EchoGuide: Active Acoustic Guidance for LLM-Based Eating Event Analysis from Egocentric Videos
2406.10750

0
0

Abstract
Self-recording eating behaviors is a step towards a healthy lifestyle recommended by many health professionals. However, the current practice of manually recording eating activities using paper records or smartphone apps is often unsustainable and inaccurate. Smart glasses have emerged as a promising wearable form factor for tracking eating behaviors, but existing systems primarily identify when eating occurs without capturing details of the eating activities (E.g., what is being eaten). In this paper, we present EchoGuide, an application and system pipeline that leverages low-power active acoustic sensing to guide head-mounted cameras to capture egocentric videos, enabling efficient and detailed analysis of eating activities. By combining active acoustic sensing for eating detection with video captioning models and large-scale language models for retrieval augmentation, EchoGuide intelligently clips and analyzes videos to create concise, relevant activity records on eating. We evaluated EchoGuide with 9 participants in naturalistic settings involving eating activities, demonstrating high-quality summarization and significant reductions in video data needed, paving the way for practical, scalable eating activity tracking.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents EchoGuide, an active acoustic guidance system for enhancing the performance of large language model (LLM)-based eating event analysis from egocentric videos.
- EchoGuide uses acoustic sensors to provide real-time feedback to users, guiding them to improve the data collection process and ultimately enhance the accuracy of the LLM-based eating event recognition.
- The proposed system aims to address the challenges associated with collecting high-quality egocentric video data for dietary intake assessment, which is crucial for various health-related applications.
Plain English Explanation
EchoGuide: Active Acoustic Guidance for LLM-Based Eating Event Analysis from Egocentric Videos is a research project that focuses on improving the analysis of eating events from video footage captured by a person wearing a camera. The researchers developed a system called EchoGuide that uses acoustic (sound) sensors to provide real-time feedback to the user during the data collection process.
The goal of EchoGuide is to help ensure that the video data being collected is of high quality, which is essential for accurately identifying and analyzing eating events using large language models (LLMs). LLMs are a type of artificial intelligence that can be trained to recognize patterns and extract information from text and other data.
By providing users with real-time acoustic guidance, EchoGuide helps them adjust their behavior and positioning to capture better video footage, leading to improved accuracy in the LLM-based analysis of eating events. This is important for various health-related applications, such as dietary intake assessment, where accurate data is crucial for understanding a person's eating habits and providing personalized recommendations.
Technical Explanation
EchoGuide: Active Acoustic Guidance for LLM-Based Eating Event Analysis from Egocentric Videos presents a system that combines active acoustic sensing and LLM-based analysis to improve the quality of egocentric video data used for dietary intake assessment.
The key components of the EchoGuide system include:
- Acoustic Sensors: The system uses a set of acoustic sensors placed in the user's environment to capture real-time audio feedback during the data collection process.
- Feedback Generation: EchoGuide analyzes the acoustic data and provides immediate feedback to the user, guiding them to adjust their behavior and positioning to improve the quality of the video footage.
- LLM-Based Eating Event Analysis: The system uses LLMs trained on high-quality egocentric video data to accurately recognize and analyze eating events, leveraging the improved data collected with the help of the acoustic feedback.
The researchers evaluated the performance of EchoGuide in a series of experiments, demonstrating its ability to enhance the accuracy of LLM-based eating event recognition compared to a baseline approach without acoustic guidance. The results suggest that the proposed system can be a valuable tool for researchers and healthcare professionals working on dietary intake assessment and related health applications.
Critical Analysis
The EchoGuide system presented in the paper addresses an important challenge in the field of egocentric video analysis for dietary intake assessment. By incorporating active acoustic guidance, the researchers aim to improve the quality of the video data used for LLM-based eating event recognition, which is a crucial step in understanding an individual's eating habits.
One potential limitation of the approach is the reliance on the user's compliance with the acoustic feedback. The effectiveness of EchoGuide may be influenced by the user's willingness to adjust their behavior based on the guidance provided. Additionally, the system's performance may be affected by factors such as environmental noise, sensor placement, and individual variations in eating habits.
Further research could explore ways to enhance the robustness of the acoustic feedback system, potentially by incorporating additional sensors or using more advanced signal processing techniques. Investigations into the long-term usability and user acceptance of the EchoGuide system would also be valuable in understanding its real-world applicability.
Conclusion
EchoGuide: Active Acoustic Guidance for LLM-Based Eating Event Analysis from Egocentric Videos presents a novel approach to enhancing the quality of egocentric video data used for dietary intake assessment. By integrating active acoustic sensing and feedback, the system aims to guide users in capturing high-quality video footage, which can then be analyzed more accurately using LLM-based techniques.
The proposed EchoGuide system has the potential to significantly improve the performance of LLM-based eating event recognition, ultimately leading to better understanding and assessment of individual dietary habits. This research contributes to the ongoing efforts to develop more robust and reliable tools for dietary monitoring and personalized healthcare applications.
Further advancements in this area, such as exploring multimodal sensor fusion and adaptive feedback mechanisms, could help expand the capabilities and practical applicability of systems like EchoGuide in the future.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

