Evaluating Usability and Engagement of Large Language Models in Virtual Reality for Traditional Scottish Curling

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Evaluates usability and engagement of large language models (LLMs) in virtual reality (VR) for traditional Scottish curling
- Examines how LLMs can enhance user experiences in cultural heritage applications
- Provides insights into the design and implementation of LLM-powered VR experiences
Plain English Explanation
This research paper explores the use of large language models (LLMs) in virtual reality (VR) for a traditional Scottish sport called curling. The researchers were interested in understanding how LLMs can be leveraged to improve the user experience and engagement in cultural heritage applications.
Curling is a popular winter sport in Scotland, where players slide heavy stones across the ice towards a target. The researchers created a VR simulation of a traditional Scottish curling event, and then integrated LLMs to enhance the user's experience. LLMs are powerful AI models that can understand and generate human-like language, and the researchers wanted to see how they could be used to make the VR experience more engaging and informative for users.
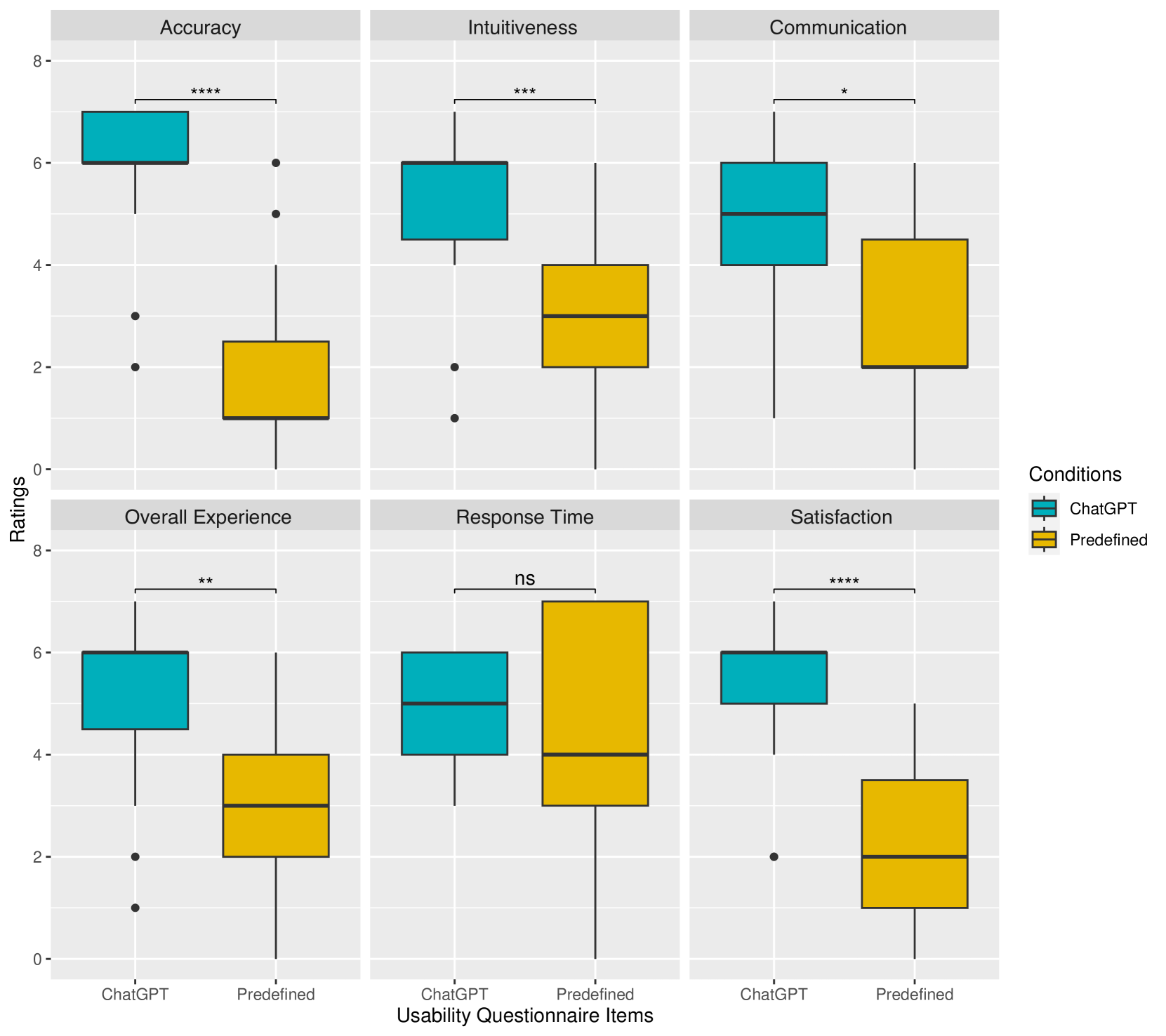
The researchers conducted experiments to evaluate the usability and engagement of the LLM-powered VR curling experience. They looked at factors such as ease of use, enjoyment, and the user's sense of presence and immersion in the virtual environment. The findings provide valuable insights into the potential of LLMs to enhance cultural heritage experiences in VR, and offer guidance for designers and developers who are interested in incorporating these technologies into their own projects.
