FAKER: Full-body Anonymization with Human Keypoint Extraction for Real-time Video Deidentification

0
⛏️
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- In the modern digital world, protecting personal information is crucial.
- The growth of media has increased concerns about anonymizing individuals in video footage.
- Traditional methods like blurring and pixelation are commonly used, while new techniques like generative adversarial networks (GANs) can redraw faces.
- This study proposes a novel approach for real-time full-body anonymization of individuals in videos using a smaller model.
Plain English Explanation
In today's digital age, keeping personal information private has become extremely important. As the media industry has grown, there are more concerns about how to hide the identities of people captured in video footage. Traditional methods like blurring and pixelating faces are commonly used, but newer technologies like generative adversarial networks (GANs) can actually redraw people's faces in videos.
This research paper introduces a new way to fully anonymize people's bodies in videos in real-time using a smaller, more efficient model. Unlike standard techniques that often fail to remove all the identifying details like skin color, clothing, accessories, and body shape, this new method successfully hides all those personal characteristics. By also using pose estimation algorithms, it can accurately represent information about people's positions, movements, and postures in the video. This system can be easily integrated into security camera or internet-connected camera systems in various settings, working in real-time to enable widespread use of full-body anonymization.
Technical Explanation
The researchers developed a novel approach for real-time full-body anonymization of individuals in videos. Unlike conventional techniques that often struggle to effectively remove personal identification details such as skin color, clothing, accessories, and body shape, their method successfully eliminates all such identifying information.
The key innovation is the use of a significantly smaller model compared to previous work, which allows the anonymization to happen in real-time. By leveraging pose estimation algorithms, the system can accurately represent individuals' positions, movements, and postures within the anonymized video feed.
This anonymization algorithm can be seamlessly integrated into CCTV or IP camera systems installed in various industrial settings, functioning in real-time. This facilitates the widespread adoption of full-body anonymization technology, addressing the growing need to protect personal privacy in the digital age.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to full-body anonymization that addresses several limitations of existing techniques. By using a smaller model, the system can operate in real-time, which is a crucial requirement for practical deployment in surveillance or monitoring applications.
However, the paper does not provide much detail on the specific model architecture or training process. Additional information on the model's performance, robustness, and potential biases would be helpful to fully evaluate the approach.
Furthermore, the researchers do not discuss potential challenges or ethical considerations around the deployment of such anonymization technology. Issues like user consent, data privacy, and potential misuse of the technology should be carefully examined before widespread adoption.
Overall, the research demonstrates an innovative step towards more comprehensive video anonymization, but more work is needed to address the practical and ethical implications of this technology.
Conclusion
This study introduces a novel real-time full-body anonymization technique that can be seamlessly integrated into existing camera systems. By using a compact model and leveraging pose estimation, the approach successfully removes personal identification details while preserving key information about individuals' movements and positions.
The development of this anonymization technology is a significant advancement in addressing growing concerns around personal privacy in the digital age. As media and surveillance systems continue to proliferate, tools like this can play a crucial role in protecting individual identities and upholding ethical data practices.
However, the deployment of such technology must be carefully considered to ensure it is used responsibly and in alignment with privacy rights. Further research and dialogue around the practical and ethical implications of video anonymization will be important as this technology matures and gains wider adoption.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
⛏️

