ELMO2EDS: Transforming Educational Credentials into Self-Sovereign Identity Paradigm

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents ELMO2EDS, a system that transforms educational credentials into a self-sovereign identity (SSI) paradigm.
- The research was funded by the IDunion project, which is organized by the German Ministry of Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWK).
- The paper explores the integration of educational credentials, such as those from the Europass and EMREX systems, into a decentralized, blockchain-based SSI framework.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a way to take your educational credentials, like diplomas and certificates, and convert them into a digital format that can be stored and verified in a decentralized, blockchain-based system. This system is called a "self-sovereign identity" (SSI) paradigm, which means you have more control over your own digital identity and information.
Currently, your educational credentials are often stored in centralized databases, which can make it difficult to share and verify them. The ELMO2EDS system aims to change this by transforming these credentials into a format that can be easily shared and verified using blockchain technology. This could make it simpler for you to prove your qualifications to potential employers or educational institutions, without having to go through multiple, centralized systems.
The researchers worked with existing standards and systems, like Europass and EMREX, to integrate educational credentials into this new SSI framework. This helps ensure the system is compatible with existing infrastructure and can be more easily adopted.
Technical Explanation
The ELMO2EDS system focuses on transforming educational credentials, such as those from the Europass and EMREX systems, into a decentralized, blockchain-based self-sovereign identity (SSI) framework.
The key components of the system include:
-
Credential Transformation: The researchers developed methods to convert the syntactic and semantic structures of existing educational credential formats, like ELMO (European Learner Mobility), into a format compatible with verifiable credentials used in SSI systems.
-
Ontology Integration: The team integrated domain-specific ontologies, such as the Credentials Occupation Ontology, to ensure the semantic integrity of the transformed credentials within the SSI paradigm.
-
Decentralized Verification: The system leverages decentralized credential verification techniques to enable tamper-resistant validation of the transformed educational credentials.
-
Privacy-Preserving Mechanisms: The researchers explored privacy-preserving pseudonym schemes to protect the personal data associated with the educational credentials within the SSI framework.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to integrating educational credentials into a self-sovereign identity paradigm. However, the researchers acknowledge several limitations and areas for further research:
- The system currently focuses on specific credential formats (e.g., ELMO, Europass) and may require additional work to support a broader range of educational credential types.
- The privacy-preserving mechanisms, while promising, may need further refinement and evaluation to ensure they adequately protect sensitive personal data.
- The adoption and integration of the ELMO2EDS system within existing educational and employment ecosystems will require careful coordination and collaboration with various stakeholders.
Nonetheless, the research demonstrates a compelling vision for empowering individuals to have greater control over their educational credentials and the associated data, which could have significant implications for lifelong learning, employment, and broader societal benefits.
Conclusion
The ELMO2EDS system presents a novel approach to transforming educational credentials into a self-sovereign identity paradigm. By leveraging blockchain technology and integrating with existing standards and systems, the researchers aim to give individuals more control over their educational data and improve the portability and verification of their qualifications.
While the research has some limitations that require further exploration, the overall concept of empowering individuals through decentralized, blockchain-based identity management systems holds significant promise for the future of education, employment, and beyond.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
ELMO2EDS: Transforming Educational Credentials into Self-Sovereign Identity Paradigm
Patrick Herbke, Hakan Yildiz
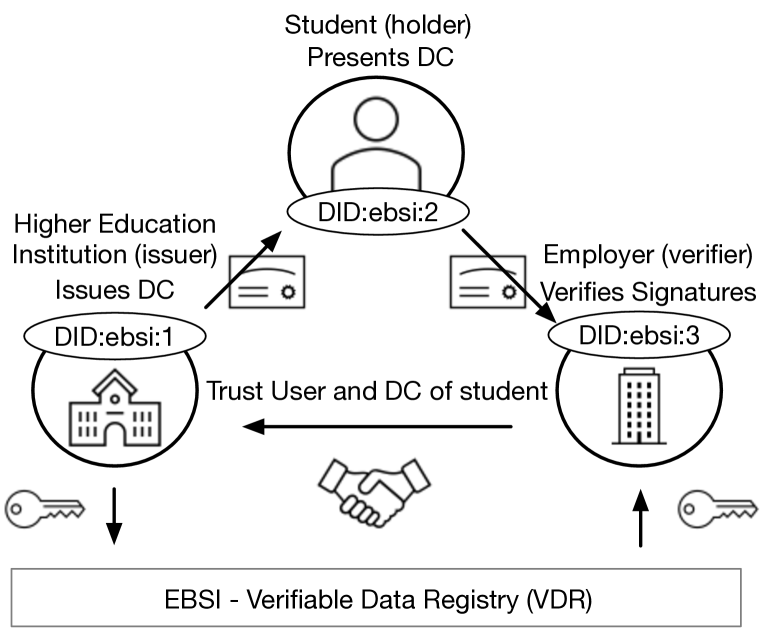
Digital credentials in education make it easier for students to apply for a course of study, a new job, or change a higher education institute. Academic networks, such as EMREX, support the exchange of digital credentials between students and education institutes. Students can fetch results from one educational institute and apply for a course of study at another educational institute. Digital signatures of the issuing institution can verify the authenticity of digital credentials. Each institution must provide the integration of EMREX using its identity management system. In this paper, we investigate how digital credentials can be integrated into the Self-Sovereign Identity ecosystem to overcome the known issues of academic networks. We examine known issues such as the authentication of students. Self-Sovereign Identity is a paradigm that gives individuals control of their digital identities. Based on our findings, we propose ELMO2EDS, a solution that 1) converts digital credentials from EMREX to a suitable Self-Sovereign Identy data format, 2) enables authenticating a student, and 3) enables issuing, storing, and verification of achieved study.
Read more6/18/2024


