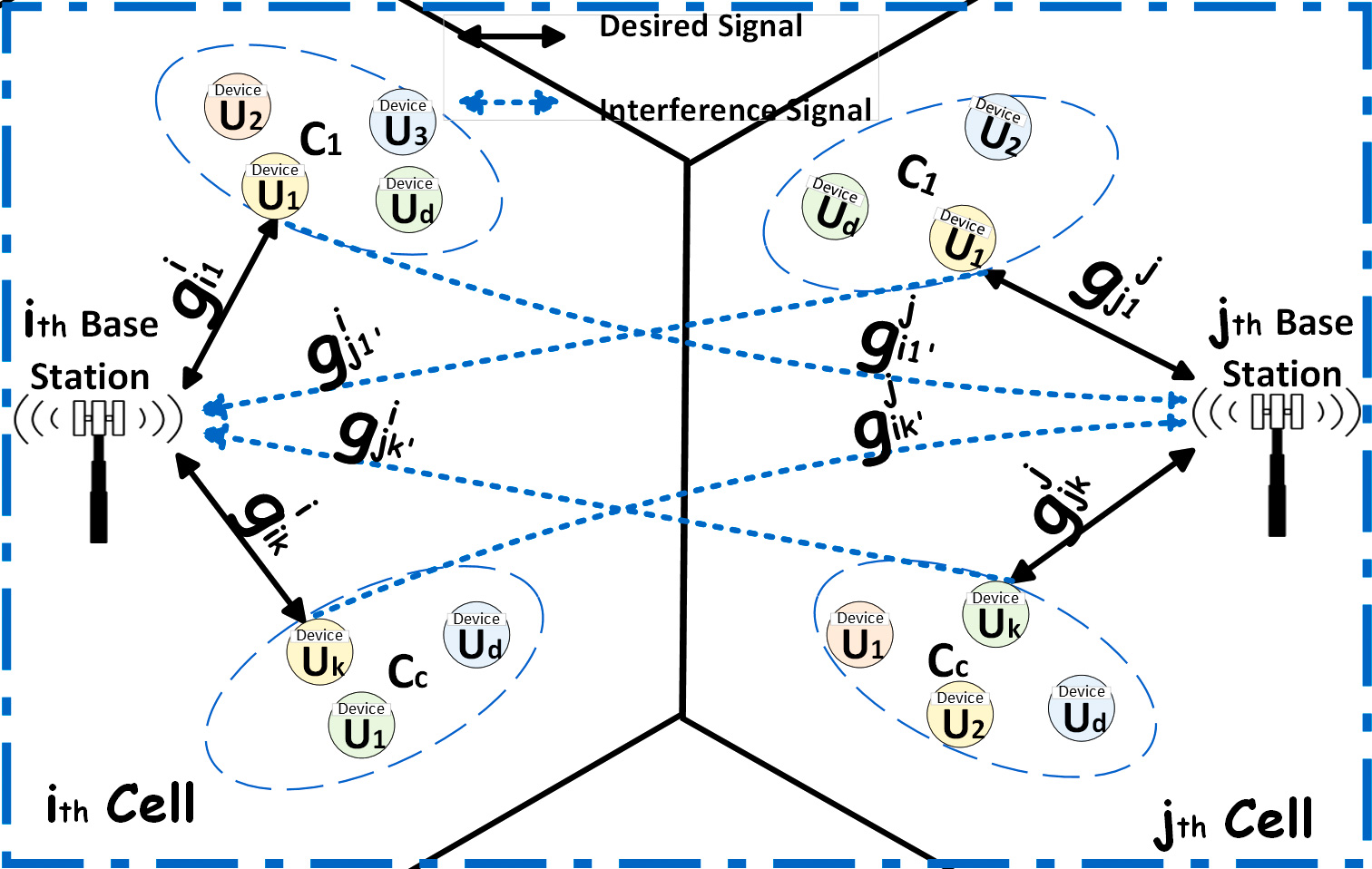
Pilot contamination is a critical issue in distributed massive MIMO networks, where the reuse of pilot sequences due to limited availability of orthogonal pilots for channel estimation leads to performance degradation. In this work, we propose a novel distributed pilot assignment scheme to effectively mitigate the impact of pilot contamination. Our proposed scheme not only reduces signaling overhead, but it also enhances fault-tolerance. Extensive numerical simulations are conducted to evaluate the performance of the proposed scheme. Our results establish that the proposed scheme outperforms existing centralized and distributed schemes in terms of mitigating pilot contamination and significantly enhancing network throughput.
Read more7/2/2024
🔄

