Enhancing Legal Compliance and Regulation Analysis with Large Language Models
2404.17522

0
0
💬
Abstract
This research explores the application of Large Language Models (LLMs) for automating the extraction of requirement-related legal content in the food safety domain and checking legal compliance of regulatory artifacts. With Industry 4.0 revolutionizing the food industry and with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) reshaping privacy policies and data processing agreements, there is a growing gap between regulatory analysis and recent technological advancements. This study aims to bridge this gap by leveraging LLMs, namely BERT and GPT models, to accurately classify legal provisions and automate compliance checks. Our findings demonstrate promising results, indicating LLMs' significant potential to enhance legal compliance and regulatory analysis efficiency, notably by reducing manual workload and improving accuracy within reasonable time and financial constraints.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This research explores using Large Language Models (LLMs) like BERT and GPT to automate the extraction of legal requirements and check compliance in the food safety domain.
- With the rapid technological advancements in the food industry (Industry 4.0) and changes in privacy regulations (GDPR), there is a growing gap between regulatory analysis and these new developments.
- This study aims to bridge this gap by leveraging the capabilities of LLMs to accurately classify legal provisions and automate compliance checks.
Plain English Explanation
The paper examines how Large Language Models (LLMs) like BERT and GPT can be used to streamline the process of identifying legal requirements and ensuring regulatory compliance in the food industry. As the food sector undergoes significant technological transformations through Industry 4.0 and privacy regulations like the GDPR evolve, there is a growing gap between the latest advancements and the ability to analyze and comply with the relevant laws and regulations. This research aims to bridge that gap by leveraging the impressive language understanding capabilities of LLMs to automatically classify legal provisions and verify regulatory compliance. The findings suggest that these advanced AI models have great potential to enhance efficiency and accuracy in legal compliance and regulatory analysis, ultimately reducing the manual workload and improving overall compliance.
Technical Explanation
The researchers in this study focused on using BERT and GPT models, which are prominent examples of LLMs, to automate the extraction of requirement-related legal content and check the compliance of regulatory artifacts in the food safety domain. They designed experiments to evaluate the performance of these LLMs in accurately classifying legal provisions and automating compliance checks, which are crucial tasks in ensuring food safety regulations are met. The results demonstrate the significant potential of LLMs to enhance legal compliance and regulatory analysis efficiency, as they were able to reduce manual workload and improve accuracy within reasonable time and financial constraints.
Critical Analysis
The paper acknowledges some caveats and limitations of the research, such as the need for further testing and validation on a larger and more diverse dataset to ensure the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the researchers note the potential challenges in adapting the models to handle the nuances and complexities of legal language and the dynamic nature of regulatory environments. While the results are promising, more research is needed to fully understand the capabilities and limitations of LLMs in this domain, as well as to address potential biases or ethical concerns that may arise from the use of these powerful AI systems in legal and regulatory compliance applications.
Conclusion
This research highlights the promising potential of Large Language Models to revolutionize the way legal requirements are identified and regulatory compliance is verified, particularly in the rapidly evolving food safety domain. By leveraging the advanced language understanding and processing capabilities of models like BERT and GPT, the study demonstrates that it is possible to automate these critical tasks, reducing manual workload and improving accuracy. As the food industry continues to transform through Industry 4.0 and privacy regulations evolve, this research offers a glimpse into how AI can help bridge the gap between technological advancements and regulatory compliance, ultimately contributing to more efficient and effective food safety practices.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
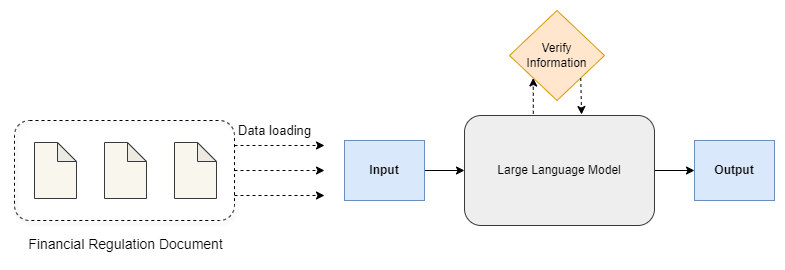
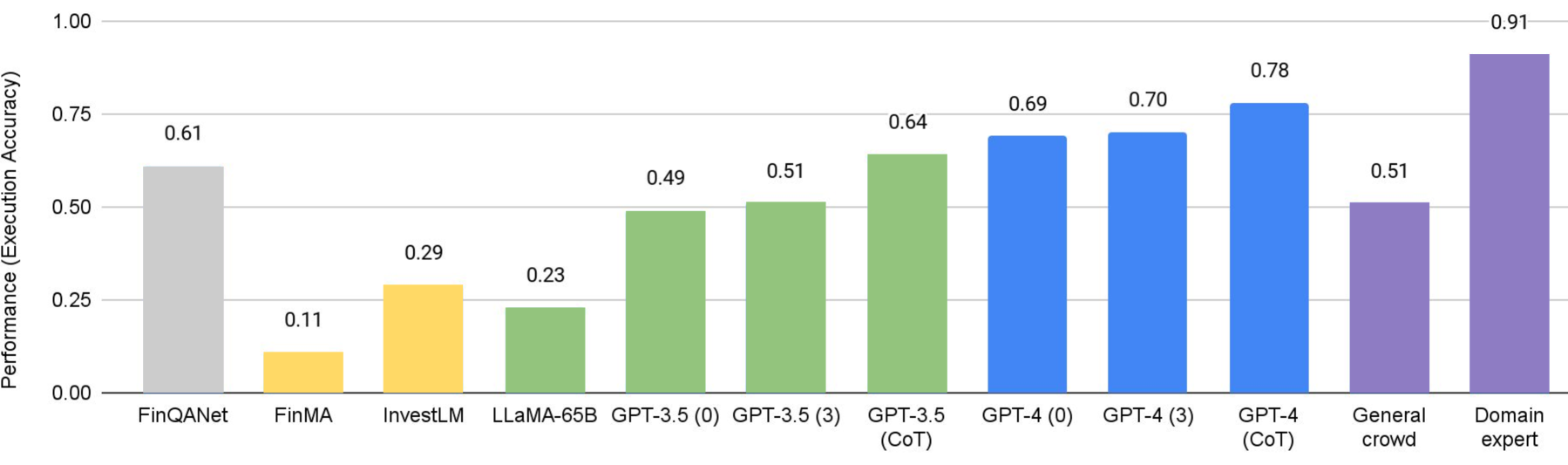
Large Language Model in Financial Regulatory Interpretation
Zhiyu Cao, Zachary Feinstein