0
FAKER: Full-body Anonymization with Human Keypoint Extraction for Real-time Video Deidentification
Byunghyun Ban, Hyoseok Lee
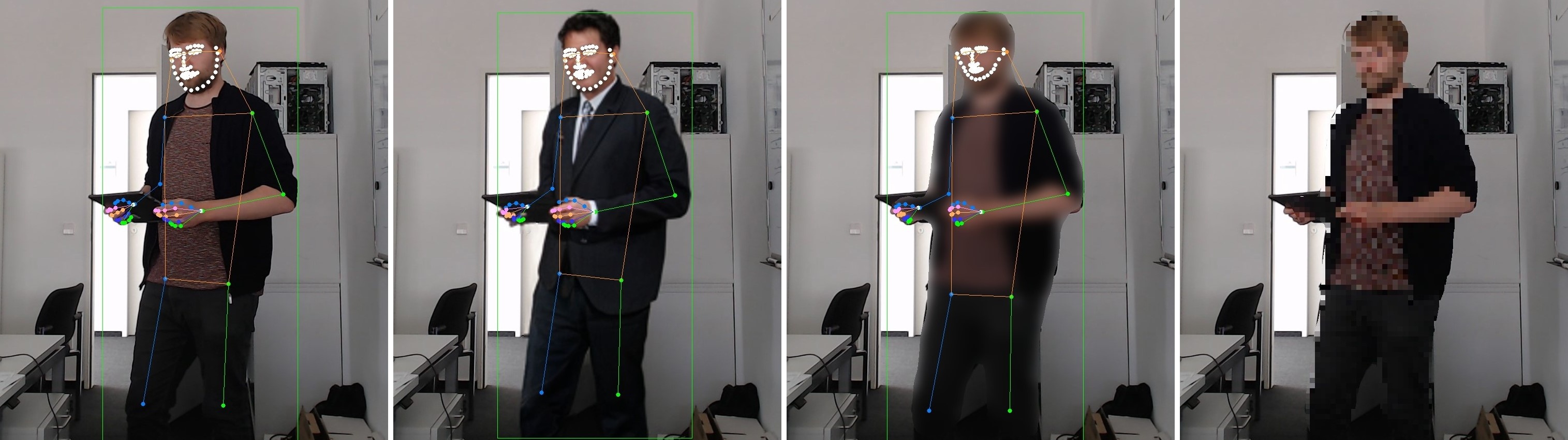
In the contemporary digital era, protection of personal information has become a paramount issue. The exponential growth of the media industry has heightened concerns regarding the anonymization of individuals captured in video footage. Traditional methods, such as blurring or pixelation, are commonly employed, while recent advancements have introduced generative adversarial networks (GAN) to redraw faces in videos. In this study, we propose a novel approach that employs a significantly smaller model to achieve real-time full-body anonymization of individuals in videos. Unlike conventional techniques that often fail to effectively remove personal identification information such as skin color, clothing, accessories, and body shape while our method successfully eradicates all such details. Furthermore, by leveraging pose estimation algorithms, our approach accurately represents information regarding individuals' positions, movements, and postures. This algorithm can be seamlessly integrated into CCTV or IP camera systems installed in various industrial settings, functioning in real-time and thus facilitating the widespread adoption of full-body anonymization technology.
Read more8/23/2024

0
Exploring AI-based Anonymization of Industrial Image and Video Data in the Context of Feature Preservation
Sabrina Cynthia Triess, Timo Leitritz, Christian Jauch
With rising technologies, the protection of privacy-sensitive information is becoming increasingly important. In industry and production facilities, image or video recordings are beneficial for documentation, tracing production errors or coordinating workflows. Individuals in images or videos need to be anonymized. However, the anonymized data should be reusable for further applications. In this work, we apply the Deep Learning-based full-body anonymization framework DeepPrivacy2, which generates artificial identities, to industrial image and video data. We compare its performance with conventional anonymization techniques. Therefore, we consider the quality of identity generation, temporal consistency, and the applicability of pose estimation and action recognition.
Read more5/30/2024


0
My Body My Choice: Human-Centric Full-Body Anonymization
Umur Aybars Ciftci, Ali Kemal Tanriverdi, Ilke Demir
In an era of increasing privacy concerns for our online presence, we propose that the decision to appear in a piece of content should only belong to the owner of the body. Although some automatic approaches for full-body anonymization have been proposed, human-guided anonymization can adapt to various contexts, such as cultural norms, personal relations, esthetic concerns, and security issues. ''My Body My Choice'' (MBMC) enables physical and adversarial anonymization by removal and swapping approaches aimed for four tasks, designed by single or multi, ControlNet or GAN modules, combining several diffusion models. We evaluate anonymization on seven datasets; compare with SOTA inpainting and anonymization methods; evaluate by image, adversarial, and generative metrics; and conduct reidentification experiments.
Read more6/17/2024


0
A Key-Driven Framework for Identity-Preserving Face Anonymization
Miaomiao Wang, Guang Hua, Sheng Li, Guorui Feng
Virtual faces are crucial content in the metaverse. Recently, attempts have been made to generate virtual faces for privacy protection. Nevertheless, these virtual faces either permanently remove the identifiable information or map the original identity into a virtual one, which loses the original identity forever. In this study, we first attempt to address the conflict between privacy and identifiability in virtual faces, where a key-driven face anonymization and authentication recognition (KFAAR) framework is proposed. Concretely, the KFAAR framework consists of a head posture-preserving virtual face generation (HPVFG) module and a key-controllable virtual face authentication (KVFA) module. The HPVFG module uses a user key to project the latent vector of the original face into a virtual one. Then it maps the virtual vectors to obtain an extended encoding, based on which the virtual face is generated. By simultaneously adding a head posture and facial expression correction module, the virtual face has the same head posture and facial expression as the original face. During the authentication, we propose a KVFA module to directly recognize the virtual faces using the correct user key, which can obtain the original identity without exposing the original face image. We also propose a multi-task learning objective to train HPVFG and KVFA. Extensive experiments demonstrate the advantages of the proposed HPVFG and KVFA modules, which effectively achieve both facial anonymity and identifiability.
Read more9/6/2024