FSGS: Real-Time Few-shot View Synthesis using Gaussian Splatting
2312.00451

0
0
Abstract
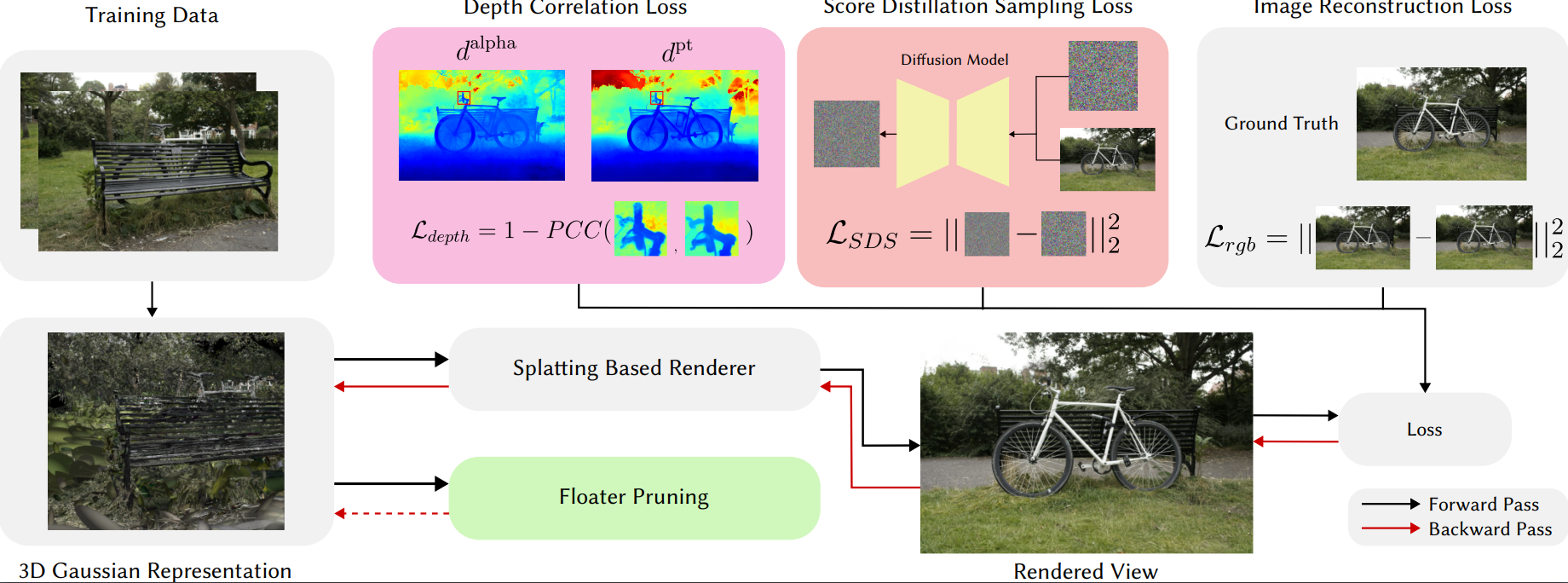
Novel view synthesis from limited observations remains an important and persistent task. However, high efficiency in existing NeRF-based few-shot view synthesis is often compromised to obtain an accurate 3D representation. To address this challenge, we propose a few-shot view synthesis framework based on 3D Gaussian Splatting that enables real-time and photo-realistic view synthesis with as few as three training views. The proposed method, dubbed FSGS, handles the extremely sparse initialized SfM points with a thoughtfully designed Gaussian Unpooling process. Our method iteratively distributes new Gaussians around the most representative locations, subsequently infilling local details in vacant areas. We also integrate a large-scale pre-trained monocular depth estimator within the Gaussians optimization process, leveraging online augmented views to guide the geometric optimization towards an optimal solution. Starting from sparse points observed from limited input viewpoints, our FSGS can accurately grow into unseen regions, comprehensively covering the scene and boosting the rendering quality of novel views. Overall, FSGS achieves state-of-the-art performance in both accuracy and rendering efficiency across diverse datasets, including LLFF, Mip-NeRF360, and Blender. Project website: https://zehaozhu.github.io/FSGS/.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper proposes a novel approach called FSGS (Few-Shot Gaussian Splatting) for real-time few-shot view synthesis, which can generate high-fidelity 360-degree images from a sparse set of input views.
- The key idea is to represent 3D scenes using a set of Gaussian splats, which can be efficiently rendered and updated in real-time as the viewpoint changes.
- FSGS leverages recent advancements in neural representations, such as SparseGS and SuperPoint Gaussian Splatting, to enable high-quality view synthesis from a small number of input images.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a new way to generate 360-degree images from just a few input photos. The key idea is to represent the 3D scene using a collection of Gaussian "splats" - these are like little blobs or blobs of information that can be efficiently rendered and updated as the viewpoint changes. This builds on recent advances in neural representations, like SparseGS and SuperPoint Gaussian Splatting, which allow high-quality images to be generated from a small number of input photos. The goal is to enable real-time, high-fidelity 360-degree view synthesis from just a few views, which could be useful for applications like virtual reality, augmented reality, and 3D content creation.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a method called FSGS (Few-Shot Gaussian Splatting) for real-time few-shot view synthesis. The core idea is to represent 3D scenes using a set of Gaussian splats, which can be efficiently rendered and updated as the viewpoint changes. This builds on recent work in neural representations for 3D reconstruction, such as SparseGS and SuperPoint Gaussian Splatting.
