Exploring the Design of Collaborative Applications via the Lens of NDN Workspace

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the design of collaborative applications through the lens of the NDN Workspace system.
- NDN Workspace is a platform that enables real-time collaboration and data sharing using the Named Data Networking (NDN) architecture.
- The paper examines how the design and features of NDN Workspace can inform the development of effective collaborative applications.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at how the NDN Workspace platform can help create collaborative applications that allow multiple users to work together effectively. NDN Workspace is built on the Named Data Networking (NDN) architecture, which is a different way of designing computer networks compared to the traditional internet model.
The key idea is that NDN Workspace provides a set of features and design principles that make it easier to build collaborative apps where people can share information, work on projects together, and coordinate their activities in real-time. For example, NDN Workspace automatically handles things like syncing changes between collaborators, managing access permissions, and routing data efficiently across the network.
By analyzing how NDN Workspace works, the paper aims to identify useful lessons and insights that can guide the development of other collaborative applications, whether they use NDN or a different underlying technology. The goal is to help create apps that enable seamless and effective teamwork, even when people are distributed across different locations.
Technical Explanation
The paper provides an overview of the NDN Workspace system, which is built on the Named Data Networking (NDN) architecture. NDN is a fundamentally different approach to computer networking compared to the traditional internet model, as it focuses on naming and retrieving data rather than addressing and routing packets.
NDN Workspace leverages NDN's content-centric design to enable real-time collaboration and data sharing between users. Key features of the system include:
- Automatic Synchronization: NDN Workspace automatically synchronizes changes made by collaborators to shared documents or workspaces.
- Access Control: The system provides granular access control, allowing collaborators to have different levels of permissions (e.g. read-only, edit, admin) for specific content.
- Offline Support: Users can continue working offline, and their changes will be automatically synchronized when they reconnect.
- Efficient Data Routing: NDN's content-centric networking model allows NDN Workspace to route data efficiently across the network, reducing latency and bandwidth usage.
The paper examines how these features and design principles of NDN Workspace can inform the development of effective collaborative applications in general. It discusses the advantages of the NDN approach compared to traditional client-server or peer-to-peer models, and how the lessons learned from NDN Workspace could be applied to other collaboration tools and platforms.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough overview of the NDN Workspace system and its potential benefits for collaborative applications. However, it does not delve deeply into any potential limitations or areas for further research.
One potential concern that could be explored is the scalability of the NDN architecture, particularly as the number of users and the amount of shared data grows. The paper does not address how NDN Workspace would handle large-scale deployments or high-concurrency usage scenarios.
Additionally, the paper does not discuss any specific user studies or real-world deployments of NDN Workspace. While the technical design is sound, it would be helpful to understand how the system performs in practice and how users respond to its features and user experience.
Further research could also investigate how NDN Workspace compares to other collaborative platforms that use different networking models or architectural approaches. This could provide a more comprehensive understanding of the tradeoffs and design considerations for building effective collaboration tools.
Conclusion
This paper offers a detailed examination of the NDN Workspace system and its potential to inform the design of collaborative applications. By leveraging the content-centric networking principles of NDN, NDN Workspace provides a set of features that can facilitate seamless real-time collaboration, including automatic synchronization, fine-grained access control, and efficient data routing.
The insights and lessons learned from NDN Workspace could be valuable for developers looking to create collaborative tools and platforms that enable distributed teams to work together effectively, regardless of their location. While the paper does not address all potential limitations or areas for further research, it provides a solid foundation for understanding how the NDN approach can be applied to collaborative application design.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Exploring the Design of Collaborative Applications via the Lens of NDN Workspace
Tianyuan Yu, Xinyu Ma, Varun Patil, Yekta Kocaogullar, Lixia Zhang
Metaverse applications desire to communicate with semantically identified objects among a diverse set of cyberspace entities, such as cameras for collecting images from, sensors for sensing environment, and users collaborating with each other, all could be nearby or far away, in a timely and secure way. However, supporting the above function faces networking challenges. Today's metaverse implementations are, by and large, use secure transport connections to communicate with cloud servers instead of letting participating entities communicate directly. In this paper, we use the design and implementation of NDN Workspace, a web-based, multi-user collaborative app to showcase a new way to networking that supports many-to-many secure data exchanges among communicating entities directly. NDN Workspace users establish trust relations among each other, exchange URI-identified objects directly, and can collaborate through intermittent connectivity, all in the absence of cloud servers. Its data-centric design offers an exciting new approach to metaverse app development.
Read more7/23/2024


