Experimental Evaluation of Interactive Edge/Cloud Virtual Reality Gaming over Wi-Fi using Unity Render Streaming

0
🛠️
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Virtual Reality (VR) streaming allows users to immerse themselves in interactive virtual environments using even low-end devices.
- The quality of the VR experience heavily depends on Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) performance, as it is the last step in the network chain.
- This study explores the relationship between Wi-Fi and VR traffic, using empirical data and a Wi-Fi simulator.
- It evaluates Wi-Fi's suitability for VR streaming in terms of the Quality of Service (QoS) it provides.
Plain English Explanation
Virtual reality (VR) technology allows people to feel like they are in a completely different, interactive environment, even when using basic devices. However, the quality of this VR experience relies a lot on the performance of the wireless (Wi-Fi) network that connects the VR device to the internet.
This research study looked closely at how the Wi-Fi network affects VR streaming. The researchers used real-world data and a Wi-Fi simulation tool to understand the relationship between the Wi-Fi network and the VR video data being transmitted. They wanted to see if Wi-Fi is a good fit for providing the level of quality and responsiveness needed for a high-quality VR experience.
The study used a technology called Unity Render Streaming to stream real-time VR game content over a Wi-Fi 6 network. This content was streamed from a server located close to the user, at the "edge" of the network.
The researchers found that the system maintained good network performance, with minimal delays and jitter (variations in delay) at frame rates of 60 and 90 frames per second. They also discovered an interesting pattern in how the VR video data was transmitted - the video frames were broken up into small packets and sent in batches at regular intervals, rather than continuously. This approach helped keep the video packet delays consistent across different frame rates, but it also meant the Wi-Fi network had to work harder to transmit all the packets.
The key insight is that shortening the interval between these batches of video packets can make the Wi-Fi network more efficient and reduce delays in delivering complete video frames to the VR device.
Technical Explanation
The researchers used Unity Render Streaming to remotely stream real-time VR gaming content over a Wi-Fi 6 network, with the server located at the network edge, close to the end-user. They evaluated the system's network performance in terms of round-trip time (RTT) and jitter at 60 and 90 frames per second (fps).
The study revealed a distinctive video transmission approach inherent to WebRTC-based services: the systematic packetization of video frames (VFs) and their transmission in discrete batches at regular intervals, regardless of the targeted frame rate. This interval-based transmission strategy maintains consistent video packet delays across video frame rates, but it also leads to increased Wi-Fi airtime consumption.
The researchers found that shortening the interval between these batches of video packets is advantageous, as it enhances Wi-Fi efficiency and reduces delays in delivering complete frames to the VR device.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a detailed technical analysis of the impact of Wi-Fi performance on VR streaming quality, using a real-world VR streaming system and a Wi-Fi simulation environment. The researchers' findings offer valuable insights into the unique characteristics of WebRTC-based VR video transmission and the trade-offs between consistent packet delays and Wi-Fi efficiency.
One potential caveat is that the study was conducted in a controlled, lab-like environment, and the results may not fully capture the complexities of real-world network conditions, user movements, and other factors that could affect VR streaming performance. Further research may be needed to validate the findings in more diverse and dynamic network settings.
Additionally, the paper does not explore the implications of the interval-based transmission strategy on other aspects of the VR experience, such as the perceived smoothness of the visual rendering or the responsiveness of user interactions. These factors could also be important in evaluating the overall quality of the VR experience.
Conclusion
This study offers a comprehensive understanding of the interplay between Wi-Fi performance and VR streaming quality. By uncovering the unique transmission patterns of WebRTC-based VR video and demonstrating the benefits of shorter transmission intervals, the researchers provide valuable insights that can inform the design and optimization of future VR streaming systems. These findings have the potential to help ensure that users can enjoy seamless, high-quality VR experiences, even when relying on wireless network connections.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🛠️

0
Experimental Evaluation of Interactive Edge/Cloud Virtual Reality Gaming over Wi-Fi using Unity Render Streaming
Miguel Casasnovas, Costas Michaelides, Marc Carrascosa-Zamacois, Boris Bellalta
Virtual Reality (VR) streaming enables end-users to seamlessly immerse themselves in interactive virtual environments using even low-end devices. However, the quality of the VR experience heavily relies on Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) performance, since it serves as the last hop in the network chain. Our study delves into the intricate interplay between Wi-Fi and VR traffic, drawing upon empirical data and leveraging a Wi-Fi simulator. In this work, we further evaluate Wi-Fi's suitability for VR streaming in terms of the Quality of Service (QoS) it provides. In particular, we employ Unity Render Streaming to remotely stream real-time VR gaming content over Wi-Fi 6 using Web Real-Time Communication (WebRTC), considering a server physically located at the network's edge, near the end user. Our findings demonstrate the system's sustained network performance, showcasing minimal round-trip time (RTT) and jitter at 60 and 90 frames per second (fps). In addition, we uncover the characteristics and patterns of the generated traffic streams, unveiling a distinctive video transmission approach inherent to WebRTC-based services: the systematic packetization of video frames (VFs) and their transmission in discrete batches at regular intervals, regardless of the targeted frame rate. This interval-based transmission strategy maintains consistent video packet delays across video frame rates but leads to increased Wi-Fi airtime consumption. Our results demonstrate that shortening the interval between batches is advantageous, as it enhances Wi-Fi efficiency and reduces delays in delivering complete frames.
Read more8/7/2024