0
Mitigating Pilot Contamination and Enabling IoT Scalability in Massive MIMO Systems
Muhammad Kamran Saeed, Ahmed E. Kamal, Ashfaq Khokhar
Massive MIMO is expected to play an important role in the development of 5G networks. This paper addresses the issue of pilot contamination and scalability in massive MIMO systems. The current practice of reusing orthogonal pilot sequences in adjacent cells leads to difficulty in differentiating incoming inter- and intra-cell pilot sequences. One possible solution is to increase the number of orthogonal pilot sequences, which results in dedicating more space of coherence block to pilot transmission than data transmission. This, in turn, also hinders the scalability of massive MIMO systems, particularly in accommodating a large number of IoT devices within a cell. To overcome these challenges, this paper devises an innovative pilot allocation scheme based on the data transfer patterns of IoT devices. The scheme assigns orthogonal pilot sequences to clusters of devices instead of individual devices, allowing multiple devices to utilize the same pilot for periodically transmitting data. Moreover, we formulate the pilot assignment problem as a graph coloring problem and use the max k-cut graph partitioning approach to overcome the pilot contamination in a multicell massive MIMO system. The proposed scheme significantly improves the spectral efficiency and enables the scalability of massive MIMO systems; for instance, by using ten orthogonal pilot sequences, we are able to accommodate 200 devices with only a 12.5% omission rate.
Read more5/1/2024
✨

0
Pilot Contamination in Massive MIMO Systems: Challenges and Future Prospects
Muhammad Kamran Saeed, Ashfaq Khokhar, Shakil Ahmed
Massive multiple input multiple output (M-MIMO) technology plays a pivotal role in fifth-generation (5G) and beyond communication systems, offering a wide range of benefits, from increased spectral efficiency (SE) to enhanced energy efficiency and higher reliability. However, these advantages are contingent upon precise channel state information (CSI) availability at the base station (BS). Ensuring precise CSI is challenging due to the constrained size of the coherence interval and the resulting limitations on pilot sequence length. Therefore, reusing pilot sequences in adjacent cells introduces pilot contamination, hindering SE enhancement. This paper reviews recent advancements and addresses research challenges in mitigating pilot contamination and improving channel estimation, categorizing the existing research into three broader categories: pilot assignment schemes, advanced signal processing methods, and advanced channel estimation techniques. Salient representative pilot mitigation/assignment techniques are analyzed and compared in each category. Lastly, possible future research directions are discussed.
Read more5/3/2024

0
Smart Pilot Assignment for IoT in Massive MIMO Systems: A Path Towards Scalable IoT Infrastructure
Muhammad Kamran Saeed, Ashfaq Khokhar
5G sets the foundation for an era of creativity with its faster speeds, increased data throughput, reduced latency, and enhanced IoT connectivity, all enabled by Massive MIMO (M-MIMO) technology. M-MIMO boosts network efficiency and enhances user experience by employing intelligent user scheduling. This paper presents a user scheduling scheme and pilot assignment strategy designed for IoT devices, emphasizing mitigating pilot contamination, a key obstacle to improving spectral efficiency (SE) and system scalability in M-MIMO networks. We utilize a user clustering-based pilot allocation scheme to boost IoT device scalability in M-MIMO systems. Additionally, our smart pilot allocation minimizes interference and enhances SE by treating pilot assignment as a graph coloring problem, optimizing it through integer linear programming (ILP). Recognizing the computational complexity of ILP, we introduced a binary search-based heuristic predicated on interference threshold to expedite the computation, while maintaining a near-optimal solution. The simulation results show a significant decrease in the required pilot overhead (about 17%), and substantial enhancement in SE (about 8-14%).
Read more5/1/2024