0
Secure Web Objects: Building Blocks for Metaverse Interoperability and Decentralization
Tianyuan Yu, Xinyu Ma, Varun Patil, Yekta Kocaogullar, Yulong Zhang, Jeff Burke, Dirk Kutscher, Lixia Zhang
This position paper explores how to support the Web's evolution through an underlying data-centric approach that better matches the data-orientedness of modern and emerging applications. We revisit the original vision of the Web as a hypermedia system that supports document composability and application interoperability via name-based data access. We propose the use of secure web objects (SWO), a data-oriented communication approach that can reduce complexity, centrality, and inefficiency, particularly for collaborative and local-first applications, such as the Metaverse and other collaborative applications. SWO are named, signed, application-defined objects that are secured independently of their containers or communications channels, an approach that leverages the results from over a decade-long data-centric networking research. This approach does not require intermediation by aggregators of identity, storage, and other services that are common today. We present a brief design overview, illustrated through prototypes for two editors of shared hypermedia documents: one for 3D and one for LaTeX. We also discuss our findings and suggest a roadmap for future research.
Read more7/23/2024


0
WebXR, A-Frame and Networked-Aframe as a Basis for an Open Metaverse: A Conceptual Architecture
Giuseppe Macario
This work proposes a WebXR-based cross-platform conceptual architecture, leveraging the A-Frame and Networked-Aframe frameworks, in order to facilitate the development of an open, accessible, and interoperable metaverse. By introducing the concept of spatial web app, this research contributes to the discourse on the metaverse, offering an architecture that democratizes access to virtual environments and extended reality through the web, and aligns with Tim Berners-Lee's original vision of the World Wide Web as an open platform in the digital realm.
Read more7/2/2024

0
Wireless Multi-User Interactive Virtual Reality in Metaverse with Edge-Device Collaborative Computing
Caolu Xu, Zhiyong Chen, Meixia Tao, Wenjun Zhang
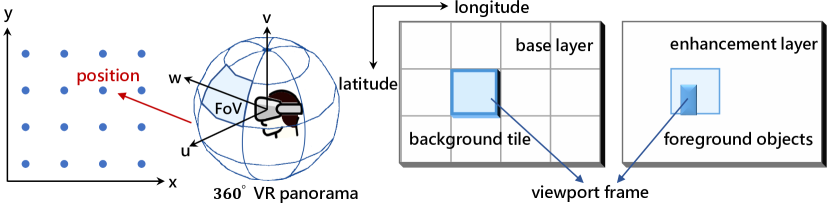
The immersive nature of the metaverse presents significant challenges for wireless multi-user interactive virtual reality (VR), such as ultra-low latency, high throughput and intensive computing, which place substantial demands on the wireless bandwidth and rendering resources of mobile edge computing (MEC). In this paper, we propose a wireless multi-user interactive VR with edge-device collaborative computing framework to overcome the motion-to-photon (MTP) threshold bottleneck. Specifically, we model the serial-parallel task execution in queues within a foreground and background separation architecture. The rendering indices of background tiles within the prediction window are determined, and both the foreground and selected background tiles are loaded into respective processing queues based on the rendering locations. To minimize the age of sensor information and the power consumption of mobile devices, we optimize rendering decisions and MEC resource allocation subject to the MTP constraint. To address this optimization problem, we design a safe reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm, active queue management-constrained updated projection (AQM-CUP). AQM-CUP constructs an environment suitable for queues, incorporating expired tiles actively discarded in processing buffers into its state and reward system. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework significantly enhances user immersion while reducing device power consumption, and the superiority of the proposed AQM-CUP algorithm over conventional methods in terms of the training convergence and performance metrics.
Read more7/31/2024