MunchSonic: Tracking Fine-grained Dietary Actions through Active Acoustic Sensing on Eyeglasses
Saif Mahmud, Devansh Agarwal, Ashwin Ajit, Qikang Liang, Thalia Viranda, Francois Guimbretiere, Cheng Zhang

0
0
We introduce MunchSonic, an AI-powered active acoustic sensing system integrated into eyeglasses, designed to track fine-grained dietary actions like hand-to-mouth movements for food intake, chewing, and drinking. MunchSonic emits inaudible ultrasonic waves from a commodity eyeglass frame. The reflected signals contain rich information about the position and movements of various body parts, including the mouth, jaw, arms, and hands, all of which are involved in eating activities. These signals are then processed by a custom deep-learning pipeline to classify six actions: food intake, chewing, drinking, talking, face-hand touching, and other activities (null). In an unconstrained user study with 12 participants, MunchSonic achieves a 93.5% macro F1-score in a user-independent evaluation with a 2-second time resolution, demonstrating its effectiveness. Additionally, MunchSonic accurately tracks eating episodes and the frequency of food intake within those episodes.
6/3/2024

ActSonic: Everyday Activity Recognition on Smart Glasses using Active Acoustic Sensing
Saif Mahmud, Vineet Parikh, Qikang Liang, Ke Li, Ruidong Zhang, Ashwin Ajit, Vipin Gunda, Devansh Agarwal, Franc{c}ois Guimbreti`ere, Cheng Zhang

0
0
We present ActSonic, an intelligent, low-power active acoustic sensing system integrated into eyeglasses that can recognize 27 different everyday activities (e.g., eating, drinking, toothbrushing) from inaudible acoustic waves around the body with a time resolution of one second. It only needs a pair of miniature speakers and microphones mounted on each hinge of eyeglasses to emit ultrasonic waves to create an acoustic aura around the body. Based on the position and motion of various body parts, the acoustic signals are reflected with unique patterns captured by the microphone and analyzed by a customized self-supervised deep learning framework to infer the performed activities. ActSonic was deployed in a user study with 19 participants across 19 households to evaluate its efficacy. Without requiring any training data from a new user (leave-one-participant-out evaluation), ActSonic was able to detect 27 activities, achieving an average F1-score of 86.6% in fully unconstrained scenarios and 93.4% in prompted settings at participants' homes.
5/9/2024

MeciFace: Mechanomyography and Inertial Fusion-based Glasses for Edge Real-Time Recognition of Facial and Eating Activities
Hymalai Bello, Sungho Suh, Bo Zhou, Paul Lukowicz

