StoryVerse: Towards Co-authoring Dynamic Plot with LLM-based Character Simulation via Narrative Planning
2405.13042

0
0
👁️
Abstract
Automated plot generation for games enhances the player's experience by providing rich and immersive narrative experience that adapts to the player's actions. Traditional approaches adopt a symbolic narrative planning method which limits the scale and complexity of the generated plot by requiring extensive knowledge engineering work. Recent advancements use Large Language Models (LLMs) to drive the behavior of virtual characters, allowing plots to emerge from interactions between characters and their environments. However, the emergent nature of such decentralized plot generation makes it difficult for authors to direct plot progression. We propose a novel plot creation workflow that mediates between a writer's authorial intent and the emergent behaviors from LLM-driven character simulation, through a novel authorial structure called abstract acts. The writers define high-level plot outlines that are later transformed into concrete character action sequences via an LLM-based narrative planning process, based on the game world state. The process creates living stories that dynamically adapt to various game world states, resulting in narratives co-created by the author, character simulation, and player. We present StoryVerse as a proof-of-concept system to demonstrate this plot creation workflow. We showcase the versatility of our approach with examples in different stories and game environments.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores a novel approach to automated plot generation for games using Large Language Models (LLMs) to drive the behavior of virtual characters, allowing narratives to emerge from their interactions.
- Traditional symbolic narrative planning methods are limited in scale and complexity, requiring extensive knowledge engineering work.
- The proposed workflow mediates between a writer's authorial intent and the emergent behaviors from LLM-driven character simulation, using a novel authorial structure called abstract acts.
Plain English Explanation
The paper presents a way to automatically create engaging stories for video games by having the characters interact with each other and their environment in a lifelike way. Previous approaches relied on pre-written scripts, which limited the complexity of the stories.
The new method uses advanced language models to control the characters' behaviors, allowing the story to unfold naturally as the characters respond to each other and the game world. This creates a more immersive and adaptable narrative experience that can change based on the player's actions.
However, this emergent approach makes it harder for writers to direct the plot progression. To address this, the authors introduce "abstract acts" - high-level story outlines that are then translated into specific character actions by the language model. This allows writers to maintain creative control while still taking advantage of the dynamic storytelling capabilities of the language model.
The result is a "living story" that adapts to the game environment and the player's choices, with the narrative co-created by the writer, the character simulations, and the player.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a novel plot creation workflow that combines a writer's authorial intent with the emergent behaviors from LLM-driven character simulation. This is achieved through the use of "abstract acts" - high-level plot outlines defined by the writer that are then transformed into concrete character action sequences by an LLM-based narrative planning process.
The workflow works as follows:
- The writer defines abstract acts - high-level story beats or plot points.
- An LLM-based narrative planning system takes the abstract acts and the current state of the game world, and generates a sequence of character actions that fulfill those plot points.
- The character actions are executed in the game environment, with the characters' behaviors driven by the LLM, resulting in a dynamically unfolding narrative.
This approach allows for greater authorial control than pure emergent storytelling, while still leveraging the dynamic and adaptable nature of LLM-driven character interactions. The authors present StoryVerse as a proof-of-concept system to demonstrate this plot creation workflow.
Critical Analysis
The proposed workflow offers a promising solution to the challenge of balancing authorial intent with the emergent nature of LLM-driven narratives. By introducing the concept of "abstract acts," the authors provide a structured way for writers to guide the overall plot progression while still allowing for dynamic and adaptive storytelling at the character level.
However, the paper does not delve deeply into the technical details of the LLM-based narrative planning process or the specific challenges involved in translating abstract acts into concrete character actions. Additionally, the authors do not provide a comprehensive evaluation of the system's performance or the quality of the generated narratives.
Further research is needed to explore the scalability of this approach, as well as its ability to handle more complex and nuanced narrative structures. The integration of synchronized video storytelling techniques could also enhance the overall player experience by aligning the visual and narrative elements of the game.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel approach to automated plot generation for games that combines a writer's authorial intent with the emergent behaviors of LLM-driven character simulations. By introducing the concept of "abstract acts," the authors have developed a workflow that allows for greater creative control while still leveraging the dynamic and adaptable nature of language models.
The proof-of-concept system, StoryVerse, demonstrates the potential of this approach to create living, player-driven narratives that adapt to the game environment and the player's choices. While further research is needed to fully realize the potential of this technology, the paper offers a compelling vision for the future of interactive storytelling in games.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
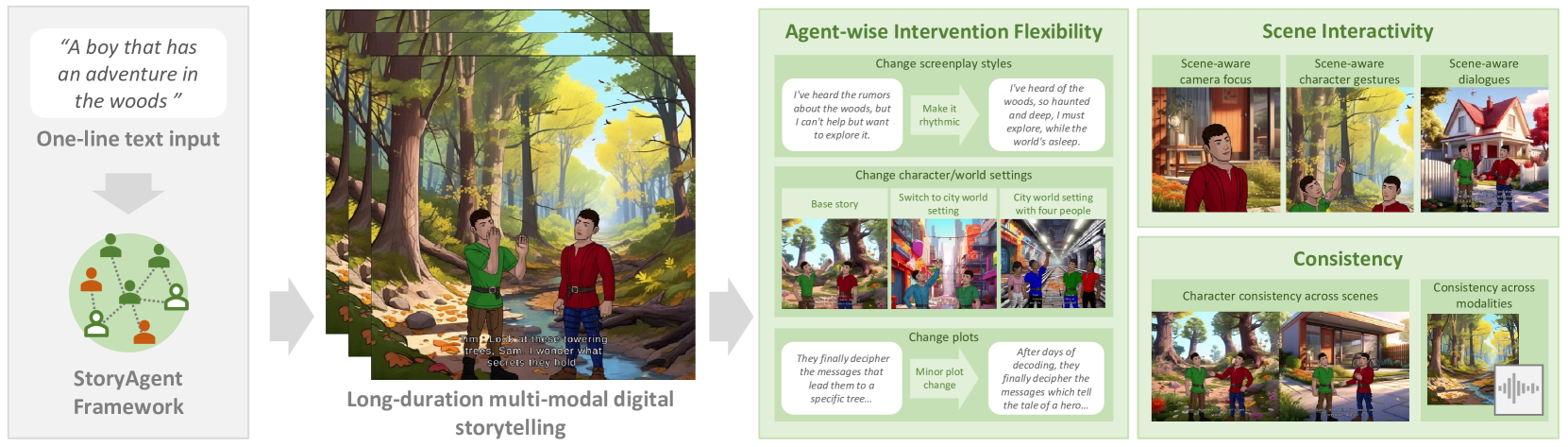
From Words to Worlds: Transforming One-line Prompt into Immersive Multi-modal Digital Stories with Communicative LLM Agent
Samuel S. Sohn, Danrui Li, Sen Zhang, Che-Jui Chang, Mubbasir Kapadia