0
Decentralized Credential Status Management: A Paradigm Shift in Digital Trust
Patrick Herbke, Thomas Cory, Mauro Migliardi
Public key infrastructures are essential for Internet security, ensuring robust certificate management and revocation mechanisms. The transition from centralized to decentralized systems presents challenges such as trust distribution and privacy-preserving credential management. The transition from centralized to decentralized systems is motivated by addressing the single points of failure inherent in centralized systems and leveraging decentralized technologies' transparency and resilience. This paper explores the evolution of certificate status management from centralized to decentralized frameworks, focusing on blockchain technology and advanced cryptography. We provide a taxonomy of the challenges of centralized systems and discuss opportunities provided by existing decentralized technologies. Our findings reveal that, although blockchain technologies enhance security and trust distribution, they represent a bottleneck for parallel computation and face inefficiencies in cryptographic computations. For this reason, we propose a framework of decentralized technology components that addresses such shortcomings to advance the paradigm shift toward decentralized credential status management.
Read more6/18/2024


0
Self-Sovereign Identity for Consented and Content-Based Access to Medical Records using Blockchain
Marie Tcholakian, Karolina Gorna, Maryline Laurent, Hella Kaffel Ben Ayed, Montassar Naghmouchi
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and Medical Data are classified as personal data in every privacy law, meaning that any related service that includes processing such data must come with full security, confidentiality, privacy and accountability. Solutions for health data management, as in storing it, sharing and processing it, are emerging quickly and were significantly boosted by the Covid-19 pandemic that created a need to move things online. EHRs makes a crucial part of digital identity data, and the same digital identity trends -- as in self sovereign identity powered by decentralized ledger technologies like Blockchain, are being researched or implemented in contexts managing digital interactions between health facilities, patients and health professionals. In this paper, we propose a blockchain-based solution enabling secure exchange of EHRs between different parties powered by a self-sovereign identity (SSI) wallet and decentralized identifiers. We also make use of a consortium IPFS network for off-chain storage and attribute-based encryption (ABE) to ensure data confidentiality and integrity. Through our solution, we grant users full control over their medical data, and enable them to securely share it in total confidentiality over secure communication channels between user wallets using encryption. We also use DIDs for better user privacy and limit any possible correlations or identification by using pairwise DIDs. Overall, combining this set of technologies guarantees secure exchange of EHRs, secure storage and management along with by-design features inherited from the technological stack.
Read more8/1/2024
🗣️

0
SSI4IoT: Unlocking the Potential of IoT Tailored Self-Sovereign Identity
Thusitha Dayaratne, Xinxin Fan, Yuhong Liu, Carsten Rudolph
The emerging Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) techniques, such as Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) and Verifiable Credentials (VCs), move control of digital identity from conventional identity providers to individuals and lay down the foundation for people, organizations, and things establishing rich digital relationship. The existing applications of SSI mainly focus on creating person-to-person and person-to-service relationships, whereas person-to-device and device-to-device interactions have been largely overlooked. In this paper, we close this gap by identifying a number of key challenges of applying SSI to the Internet of Things (IoT) and providing a comprehensive taxonomy and usage of VCs in the IoT context with respect to their validity period, trust and interoperability level, and scope of usage. The life-cycle management of VCs as well as various optimization techniques for realizing SSI in IoT environments are also addressed in great detail. This work is a noteworthy step towards massive adoption of SSI for securing existing and future IoT applications in practice.
Read more5/7/2024