Technical Explanation
The researchers designed and developed a virtual reality (VR) simulation of a traditional Scottish curling event, which they then integrated with large language models (LLMs) to enhance the user experience. The VR environment was created using Unity, a popular game engine, and the LLMs were integrated using natural language processing techniques.
The researchers conducted a series of user studies to evaluate the usability and engagement of the LLM-powered VR curling experience. Participants were recruited to try the VR simulation and provide feedback on factors such as ease of use, enjoyment, and their sense of presence and immersion in the virtual environment. The researchers used a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods, including surveys, interviews, and behavioral observations, to gather data and analyze the user experience.
The results of the study suggest that the integration of LLMs can significantly enhance the user experience in cultural heritage applications like the VR curling simulation. Participants reported higher levels of engagement, improved understanding of the sport, and a greater sense of presence and immersion in the virtual environment when the LLMs were enabled. The researchers also identified design considerations and technical challenges that should be addressed when incorporating LLMs into VR experiences.
Critical Analysis
The research presented in this paper provides valuable insights into the potential of large language models (LLMs) to enhance cultural heritage applications in virtual reality (VR). The researchers have demonstrated that LLMs can be effectively integrated into VR experiences to improve user engagement, understanding, and sense of presence.
One of the key strengths of this study is the rigorous experimental design and data collection methods. The researchers used a combination of quantitative and qualitative measures to assess the user experience, which provides a well-rounded understanding of the impact of LLMs in the VR curling simulation.
However, the researchers also acknowledge several limitations and areas for further research. For example, the study was conducted with a relatively small sample size, and the generalizability of the findings to other cultural heritage applications or user demographics remains to be explored. Additionally, the researchers did not investigate the long-term effects of LLM-powered VR experiences on user engagement and knowledge retention.
Further research could also explore the technical and design challenges associated with integrating LLMs into VR, such as optimizing the performance and seamless integration of these models, and developing guidelines for designers and developers on how to best leverage LLMs to enhance cultural heritage experiences.
Conclusion
This research paper provides a compelling demonstration of how large language models (LLMs) can be used to enhance user experiences in virtual reality (VR) for cultural heritage applications. The researchers' evaluation of the usability and engagement of an LLM-powered VR curling simulation offers valuable insights for designers, developers, and researchers interested in leveraging these technologies to create more immersive and informative cultural experiences.
The findings suggest that the integration of LLMs can significantly improve user engagement, understanding, and sense of presence in VR environments. This has important implications for the preservation and dissemination of cultural heritage, as VR experiences powered by LLMs can provide engaging and educational opportunities for people to learn about and appreciate traditional practices and customs.
