From Role-Play to Drama-Interaction: An LLM Solution
2405.14231

0
0
⛏️
Abstract
Drama is a form of storytelling inspired by human creativity, proceeding with a predefined storyline, carrying emotions and thoughts. This paper introduces emph{LLM-based interactive drama}, which endows traditional drama with an unprecedented immersion, where a person is allowed to walk into it and interact with the characters and scenes. We define this new artistic genre by 6 essential elements-plot, character, thought, diction, spectacle and interaction-and study the entire pipeline to forge a backbone emph{drama LLM} to drive the playing process, which is challenged by limited drama resources, uncontrollable narrative development, and complicated instruction following. We propose emph{Narrative Chain} to offer finer control over the narrative progression during interaction with players; emph{Auto-Drama} to synthesize drama scripts given arbitrary stories; emph{Sparse Instruction Tuning} to allow the model to follow sophisticated instructions. We manually craft 3 scripts, emph{Detective Conan}, emph{Harry Potter}, emph{Romeo and Juliet}, and design a 5-dimension principle to evaluate the drama LLM comprehensively.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper introduces the concept of LLM-based interactive drama, which combines traditional drama with the ability for people to immerse themselves and interact with the characters and scenes.
- The authors define 6 essential elements of this new artistic genre: plot, character, thought, diction, spectacle, and interaction.
- They propose several technical approaches to address challenges in this domain, including Narrative Chain, Auto-Drama, and Sparse Instruction Tuning.
- The authors manually craft 3 example scripts and introduce a 5-dimension principle to comprehensively evaluate their "drama LLM" system.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a new type of interactive storytelling called "LLM-based interactive drama." This allows people to step into a dramatic story and interact with the characters and scenes, rather than just watching passively.
The authors define 6 key elements that make up this interactive drama, including the plot, the characters, the themes and ideas explored, the language used, the visual elements, and the ability for the audience to influence the story.
To create this interactive drama system, the researchers had to overcome some significant challenges. These include the limited availability of dramatic scripts and stories, the difficulty of controlling the narrative as it develops, and the complexity of getting the system to properly understand and follow complex instructions from the audience.
To address these challenges, the authors propose several technical approaches, such as Narrative Chain to better control the story progression, Auto-Drama to generate drama scripts from scratch, and Sparse Instruction Tuning to allow the system to follow complex audience instructions.
The researchers also manually created 3 example drama scripts (for Detective Conan, Harry Potter, and Romeo and Juliet) and developed a 5-part evaluation framework to assess the quality and capabilities of their "drama LLM" system.
Technical Explanation
The paper introduces the concept of "LLM-based interactive drama," which aims to endow traditional drama with a new level of audience immersion and interactivity. The authors define 6 essential elements of this new genre: plot, character, thought, diction, spectacle, and interaction.
To address the technical challenges in this domain, the researchers propose several key innovations:
-
Narrative Chain: This approach provides finer control over the narrative progression during interaction with players, helping to ensure a coherent and engaging story flow.
-
Auto-Drama: This technique synthesizes full drama scripts given arbitrary stories, allowing the system to generate original interactive dramas rather than just relying on pre-written content.
-
Sparse Instruction Tuning: This method enables the drama LLM model to follow sophisticated instructions from players, allowing for a greater degree of interactive influence over the unfolding narrative.
The authors manually crafted 3 example drama scripts (for Detective Conan, Harry Potter, and Romeo and Juliet) and designed a 5-dimension evaluation framework to assess their system's performance comprehensively. This framework considers factors like narrative coherence, character expressiveness, thematic depth, language quality, and overall audience engagement.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a compelling vision for the future of interactive storytelling, but also acknowledges several key challenges and limitations that will need to be addressed.
One significant limitation is the reliance on manually crafted drama scripts. While the Auto-Drama approach aims to generate original scripts, the authors note that this remains a difficult technical challenge. Fully autonomous and generative drama creation is an area that likely requires further research and innovation.
Additionally, the authors highlight the difficulty of controlling the narrative progression during interactive sessions, even with their proposed Narrative Chain approach. Maintaining a coherent and engaging story in the face of unpredictable player actions is an inherently challenging problem that may require more sophisticated techniques.
Finally, while the Sparse Instruction Tuning method aims to improve the system's ability to follow complex instructions, the authors acknowledge that this remains a significant hurdle. Robust natural language understanding and execution is crucial for truly engaging interactive drama experiences.
Overall, the paper presents an exciting vision and several technical advancements, but also highlights the substantial research challenges that remain in this emerging field of LLM-based situational dialogues and co-creative storytelling.
Conclusion
This paper introduces the concept of "LLM-based interactive drama," a new artistic genre that combines traditional drama with the ability for people to immerse themselves and directly influence the unfolding narrative. The authors define 6 key elements of this genre and propose several technical innovations to address the significant challenges involved.
While the paper presents an exciting vision and promising initial work, it also acknowledges the substantial research challenges that remain in areas like autonomous script generation, narrative control, and robust natural language understanding. Continued advancements in these areas, as well as further exploration of the artistic and experiential potential of interactive drama, will be crucial for realizing the full promise of this emerging field.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Player-Driven Emergence in LLM-Driven Game Narrative
Xiangyu Peng, Jessica Quaye, Sudha Rao, Weijia Xu, Portia Botchway, Chris Brockett, Nebojsa Jojic, Gabriel DesGarennes, Ken Lobb, Michael Xu, Jorge Leandro, Claire Jin, Bill Dolan