0
0
Digital storytelling, essential in entertainment, education, and marketing, faces challenges in production scalability and flexibility. The StoryAgent framework, introduced in this paper, utilizes Large Language Models and generative tools to automate and refine digital storytelling. Employing a top-down story drafting and bottom-up asset generation approach, StoryAgent tackles key issues such as manual intervention, interactive scene orchestration, and narrative consistency. This framework enables efficient production of interactive and consistent narratives across multiple modalities, democratizing content creation and enhancing engagement. Our results demonstrate the framework's capability to produce coherent digital stories without reference videos, marking a significant advancement in automated digital storytelling.
6/24/2024
Player-Driven Emergence in LLM-Driven Game Narrative
Xiangyu Peng, Jessica Quaye, Sudha Rao, Weijia Xu, Portia Botchway, Chris Brockett, Nebojsa Jojic, Gabriel DesGarennes, Ken Lobb, Michael Xu, Jorge Leandro, Claire Jin, Bill Dolan

0
0
We explore how interaction with large language models (LLMs) can give rise to emergent behaviors, empowering players to participate in the evolution of game narratives. Our testbed is a text-adventure game in which players attempt to solve a mystery under a fixed narrative premise, but can freely interact with non-player characters generated by GPT-4, a large language model. We recruit 28 gamers to play the game and use GPT-4 to automatically convert the game logs into a node-graph representing the narrative in the player's gameplay. We find that through their interactions with the non-deterministic behavior of the LLM, players are able to discover interesting new emergent nodes that were not a part of the original narrative but have potential for being fun and engaging. Players that created the most emergent nodes tended to be those that often enjoy games that facilitate discovery, exploration and experimentation.
6/5/2024

Guiding and Diversifying LLM-Based Story Generation via Answer Set Programming
Phoebe J. Wang, Max Kreminski

0
0
Instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs) are capable of generating stories in response to open-ended user requests, but the resulting stories tend to be limited in their diversity. Older, symbolic approaches to story generation (such as planning) can generate substantially more diverse plot outlines, but are limited to producing stories that recombine a fixed set of hand-engineered character action templates. Can we combine the strengths of these approaches while mitigating their weaknesses? We propose to do so by using a higher-level and more abstract symbolic specification of high-level story structure -- implemented via answer set programming (ASP) -- to guide and diversify LLM-based story generation. Via semantic similarity analysis, we demonstrate that our approach produces more diverse stories than an unguided LLM, and via code excerpts, we demonstrate the improved compactness and flexibility of ASP-based outline generation over full-fledged narrative planning.
6/4/2024
🤿
GENEVA: GENErating and Visualizing branching narratives using LLMs
Jorge Leandro, Sudha Rao, Michael Xu, Weijia Xu, Nebosja Jojic, Chris Brockett, Bill Dolan

0
0
Dialogue-based Role Playing Games (RPGs) require powerful storytelling. The narratives of these may take years to write and typically involve a large creative team. In this work, we demonstrate the potential of large generative text models to assist this process. textbf{GENEVA}, a prototype tool, generates a rich narrative graph with branching and reconverging storylines that match a high-level narrative description and constraints provided by the designer. A large language model (LLM), GPT-4, is used to generate the branching narrative and to render it in a graph format in a two-step process. We illustrate the use of GENEVA in generating new branching narratives for four well-known stories under different contextual constraints. This tool has the potential to assist in game development, simulations, and other applications with game-like properties.
6/7/2024