Fast Numerical Solver of Ising Optimization Problems via Pruning and Domain Selection

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a fast numerical solver for Ising optimization problems, which are a type of quantum-inspired optimization problem.
- The solver uses pruning and domain selection techniques to significantly improve the speed and efficiency of solving these problems.
- The paper demonstrates the effectiveness of the solver on a range of benchmark problems, showing substantial performance improvements over existing methods.
Plain English Explanation
The Ising problem is a type of optimization problem that is inspired by quantum computing concepts. It involves finding the lowest-energy configuration of a system of interacting binary variables, which can be used to solve a variety of real-world optimization problems.
The paper describes a new numerical solver that can solve Ising problems much more quickly than previous methods. It does this by using pruning and domain selection techniques to focus the solver's search on the most promising parts of the solution space.
By reducing the computational effort required, this solver can tackle larger and more complex Ising optimization problems than was previously possible. This could lead to breakthroughs in areas like materials science, logistics, and finance where these types of optimization problems are important.
Technical Explanation
The paper introduces a fast numerical solver for Ising optimization problems, which are a type of quadratic unconstrained binary optimization (QUBO) problem inspired by quantum computing concepts.
The key innovations of the solver are pruning and domain selection techniques that significantly reduce the search space that needs to be explored. The pruning step identifies and eliminates variables that can be fixed to their optimal values, while the domain selection step focuses the search on the most promising regions of the solution space.
The authors demonstrate the effectiveness of their solver on a range of benchmark Ising optimization problems, showing substantial performance improvements over existing numerical and quantum annealing-based methods. For the largest problem instances, the new solver was over 100 times faster than previous state-of-the-art approaches.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough evaluation of the proposed solver's performance, comparing it to leading quantum annealing hardware and other numerical optimization techniques across a wide range of problem sizes and structures. However, the analysis is limited to synthetic benchmark problems, and more work is needed to assess the solver's real-world applicability to large-scale optimization problems in domains like materials science, logistics, and finance.
Additionally, while the pruning and domain selection techniques are shown to be highly effective, the paper does not provide a deep theoretical analysis of why these techniques work so well. Further research could explore the underlying mathematical principles that enable such significant performance gains.
Overall, this work represents an important step forward in the field of Ising optimization, demonstrating the potential for classical numerical solvers to outperform quantum annealing approaches on certain problem classes. Continued research in this area could lead to transformative breakthroughs in a wide range of optimization-heavy applications.
Conclusion
This paper introduces a fast numerical solver for Ising optimization problems that uses novel pruning and domain selection techniques to dramatically improve computational efficiency. The solver's performance is shown to significantly outperform existing methods, both classical and quantum, on a range of benchmark problems.
While further research is needed to fully understand the theoretical underpinnings of the solver's success and to validate its real-world applicability, this work represents an important advance in the field of Ising optimization. By enabling the solution of larger and more complex problems, the new solver could lead to breakthroughs in areas like materials science, logistics, and finance where these types of optimization problems are critical.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Fast Numerical Solver of Ising Optimization Problems via Pruning and Domain Selection
Langyu Li, Daoyi Dong, Yu Pan
Quantum annealers, coherent Ising machines and digital Ising machines for solving quantum-inspired optimization problems have been developing rapidly due to their near-term applications. The numerical solvers of the digital Ising machines are based on traditional computing devices. In this work, we propose a fast and efficient solver for the Ising optimization problems. The algorithm consists of a pruning method that exploits the graph information of the Ising model to reduce the computational complexity, and a domain selection method which introduces significant acceleration by relaxing the discrete feasible domain into a continuous one to incorporate the efficient gradient descent method. The experiment results show that our solver can be an order of magnitude faster than the classical solver, and at least two times faster than the quantum-inspired annealers including the simulated quantum annealing on the benchmark problems. With more relaxed requirements on hardware and lower cost than quantum annealing, the proposed solver has the potential for near-term application in solving challenging optimization problems as well as serving as a benchmark for evaluating the advantage of quantum devices.
Read more9/4/2024
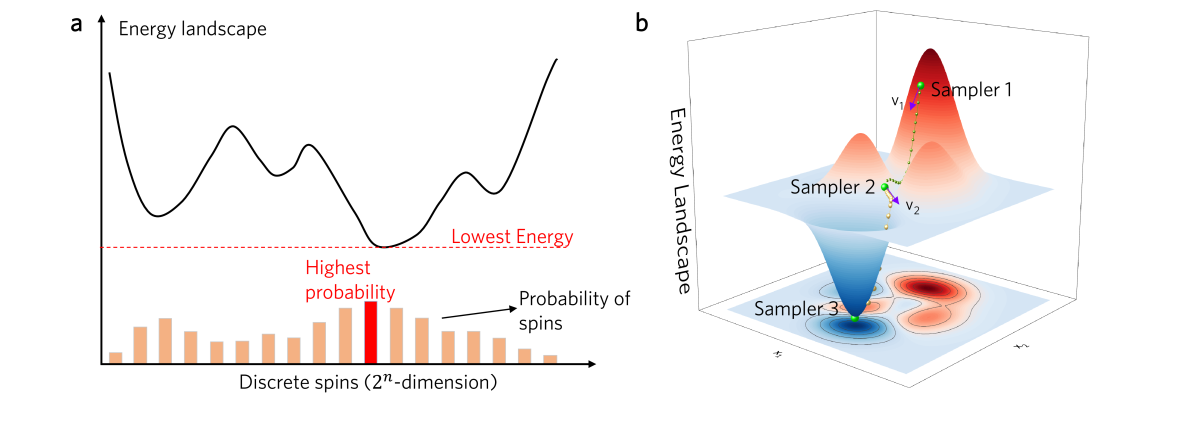