0
Experimenting with Adaptive Bitrate Algorithms for Virtual Reality Streaming over Wi-Fi
Ferran Maura, Miguel Casasnovas, Boris Bellalta
Interactive Virtual Reality (VR) streaming over Wi-Fi networks encounters significant challenges due to bandwidth fluctuations caused by channel contention and user mobility. Adaptive BitRate (ABR) algorithms dynamically adjust the video encoding bitrate based on the available network capacity, aiming to maximize image quality while mitigating congestion and preserving the user's Quality of Experience (QoE). In this paper, we experiment with ABR algorithms for VR streaming using Air Light VR (ALVR), an open-source VR streaming solution. We extend ALVR with a comprehensive set of metrics that provide a robust characterization of the network's state, enabling more informed bitrate adjustments. To demonstrate the utility of these performance indicators, we develop and test the Network-aware Step-wise ABR algorithm for VR streaming (NeSt-VR). Results validate the accuracy of the newly implemented network performance metrics and demonstrate NeSt-VR's video bitrate adaptation capabilities.
Read more7/23/2024


0
Virtual Reality Traffic Prioritization for Wi-Fi Quality of Service Improvement using Machine Learning Classification Techniques
Seyedeh Soheila Shaabanzadeh (Universitat Polit`ecnica de Catalunya), Marc Carrascosa-Zamacois (Universitat Pompeu Fabra), Juan S'anchez-Gonz'alez (Universitat Polit`ecnica de Catalunya), Costas Michaelides (Universitat Pompeu Fabra), Boris Bellalta (Universitat Pompeu Fabra)
The increase in the demand for eXtended Reality (XR)/Virtual Reality (VR) services in the recent years, poses a great challenge for Wi-Fi networks to maintain the strict latency requirements. In VR over Wi-Fi, latency is a significant issue. In fact, VR users expect instantaneous responses to their interactions, and any noticeable delay can disrupt user experience. Such disruptions can cause motion sickness, and users might end up quitting the service. Differentiating interactive VR traffic from Non-VR traffic within a Wi-Fi network can aim to decrease latency for VR users and improve Wi-Fi Quality of Service (QoS) with giving priority to VR users in the access point (AP) and efficiently handle VR traffic. In this paper, we propose a machine learning-based approach for identifying interactive VR traffic in a Cloud-Edge VR scenario. The correlation between downlink and uplink is crucial in our study. First, we extract features from single-user traffic characteristics and then, we compare six common classification techniques (i.e., Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machines, k-Nearest Neighbors, Decision Trees, Random Forest, and Naive Bayes). For each classifier, a process of hyperparameter tuning and feature selection, namely permutation importance is applied. The model created is evaluated using datasets generated by different VR applications, including both single and multi-user cases. Then, a Wi-Fi network simulator is used to analyze the VR traffic identification and prioritization QoS improvements. Our simulation results show that we successfully reduce VR traffic delays by a factor of 4.2x compared to scenarios without prioritization, while incurring only a 2.3x increase in delay for background (BG) traffic related to Non-VR services.
Read more8/19/2024
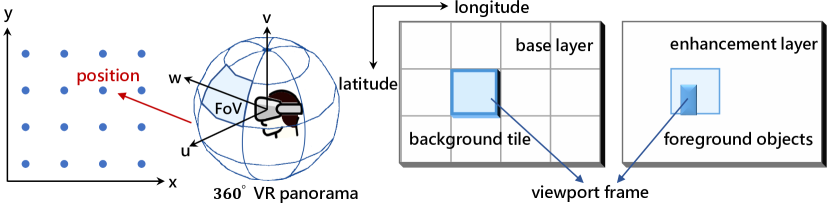

0
Wireless Multi-User Interactive Virtual Reality in Metaverse with Edge-Device Collaborative Computing
Caolu Xu, Zhiyong Chen, Meixia Tao, Wenjun Zhang
The immersive nature of the metaverse presents significant challenges for wireless multi-user interactive virtual reality (VR), such as ultra-low latency, high throughput and intensive computing, which place substantial demands on the wireless bandwidth and rendering resources of mobile edge computing (MEC). In this paper, we propose a wireless multi-user interactive VR with edge-device collaborative computing framework to overcome the motion-to-photon (MTP) threshold bottleneck. Specifically, we model the serial-parallel task execution in queues within a foreground and background separation architecture. The rendering indices of background tiles within the prediction window are determined, and both the foreground and selected background tiles are loaded into respective processing queues based on the rendering locations. To minimize the age of sensor information and the power consumption of mobile devices, we optimize rendering decisions and MEC resource allocation subject to the MTP constraint. To address this optimization problem, we design a safe reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm, active queue management-constrained updated projection (AQM-CUP). AQM-CUP constructs an environment suitable for queues, incorporating expired tiles actively discarded in processing buffers into its state and reward system. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework significantly enhances user immersion while reducing device power consumption, and the superiority of the proposed AQM-CUP algorithm over conventional methods in terms of the training convergence and performance metrics.
Read more7/31/2024