The FSGS architecture consists of three main components:
- A neural encoder that takes a sparse set of input views and predicts the parameters of a Gaussian splat field representing the 3D scene.
- A neural renderer that can efficiently render the Gaussian splat field from arbitrary viewpoints.
- A neural updater that can efficiently update the Gaussian splat field as the viewpoint changes, without the need for expensive re-rendering.
The authors evaluate FSGS on several benchmark datasets for view synthesis, demonstrating its ability to generate high-fidelity 360-degree images from just a few input views, in real-time. They also show that FSGS outperforms prior state-of-the-art methods in terms of both visual quality and rendering speed.
Critical Analysis
The FSGS approach represents an interesting advance in the field of few-shot view synthesis, leveraging neural representations to enable high-quality results from a small number of input views. However, the paper does not address some potential limitations of the approach:
- Scalability: While FSGS can handle view synthesis for relatively simple scenes, it's unclear how well the method would scale to more complex, cluttered 3D environments with a large number of objects and details.
- Generalization: The paper focuses on evaluating FSGS on a limited set of benchmark datasets. Further research would be needed to assess the method's ability to generalize to a wider range of scenes and viewing conditions.
- Robustness: The paper does not explore the sensitivity of FSGS to factors like noise, occlusions, or variations in lighting and camera parameters in the input views.
Additionally, the authors do not provide much discussion of potential societal implications or ethical considerations around the use of such view synthesis technologies, which could be an important area for further exploration.
Conclusion
Overall, the FSGS approach represents a promising step forward in the field of few-shot view synthesis, demonstrating the ability to generate high-quality 360-degree images from just a sparse set of input views. By leveraging neural representations and efficient rendering techniques, the method achieves real-time performance, which could have applications in areas like virtual reality, augmented reality, and 3D content creation. However, further research is needed to address potential limitations around scalability, generalization, and robustness, as well as to explore the broader societal implications of such technologies.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
SparseGS: Real-Time 360{deg} Sparse View Synthesis using Gaussian Splatting
Haolin Xiong, Sairisheek Muttukuru, Rishi Upadhyay, Pradyumna Chari, Achuta Kadambi