0
Parallel Ising Annealer via Gradient-based Hamiltonian Monte Carlo
Hao Wang, Zixuan Liu, Zhixin Xie, Langyu Li, Zibo Miao, Wei Cui, Yu Pan
Ising annealer is a promising quantum-inspired computing architecture for combinatorial optimization problems. In this paper, we introduce an Ising annealer based on the Hamiltonian Monte Carlo, which updates the variables of all dimensions in parallel. The main innovation is the fusion of an approximate gradient-based approach into the Ising annealer which introduces significant acceleration and allows a portable and scalable implementation on the commercial FPGA. Comprehensive simulation and hardware experiments show that the proposed Ising annealer has promising performance and scalability on all types of benchmark problems when compared to other Ising annealers including the state-of-the-art hardware. In particular, we have built a prototype annealer which solves Ising problems of both integer and fraction coefficients with up to 200 spins on a single low-cost FPGA board, whose performance is demonstrated to be better than the state-of-the-art quantum hardware D-Wave 2000Q and similar to the expensive coherent Ising machine. The sub-linear scalability of the annealer signifies its potential in solving challenging combinatorial optimization problems and evaluating the advantage of quantum hardware.
Read more7/16/2024
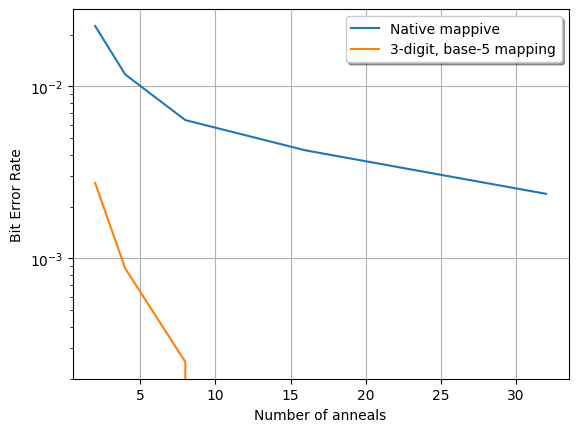

0
Multi Digit Ising Mapping for Low Precision Ising Solvers
Abhishek Kumar Singh, Kyle Jamieson
The last couple of years have seen an ever-increasing interest in using different Ising solvers, like Quantum annealers, Coherent Ising machines, and Oscillator-based Ising machines, for solving tough computational problems in various domains. Although the simulations predict massive performance improvements for several tough computational problems, the real implementations of the Ising solvers tend to have limited precision, which can cause significant performance deterioration. This paper presents a novel methodology for mapping the problem on the Ising solvers to artificially increase the effective precision. We further evaluate our method for the Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output signal detection problem.
Read more4/9/2024


0
Toward Practical Benchmarks of Ising Machines: A Case Study on the Quadratic Knapsack Problem
Kentaro Ohno, Tatsuhiko Shirai, Nozomu Togawa
Combinatorial optimization has wide applications from industry to natural science. Ising machines bring an emerging computing paradigm for efficiently solving a combinatorial optimization problem by searching a ground state of a given Ising model. Current cutting-edge Ising machines achieve fast sampling of near-optimal solutions of the max-cut problem. However, for problems with additional constraint conditions, their advantages have been hardly shown due to difficulties in handling the constraints. In this work, we focus on benchmarks of Ising machines on the quadratic knapsack problem (QKP). To bring out their practical performance, we propose fast two-stage post-processing for Ising machines, which makes handling the constraint easier. Simulation based on simulated annealing shows that the proposed method substantially improves the solving performance of Ising machines and the improvement is robust to a choice of encoding of the constraint condition. Through evaluation using an Ising machine called Amplify Annealing Engine, the proposed method is shown to dramatically improve its solving performance on the QKP. These results are a crucial step toward showing advantages of Ising machines on practical problems involving various constraint conditions.
Read more7/16/2024