0
0
We explore how interaction with large language models (LLMs) can give rise to emergent behaviors, empowering players to participate in the evolution of game narratives. Our testbed is a text-adventure game in which players attempt to solve a mystery under a fixed narrative premise, but can freely interact with non-player characters generated by GPT-4, a large language model. We recruit 28 gamers to play the game and use GPT-4 to automatically convert the game logs into a node-graph representing the narrative in the player's gameplay. We find that through their interactions with the non-deterministic behavior of the LLM, players are able to discover interesting new emergent nodes that were not a part of the original narrative but have potential for being fun and engaging. Players that created the most emergent nodes tended to be those that often enjoy games that facilitate discovery, exploration and experimentation.
6/5/2024
👁️
StoryVerse: Towards Co-authoring Dynamic Plot with LLM-based Character Simulation via Narrative Planning
Yi Wang, Qian Zhou, David Ledo

0
0
Automated plot generation for games enhances the player's experience by providing rich and immersive narrative experience that adapts to the player's actions. Traditional approaches adopt a symbolic narrative planning method which limits the scale and complexity of the generated plot by requiring extensive knowledge engineering work. Recent advancements use Large Language Models (LLMs) to drive the behavior of virtual characters, allowing plots to emerge from interactions between characters and their environments. However, the emergent nature of such decentralized plot generation makes it difficult for authors to direct plot progression. We propose a novel plot creation workflow that mediates between a writer's authorial intent and the emergent behaviors from LLM-driven character simulation, through a novel authorial structure called abstract acts. The writers define high-level plot outlines that are later transformed into concrete character action sequences via an LLM-based narrative planning process, based on the game world state. The process creates living stories that dynamically adapt to various game world states, resulting in narratives co-created by the author, character simulation, and player. We present StoryVerse as a proof-of-concept system to demonstrate this plot creation workflow. We showcase the versatility of our approach with examples in different stories and game environments.
5/24/2024

Designing and Evaluating Dialogue LLMs for Co-Creative Improvised Theatre
Boyd Branch, Piotr Mirowski, Kory Mathewson, Sophia Ppali, Alexandra Covaci

0
0
Social robotics researchers are increasingly interested in multi-party trained conversational agents. With a growing demand for real-world evaluations, our study presents Large Language Models (LLMs) deployed in a month-long live show at the Edinburgh Festival Fringe. This case study investigates human improvisers co-creating with conversational agents in a professional theatre setting. We explore the technical capabilities and constraints of on-the-spot multi-party dialogue, providing comprehensive insights from both audience and performer experiences with AI on stage. Our human-in-the-loop methodology underlines the challenges of these LLMs in generating context-relevant responses, stressing the user interface's crucial role. Audience feedback indicates an evolving interest for AI-driven live entertainment, direct human-AI interaction, and a diverse range of expectations about AI's conversational competence and utility as a creativity support tool. Human performers express immense enthusiasm, varied satisfaction, and the evolving public opinion highlights mixed emotions about AI's role in arts.
5/14/2024
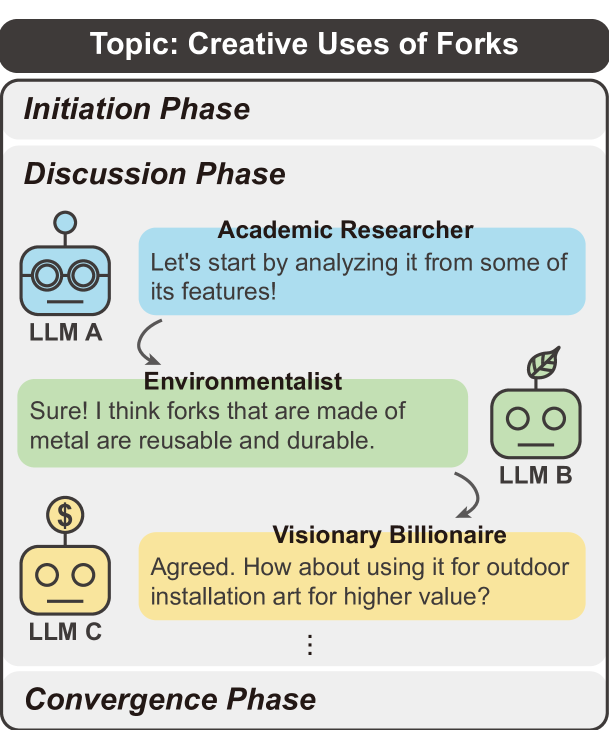
LLM Discussion: Enhancing the Creativity of Large Language Models via Discussion Framework and Role-Play
Li-Chun Lu, Shou-Jen Chen, Tsung-Min Pai, Chan-Hung Yu, Hung-yi Lee, Shao-Hua Sun

0
0
Large language models (LLMs) have shown exceptional proficiency in natural language processing but often fall short of generating creative and original responses to open-ended questions. To enhance LLM creativity, our key insight is to emulate the human process of inducing collective creativity through engaging discussions with participants from diverse backgrounds and perspectives. To this end, we propose LLM Discussion, a three-phase discussion framework that facilitates vigorous and diverging idea exchanges and ensures convergence to creative answers. Moreover, we adopt a role-playing technique by assigning distinct roles to LLMs to combat the homogeneity of LLMs. We evaluate the efficacy of the proposed framework with the Alternative Uses Test, Similarities Test, Instances Test, and Scientific Creativity Test through both LLM evaluation and human study. Our proposed framework outperforms single-LLM approaches and existing multi-LLM frameworks across various creativity metrics.
5/21/2024