As the capabilities of LLMs continue to evolve, and the accessibility of VR technology increases, the potential for these technologies to transform the way we experience and interact with cultural heritage is poised to grow. The insights from this research can help guide the development of future LLM-powered VR applications, and inspire further exploration into the ways in which these technologies can be leveraged to enhance our understanding and appreciation of the world's rich cultural diversity.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Evaluating Usability and Engagement of Large Language Models in Virtual Reality for Traditional Scottish Curling
Ka Hei Carrie Lau, Efe Bozkir, Hong Gao, Enkelejda Kasneci
This paper explores the innovative application of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Virtual Reality (VR) environments to promote heritage education, focusing on traditional Scottish curling presented in the game ``Scottish Bonspiel VR''. Our study compares the effectiveness of LLM-based chatbots with pre-defined scripted chatbots, evaluating key criteria such as usability, user engagement, and learning outcomes. The results show that LLM-based chatbots significantly improve interactivity and engagement, creating a more dynamic and immersive learning environment. This integration helps document and preserve cultural heritage and enhances dissemination processes, which are crucial for safeguarding intangible cultural heritage (ICH) amid environmental changes. Furthermore, the study highlights the potential of novel technologies in education to provide immersive experiences that foster a deeper appreciation of cultural heritage. These findings support the wider application of LLMs and VR in cultural education to address global challenges and promote sustainable practices to preserve and enhance cultural heritage.
Read more9/26/2024
💬

0
Embedding Large Language Models into Extended Reality: Opportunities and Challenges for Inclusion, Engagement, and Privacy
Efe Bozkir, Suleyman Ozdel, Ka Hei Carrie Lau, Mengdi Wang, Hong Gao, Enkelejda Kasneci
Advances in artificial intelligence and human-computer interaction will likely lead to extended reality (XR) becoming pervasive. While XR can provide users with interactive, engaging, and immersive experiences, non-player characters are often utilized in pre-scripted and conventional ways. This paper argues for using large language models (LLMs) in XR by embedding them in avatars or as narratives to facilitate inclusion through prompt engineering and fine-tuning the LLMs. We argue that this inclusion will promote diversity for XR use. Furthermore, the versatile conversational capabilities of LLMs will likely increase engagement in XR, helping XR become ubiquitous. Lastly, we speculate that combining the information provided to LLM-powered spaces by users and the biometric data obtained might lead to novel privacy invasions. While exploring potential privacy breaches, examining user privacy concerns and preferences is also essential. Therefore, despite challenges, LLM-powered XR is a promising area with several opportunities.
Read more6/21/2024
💬

0
How Can Large Language Models Enable Better Socially Assistive Human-Robot Interaction: A Brief Survey
Zhonghao Shi, Ellen Landrum, Amy O' Connell, Mina Kian, Leticia Pinto-Alva, Kaleen Shrestha, Xiaoyuan Zhu, Maja J Matari'c
Socially assistive robots (SARs) have shown great success in providing personalized cognitive-affective support for user populations with special needs such as older adults, children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and individuals with mental health challenges. The large body of work on SAR demonstrates its potential to provide at-home support that complements clinic-based interventions delivered by mental health professionals, making these interventions more effective and accessible. However, there are still several major technical challenges that hinder SAR-mediated interactions and interventions from reaching human-level social intelligence and efficacy. With the recent advances in large language models (LLMs), there is an increased potential for novel applications within the field of SAR that can significantly expand the current capabilities of SARs. However, incorporating LLMs introduces new risks and ethical concerns that have not yet been encountered, and must be carefully be addressed to safely deploy these more advanced systems. In this work, we aim to conduct a brief survey on the use of LLMs in SAR technologies, and discuss the potentials and risks of applying LLMs to the following three major technical challenges of SAR: 1) natural language dialog; 2) multimodal understanding; 3) LLMs as robot policies.
Read more4/9/2024
💬

0
Large Language Models for Human-Robot Interaction: Opportunities and Risks
Jesse Atuhurra
The tremendous development in large language models (LLM) has led to a new wave of innovations and applications and yielded research results that were initially forecast to take longer. In this work, we tap into these recent developments and present a meta-study about the potential of large language models if deployed in social robots. We place particular emphasis on the applications of social robots: education, healthcare, and entertainment. Before being deployed in social robots, we also study how these language models could be safely trained to ``understand'' societal norms and issues, such as trust, bias, ethics, cognition, and teamwork. We hope this study provides a resourceful guide to other robotics researchers interested in incorporating language models in their robots.
Read more5/3/2024