0
0
The problem of novel view synthesis has grown significantly in popularity recently with the introduction of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) and other implicit scene representation methods. A recent advance, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), leverages an explicit representation to achieve real-time rendering with high-quality results. However, 3DGS still requires an abundance of training views to generate a coherent scene representation. In few shot settings, similar to NeRF, 3DGS tends to overfit to training views, causing background collapse and excessive floaters, especially as the number of training views are reduced. We propose a method to enable training coherent 3DGS-based radiance fields of 360-degree scenes from sparse training views. We integrate depth priors with generative and explicit constraints to reduce background collapse, remove floaters, and enhance consistency from unseen viewpoints. Experiments show that our method outperforms base 3DGS by 6.4% in LPIPS and by 12.2% in PSNR, and NeRF-based methods by at least 17.6% in LPIPS on the MipNeRF-360 dataset with substantially less training and inference cost.
5/14/2024

Superpoint Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time High-Fidelity Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Diwen Wan, Ruijie Lu, Gang Zeng

0
0
Rendering novel view images in dynamic scenes is a crucial yet challenging task. Current methods mainly utilize NeRF-based methods to represent the static scene and an additional time-variant MLP to model scene deformations, resulting in relatively low rendering quality as well as slow inference speed. To tackle these challenges, we propose a novel framework named Superpoint Gaussian Splatting (SP-GS). Specifically, our framework first employs explicit 3D Gaussians to reconstruct the scene and then clusters Gaussians with similar properties (e.g., rotation, translation, and location) into superpoints. Empowered by these superpoints, our method manages to extend 3D Gaussian splatting to dynamic scenes with only a slight increase in computational expense. Apart from achieving state-of-the-art visual quality and real-time rendering under high resolutions, the superpoint representation provides a stronger manipulation capability. Extensive experiments demonstrate the practicality and effectiveness of our approach on both synthetic and real-world datasets. Please see our project page at https://dnvtmf.github.io/SP_GS.github.io.
6/7/2024

Self-Calibrating 4D Novel View Synthesis from Monocular Videos Using Gaussian Splatting
Fang Li, Hao Zhang, Narendra Ahuja

0
0
Gaussian Splatting (GS) has significantly elevated scene reconstruction efficiency and novel view synthesis (NVS) accuracy compared to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), particularly for dynamic scenes. However, current 4D NVS methods, whether based on GS or NeRF, primarily rely on camera parameters provided by COLMAP and even utilize sparse point clouds generated by COLMAP for initialization, which lack accuracy as well are time-consuming. This sometimes results in poor dynamic scene representation, especially in scenes with large object movements, or extreme camera conditions e.g. small translations combined with large rotations. Some studies simultaneously optimize the estimation of camera parameters and scenes, supervised by additional information like depth, optical flow, etc. obtained from off-the-shelf models. Using this unverified information as ground truth can reduce robustness and accuracy, which does frequently occur for long monocular videos (with e.g. > hundreds of frames). We propose a novel approach that learns a high-fidelity 4D GS scene representation with self-calibration of camera parameters. It includes the extraction of 2D point features that robustly represent 3D structure, and their use for subsequent joint optimization of camera parameters and 3D structure towards overall 4D scene optimization. We demonstrate the accuracy and time efficiency of our method through extensive quantitative and qualitative experimental results on several standard benchmarks. The results show significant improvements over state-of-the-art methods for 4D novel view synthesis. The source code will be released soon at https://github.com/fangli333/SC-4DGS.
6/4/2024
WE-GS: An In-the-wild Efficient 3D Gaussian Representation for Unconstrained Photo Collections
Yuze Wang, Junyi Wang, Yue Qi

0
0
Novel View Synthesis (NVS) from unconstrained photo collections is challenging in computer graphics. Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has shown promise for photorealistic and real-time NVS of static scenes. Building on 3DGS, we propose an efficient point-based differentiable rendering framework for scene reconstruction from photo collections. Our key innovation is a residual-based spherical harmonic coefficients transfer module that adapts 3DGS to varying lighting conditions and photometric post-processing. This lightweight module can be pre-computed and ensures efficient gradient propagation from rendered images to 3D Gaussian attributes. Additionally, we observe that the appearance encoder and the transient mask predictor, the two most critical parts of NVS from unconstrained photo collections, can be mutually beneficial. We introduce a plug-and-play lightweight spatial attention module to simultaneously predict transient occluders and latent appearance representation for each image. After training and preprocessing, our method aligns with the standard 3DGS format and rendering pipeline, facilitating seamlessly integration into various 3DGS applications. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets show our approach outperforms existing approaches on the rendering quality of novel view and appearance synthesis with high converge and rendering speed.
6/5/2024