0
0
The increasing prevalence of stress-related eating behaviors and their impact on overall health highlights the importance of effective and ubiquitous monitoring systems. In this paper, we present MeciFace, an innovative wearable technology designed to monitor facial expressions and eating activities in real-time on-the-edge (RTE). MeciFace aims to provide a low-power, privacy-conscious, and highly accurate tool for promoting healthy eating behaviors and stress management. We employ lightweight convolutional neural networks as backbone models for facial expression and eating monitoring scenarios. The MeciFace system ensures efficient data processing with a tiny memory footprint, ranging from 11KB to 19 KB. During RTE evaluation, the system achieves an F1-score of < 86% for facial expression recognition and 94% for eating/drinking monitoring, for the RTE of unseen users (user-independent case).
4/4/2024
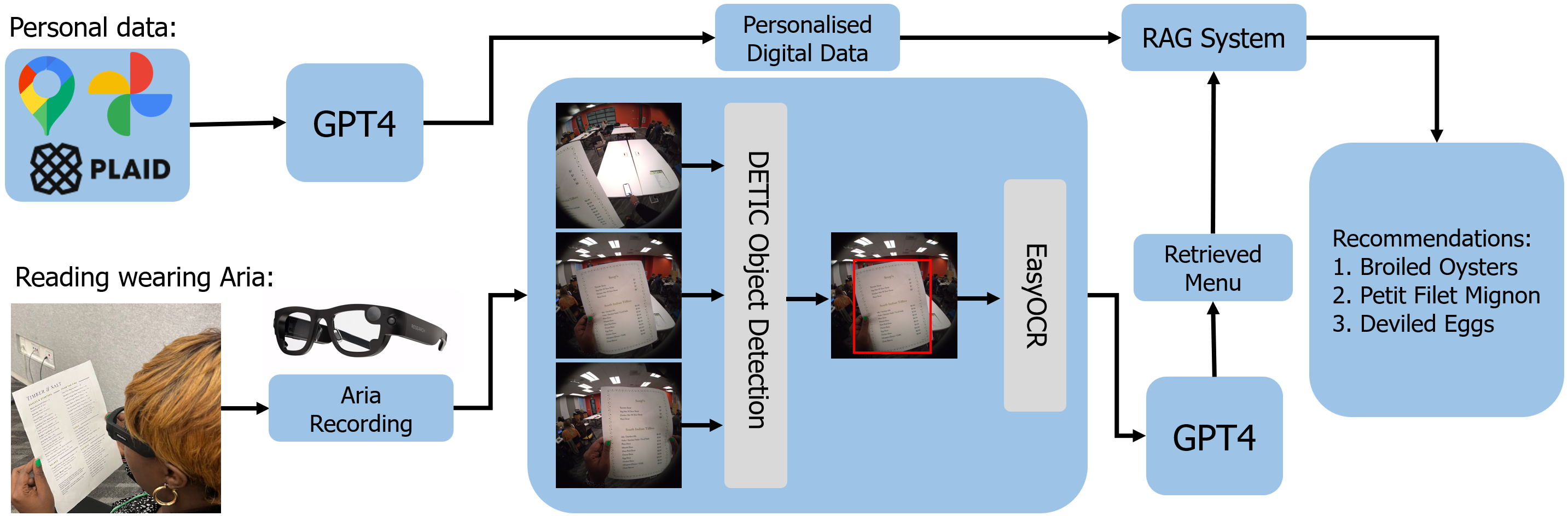
TEXT2TASTE: A Versatile Egocentric Vision System for Intelligent Reading Assistance Using Large Language Model
Wiktor Mucha, Florin Cuconasu, Naome A. Etori, Valia Kalokyri, Giovanni Trappolini

0
0
The ability to read, understand and find important information from written text is a critical skill in our daily lives for our independence, comfort and safety. However, a significant part of our society is affected by partial vision impairment, which leads to discomfort and dependency in daily activities. To address the limitations of this part of society, we propose an intelligent reading assistant based on smart glasses with embedded RGB cameras and a Large Language Model (LLM), whose functionality goes beyond corrective lenses. The video recorded from the egocentric perspective of a person wearing the glasses is processed to localise text information using object detection and optical character recognition methods. The LLM processes the data and allows the user to interact with the text and responds to a given query, thus extending the functionality of corrective lenses with the ability to find and summarize knowledge from the text. To evaluate our method, we create a chat-based application that allows the user to interact with the system. The evaluation is conducted in a real-world setting, such as reading menus in a restaurant, and involves four participants. The results show robust accuracy in text retrieval. The system not only provides accurate meal suggestions but also achieves high user satisfaction, highlighting the potential of smart glasses and LLMs in assisting people with special needs.
4/16/2024