0
0
This study explores the innovative use of Large Language Models (LLMs) as analytical tools for interpreting complex financial regulations. The primary objective is to design effective prompts that guide LLMs in distilling verbose and intricate regulatory texts, such as the Basel III capital requirement regulations, into a concise mathematical framework that can be subsequently translated into actionable code. This novel approach aims to streamline the implementation of regulatory mandates within the financial reporting and risk management systems of global banking institutions. A case study was conducted to assess the performance of various LLMs, demonstrating that GPT-4 outperforms other models in processing and collecting necessary information, as well as executing mathematical calculations. The case study utilized numerical simulations with asset holdings -- including fixed income, equities, currency pairs, and commodities -- to demonstrate how LLMs can effectively implement the Basel III capital adequacy requirements.
5/14/2024
A Survey on Large Language Models for Critical Societal Domains: Finance, Healthcare, and Law
Zhiyu Zoey Chen, Jing Ma, Xinlu Zhang, Nan Hao, An Yan, Armineh Nourbakhsh, Xianjun Yang, Julian McAuley, Linda Petzold, William Yang Wang

0
0
In the fast-evolving domain of artificial intelligence, large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-3 and GPT-4 are revolutionizing the landscapes of finance, healthcare, and law: domains characterized by their reliance on professional expertise, challenging data acquisition, high-stakes, and stringent regulatory compliance. This survey offers a detailed exploration of the methodologies, applications, challenges, and forward-looking opportunities of LLMs within these high-stakes sectors. We highlight the instrumental role of LLMs in enhancing diagnostic and treatment methodologies in healthcare, innovating financial analytics, and refining legal interpretation and compliance strategies. Moreover, we critically examine the ethics for LLM applications in these fields, pointing out the existing ethical concerns and the need for transparent, fair, and robust AI systems that respect regulatory norms. By presenting a thorough review of current literature and practical applications, we showcase the transformative impact of LLMs, and outline the imperative for interdisciplinary cooperation, methodological advancements, and ethical vigilance. Through this lens, we aim to spark dialogue and inspire future research dedicated to maximizing the benefits of LLMs while mitigating their risks in these precision-dependent sectors. To facilitate future research on LLMs in these critical societal domains, we also initiate a reading list that tracks the latest advancements under this topic, which will be continually updated: url{https://github.com/czyssrs/LLM_X_papers}.
5/6/2024

Large Language Models: A New Approach for Privacy Policy Analysis at Scale
David Rodriguez, Ian Yang, Jose M. Del Alamo, Norman Sadeh

0
0
The number and dynamic nature of web and mobile applications presents significant challenges for assessing their compliance with data protection laws. In this context, symbolic and statistical Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques have been employed for the automated analysis of these systems' privacy policies. However, these techniques typically require labor-intensive and potentially error-prone manually annotated datasets for training and validation. This research proposes the application of Large Language Models (LLMs) as an alternative for effectively and efficiently extracting privacy practices from privacy policies at scale. Particularly, we leverage well-known LLMs such as ChatGPT and Llama 2, and offer guidance on the optimal design of prompts, parameters, and models, incorporating advanced strategies such as few-shot learning. We further illustrate its capability to detect detailed and varied privacy practices accurately. Using several renowned datasets in the domain as a benchmark, our evaluation validates its exceptional performance, achieving an F1 score exceeding 93%. Besides, it does so with reduced costs, faster processing times, and fewer technical knowledge requirements. Consequently, we advocate for LLM-based solutions as a sound alternative to traditional NLP techniques for the automated analysis of privacy policies at scale.
6/3/2024

Exploring the Potential of Large Language Models for Improving Digital Forensic Investigation Efficiency
Akila Wickramasekara, Frank Breitinger, Mark Scanlon

0
0
The growing number of cases that require digital forensic analysis raises concerns about the ability of law enforcement to conduct investigations promptly. Consequently, this paper delves into the potential and effectiveness of integrating Large Language Models (LLMs) into digital forensic investigation to address these challenges. A comprehensive literature review is carried out, encompassing existing digital forensic models, tools, LLMs, deep learning techniques, and the use of LLMs in investigations. The review identifies current challenges within existing digital forensic processes and explores both the obstacles and possibilities of incorporating LLMs. In conclusion, the study asserts that the adoption of LLMs in digital forensics, with appropriate constraints, has the potential to improve investigation efficiency, improve traceability, and alleviate technical and judicial barriers faced by law enforcement entities.
6/12/2024